第三章 处理数据
4.处理数组
我们大多数的数据都是以数组形式存储的,我们会花费大量的工作在格式化和重组数组的数据上,为此D3为我们提供了丰富的数组操作方法,使我们的工作简单化。在本节我们将展示最常用和实用的D3数组操作方法。
先来看下面的代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Working with Array</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"/>
<script type="text/javascript" src="http://d3js.org/d3.v3.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="code">var array = [3, 2, 11, 7, 6, 4, 10, 8, 15]</div>
<div>d3.min => <span id="min"></span></div>
<div>d3.max => <span id="max"></span></div>
<div>d3.extent => <span id="extent"></span></div>
<div>d3.sum => <span id="sum"></span></div>
<div>d3.median => <span id="median"></span></div>
<div>d3.mean => <span id="mean"></span></div>
<div>array.sort(d3.ascending) => <span id="asc"></span></div>
<div>array.sort(d3.descending) => <span id="desc"></span></div>
<div>d3.quantile(array.sort(d3.ascending), 0.25) => <span id="quantile"></span></div>
<div>d3.bisect(array.sort(d3.ascending), 6) => <span id="bisect"></span></div>
<div class="code">
<pre>
var records = [
{date: "2011-11-14T16:17:54Z", quantity: 2, total: 190, tip: 100, type: "tab"},
{date: "2011-11-14T16:20:19Z", quantity: 2, total: 190, tip: 100, type: "tab"},
{date: "2011-11-14T16:28:54Z", quantity: 1, total: 300, tip: 200, type: "visa"},
{date: "2011-11-14T16:30:43Z", quantity: 2, total: 90, tip: 0, type: "tab"},
{date: "2011-11-14T16:48:46Z", quantity: 2, total: 90, tip: 0, type: "tab"},
{date: "2011-11-14T16:53:41Z", quantity: 2, total: 90, tip: 0, type: "tab"},
{date: "2011-11-14T16:54:06Z", quantity: 1, total: 100, tip: 0, type: "cash"},
{date: "2011-11-14T16:58:03Z", quantity: 2, total: 90, tip: 0, type: "tab"},
{date: "2011-11-14T17:07:21Z", quantity: 2, total: 90, tip: 0, type: "tab"},
{date: "2011-11-14T17:22:59Z", quantity: 2, total: 90, tip: 0, type: "tab"},
{date: "2011-11-14T17:25:45Z", quantity: 2, total: 200, tip: 0, type: "cash"},
{date: "2011-11-14T17:29:52Z", quantity: 1, total: 200, tip: 100, type: "visa"}
];
d3.nest()
.key(function(d){return d.type;})
.key(function(d){return d.tip;})
.entries(records) =>
</pre>
</div>
<div>
<pre id="nest"></pre>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var array = [3, 2, 11, 7, 6, 4, 10, 8, 15];
d3.select("#min").text(d3.min(array));
d3.select("#max").text(d3.max(array));
d3.select("#extent").text(d3.extent(array));
d3.select("#sum").text(d3.sum(array));
d3.select("#median").text(d3.median(array));
d3.select("#mean").text(d3.mean(array));
d3.select("#asc").text(array.sort(d3.ascending));
d3.select("#desc").text(array.sort(d3.descending));
d3.select("#quantile").text(
d3.quantile(array.sort(d3.ascending), 0.25)
);
d3.select("#bisect").text(
