MIT分布式系统课程实验1:Lab 1: MapReduce
以下是我自己实现的版本,与大家分享一下,有问题欢迎提出,也希望各位指出错误!
在common.go里面可以打开调试:
// Debugging enabled?
const debugEnabled = trueOverview
Part I: Map/Reduce input and output
第一部分主要是实现文件读写,读写内容当然就是key/value了。
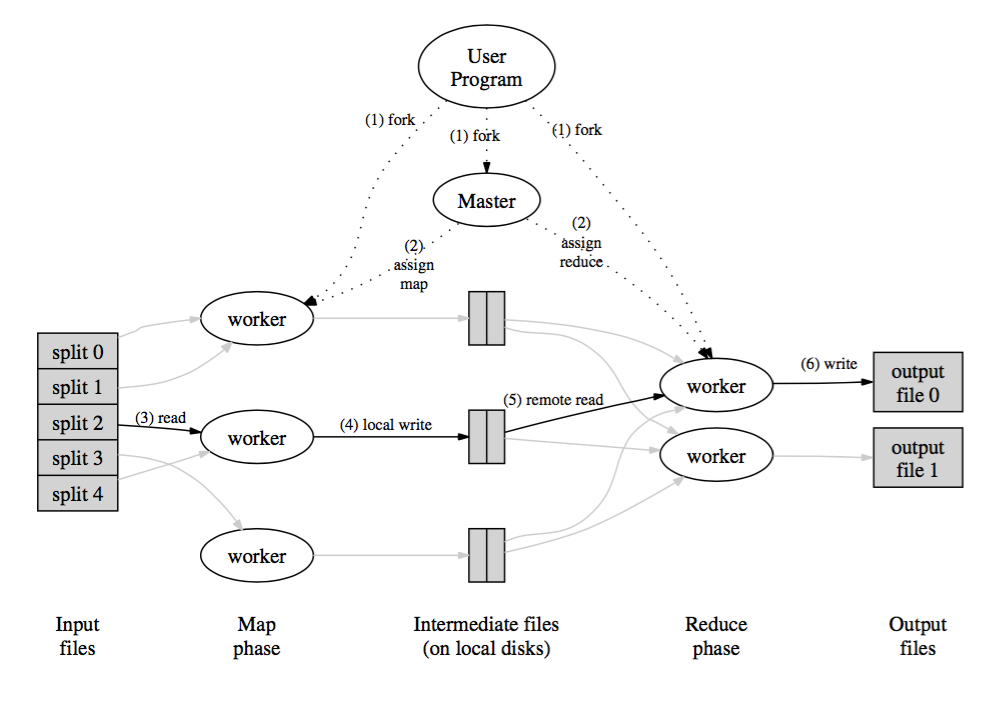
假设,
- M:Map的数目,也就是将数据集split成M份,分配给M个 Mappers 处理。如上图(3)read。
- R: Reduce的数目,也即有R个Reducers,最后有R个输出文件。每个 Mapper 会将读入的key/value 数据写到R份中间文件中,也就是分配给R个Reducers。
common_map.go
我用了一个数组存放输出文件的指针,一次过读入输入文件,用mapF函数生成key/value。遍历key/value,将每个key/value哈希到不同的输出文件中。
// doMap does the job of a map worker: it reads one of the input files
// (inFile), calls the user-defined map function (mapF) for that file's
// contents, and partitions the output into nReduce intermediate files.
func doMap(
jobName string, // the name of the MapReduce job
mapTaskNumber int, // which map task this is
inFile string,
nReduce int, // the number of reduce task that will be run ("R" in the paper)
mapF func(file string, contents string) []KeyValue,
) {
// TODO:
// You will need to write this function.
// You can find the filename for this map task's input to reduce task number
// r using reduceName(jobName, mapTaskNumber, r). The ihash function (given
// below doMap) should be used to decide which file a given key belongs into.
//
// The intermediate output of a map task is stored in the file
// system as multiple files whose name indicates which map task produced
// them, as well as which reduce task they are for. Coming up with a
// scheme for how to store the key/value pairs on disk can be tricky,
// especially when taking into account that both keys and values could
// contain newlines, quotes, and any other character you can think of.
//
// One format often used for serializing data to a byte stream that the
// other end can correctly reconstruct is JSON. You are not required to
// use JSON, but as the output of the reduce tasks *must* be JSON,
// familiarizing yourself with it here may prove useful. You can write
// out a data structure as a JSON string to a file using the commented








 这篇博客详细介绍了MIT分布式系统课程的Lab 1,涉及MapReduce的实现,包括Map/Reduce的输入输出、单个worker的单词计数、分布式任务分配及处理worker故障的方法。博主分享了自己的实现过程,并讨论了如何处理中间文件、使用哈希进行数据分布以及在遇到worker失败时的策略。
这篇博客详细介绍了MIT分布式系统课程的Lab 1,涉及MapReduce的实现,包括Map/Reduce的输入输出、单个worker的单词计数、分布式任务分配及处理worker故障的方法。博主分享了自己的实现过程,并讨论了如何处理中间文件、使用哈希进行数据分布以及在遇到worker失败时的策略。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








