1,关于蓝牙
随着这几年的发展现在越来越多的场景会用到蓝牙技术,最近非常火的共享单车都提供了打开蓝牙快速解锁的功能。它最为近场通信的一种,我们很有必要对它进行下研究和探索。
2,使用蓝牙
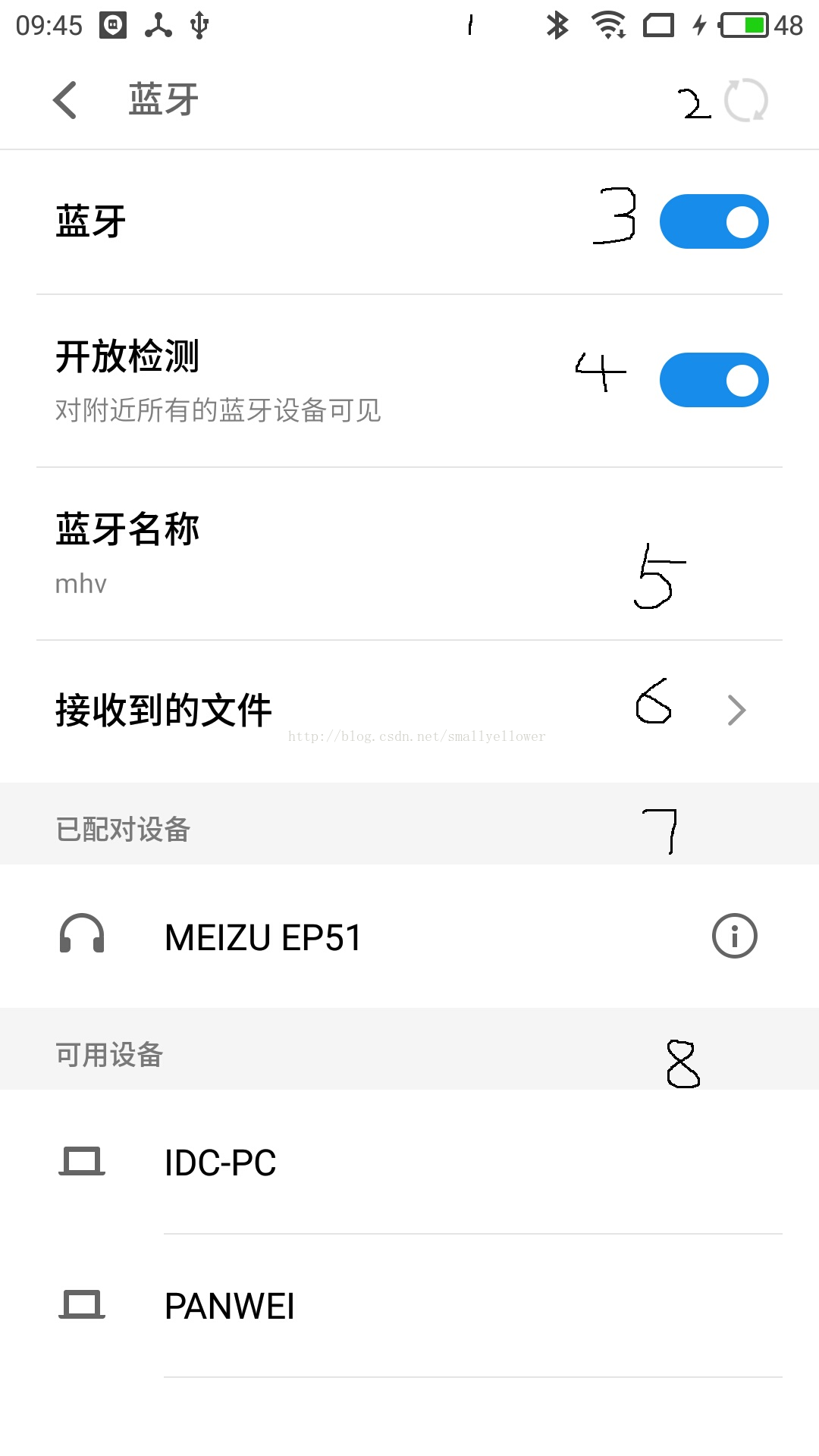
上图是手机设置中蓝牙界面。
1,当打开蓝牙时会在通知栏中有蓝牙图表展示
2,加载按钮,点击后取搜寻周围蓝牙设备。
3,打开关闭蓝牙的togglebutton
4,开发检测,关闭后周围蓝牙设备将不会搜索到本设备。
5,蓝牙的名称,一般和手机的名字一样可以自定义设置任意值。
6,接收到的文件,顾名思义我们可以通过蓝牙通信进行交换的文件例如发送一个mp3文件,在这里可以看到这个文件。
7,已配对设备:这里展示的是和本地蓝牙进行过配对的蓝牙设备,在这里通过列表的格式展示出配对设备列表的名字。
8,可用设备:已发现的蓝牙设备的列表,打开蓝牙后,点击2按钮会去搜索周围蓝牙设备,并且将搜索到的设备列表添加到这里。
注:可用设备和已配对设备的关系是,我们搜索到的设备可以进行配对,可能需要输入配对码,配对成功后将该设备加入到已配对的列表中,已配对的设备中,我们可以取消配对,将其从已配对列表中移除。
3,相关类
在Android 中关于蓝牙的类都在android.bluetooth包中,下面对几个常用的类进行概述。
BluetoothAdapter:表示本地的蓝牙适配器,bluetoothAdapter控制着执行蓝牙的基本任务,例如:搜索周围蓝牙设备,获取配对列表,通过一个已知的MAC地址(每个蓝牙设备都有一个唯一的Mac地址)构建BluetoothDevice对象,
并创建一个BluetoothServerSocket从其他设备监听连接请求,并开始一个扫描蓝牙设备。
BluetoothDevice:蓝牙设备类,代表一个远程蓝牙设备。BluetoothDevice允许您创建一个连接与各自的设备或查询相关信息,如蓝牙名字、MAC地址、class和绑定的状态(配对与否)等。
BluetoothServerSocket :这个类的用法非常像java网络编程中ServerSocket,用于监听Bluetooth Socket类。
BluetoothSocket:用法类似于Socket。一个连接上或连接中的Bluetooth Socket类。
4,连接通信过程
蓝牙的版本不一样通信的方式也有所不同,我们将分析两种不同的连接方式:classic类型蓝牙,Ble蓝牙。
classic类型蓝牙通信过程如下
1,•设置权限:
•<uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH"/>
•<uses-permissionandroid:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN"/>
2,打开蓝牙:
- 创建蓝牙适配器对象
BluetoothAdapter=
B








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 134
134











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