d3.bisect(array.sort(d3.ascending), 6)
);
var records = [
{quantity: 2, total: 190, tip: 100, type: "tab"},
{quantity: 2, total: 190, tip: 100, type: "tab"},
{quantity: 1, total: 300, tip: 200, type: "visa"},
{quantity: 2, total: 90, tip: 0, type: "tab"},
{quantity: 2, total: 90, tip: 0, type: "tab"},
{quantity: 2, total: 90, tip: 0, type: "tab"},
{quantity: 1, total: 100, tip: 0, type: "cash"},
{quantity: 2, total: 90, tip: 0, type: "tab"},
{quantity: 2, total: 90, tip: 0, type: "tab"},
{quantity: 2, total: 90, tip: 0, type: "tab"},
{quantity: 2, total: 200, tip: 0, type: "cash"},
{quantity: 1, total: 200, tip: 100, type: "visa"}
];
var nest = d3.nest()
.key(function (d) { // <- A
return d.type;
})
.key(function (d) { // <- B
return d.tip;
})
.entries(records); // <- C
d3.select("#nest").html(printNest(nest, ""));
function printNest(nest, out, i) {
if(i === undefined) i = 0;
var tab = ""; for(var j = 0; j < i; ++j) tab += " ";
nest.forEach(function (e) {
if (e.key)
out += tab + e.key + "<br>";
else
out += tab + printObject(e) + "<br>";
if (e.values)
out = printNest(e.values, out, ++i);
else
return out;
});
return out;
}
function printObject(obj) {
var s = "{";
for (var f in obj) {
s += f + ": " + obj[f] + ", ";
}
s += "}";
return s;
}
</script>
</body>
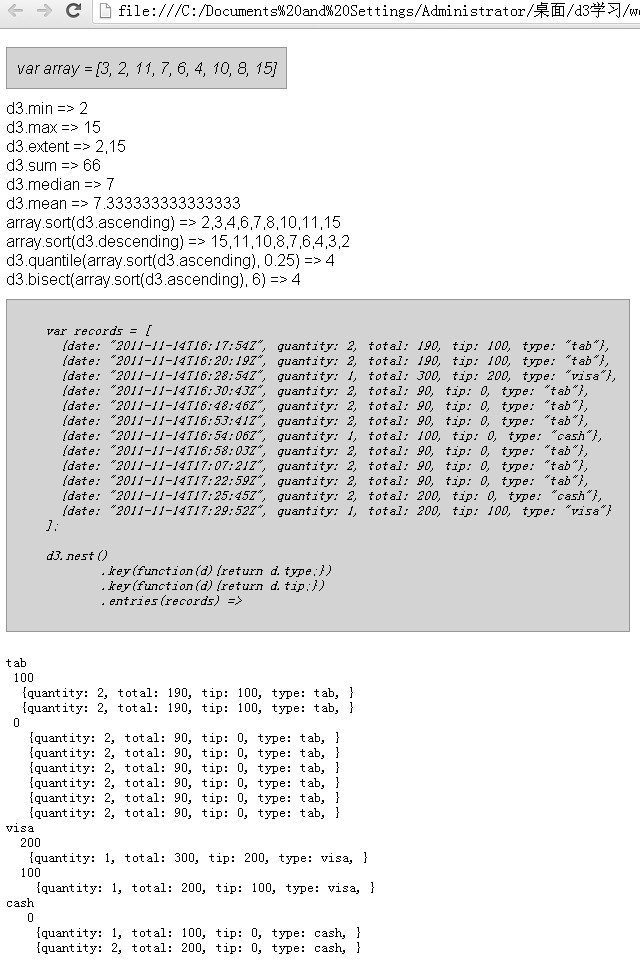
</html>以上的代码展示了D3所提供的最常用也是最有效的对数组的操作,在浏览器中运行的输出结果如下:
我们看看是如何工作的,D3提供了多种公共方法来帮助我们处理javascript数组,他们中的大多数是非常直观和直接的,然而,在本节中我们还是要简短的讨论一下他们的内在的东西。
我们看上面的代码,首先给了我们一个数组var array = [3, 2, 11, 7, 6, 4, 10, 8, 15];
d3.min(array)。d3.min这个方法用来获取数组中最小的元素,在本例中为2.
d3.max(array)。d3.max这个方法用来获取数组中最大的元素,在本例中为15.
d3.extent(array)。d3.extent这个方法返回数组中的最大值和最小值,本例中为2,15.
d3.sum(array)。d3.sum这个方法返回数组中所有元素的和,本例中为66.
d3.median(array)。d3.median这个方法返回数组中按大小顺序在中间的那个,本例中为7.
d3.mean(array)。 d3.mean这个方法返回数组中所有元素的平均值,本例为7.33.
array.sort(d3.ascending)/array.sort(d3.descending)。d3.ascending /d3.descending这个两个方法是D3内建的计算方法,可以用来对数组进行排序:
d3. ascending = function( a, b) { return a < b ? -1 : a > b ? 1 : 0;} 升序
d3. descending = function( a, b) { return b < a ? -1 : b > a ? 1 : 0;} 降序
d3.quantile(array.sort(d3.ascending), 0.25)。d3.quantile这个方法是计算已经升序排列的数组的分位数,本例中分位数为0.25的是4.
d3.bisect(array.sort(d3.ascending), 6)。d3.bisect这个方法可以获取已经排序数组中某个元素右边的元素,本例中6右边的为4.
d3.nest()方法可以用来建立一套算法,将一个平面阵列为基础的数据结构转变成一个分层嵌套结构,这种结构特别适合某些可视化项目,d3.nest()可以被看成是利用key方法链接到nest像我们在A处和B处看到的那样。
var nest = d3.nest()
.key(function (d) { // <- A
return d.type;
})
.key(function (d) { // <- B
return d.tip;
})
.entries(records); // <- C
多种key方法可以产生多层的嵌套,在本例中使用了2层,首先是type的值,然后是tip的值,最后展示的结果就是:
最后在C处entries方法用来支持平面阵列为基础的数据结构。






















 2730
2730

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








