首先熟悉三个概念:
SqlSessionFactoryBean
–为整合应用提供SqlSession对象资源
MapperFactoryBean
–根据指定的Mapper接口生成Bean实例
MapperScannerConfigurer
–根据指定包批量扫描Mapper接口并生成实例
SqlSessionFactoryBean:
在单独使用MyBatis时,所有操作都是围绕SqlSession展开的,SqlSession是通过SqlSessionFactory获取的,SqlSessionFactory又是通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建生成的。
在SpringMvc+MyBatis整合时,同样需要SqlSession。SqlSessionFactoryBean这个组件通过原来的SqlSessionFactoryBuilder生成SqlSessionFactory对象,为整合应用提供SqlSession对象。
Java代码
<bean id="myDataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:XE" />
<property name="username" value="jsd1403" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
</bean>
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="myDataSource" />
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:com/lydia/entity/*.xml" />
</bean> MapperFactoryBean:
其作用是根据Mapper接口获取我们想要的Mapper对象,它封装了原有的session.getMapper()功能的实现。
在定义MapperFactoryBean时,需要注入一下两个属性:
–SqlSessionFactoryBean对象,用于提供SqlSession
–要返回Mapper对象的Mapper接口
MapperFactoryBean配置如下:
Java代码
<!-- 方法一:定义mapper -->
<bean id="deptMapper" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean">
<property name="mapperInterface" value="com.lydia.entity.DeptMapper"></property>
<!-- 指定SqlSessionFactoryBean对象 -->
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"></property>
</bean> MapperScannerConfigurer配置使用:
注意:使用MapperFactoryBean时,当有一个Mapper(可以理解为表对应的映射文件)就MapperFactoryBean,当mapper少数可以通过applicationContext配置文件,通过id获取。
如果大量的mapper,需要使用mybatis-spring.jar通过的MapperScannerConfigurer组件,通过这个组件可以自动扫描指定包下的各个Mapper接口,并注册对应的MapperFactoryBean对象。
把之前的MapperFactoryBean的配置注释掉,换成如下配置依然执行通过:
Java代码
<!--方法2:
可以把扫描到的Mapper接口变成Mapper对象-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<!--指定要扫描包: 多个包用逗号隔开 -->
<property name="basePackage" value="com.lydia,com.tarena" />
<!--指定sqlSessionFactory -->
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"></property>
</bean> 注意:上面sqlSessionFactory属性也可以不用指定,默认会以Autowired方式注入。
如果指定的某个包下并不完全是我们定义的Mapper接口,我们也可以通过自定义注解的方式指定生成MapperFactoryBean对象。
配置如下:
<!--方法3:
只要Mapper类前面加上@MyBatisRepository 这个自己指定的注解就OK-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.lydia" />
<property name="annotationClass" value="com.lydia.annotation.MyBatisRepository" />
</bean> 自定义注解:MyBatisRepository.java
Java代码
public @interface MyBatisRepository {
} 在DeptMapper接口中使用:
//@Repository("deptMapper")
@MyBatisRepository
public interface DeptMapper {
void addDept(Dept dept);
void deleteDept(Dept dept);
void updateDept(Dept dept);
......
} 测试:
public class TestCase {
@Test
public void testFindAll() throws Exception {
String conf = "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf);
//获取对应的mapper对象,并调用mapper接口中对应的方法
DeptMapper mapper = ac.getBean("deptMapper", DeptMapper.class);
List<Dept> lists = mapper.findAllDept();
for (Dept dept : lists) {
System.out.println(dept);
}
}
} 以上内容来源于http://lydia-fly.iteye.com/blog/2153076
MapperScannerConfigurer处理过程源码分析
本文将分析mybatis与spring整合的MapperScannerConfigurer的底层原理,之前已经分析过java中实现动态,可以使用jdk自带api和cglib第三方库生成动态代理。本文分析的mybatis版本3.2.7,mybatis-spring版本1.2.2。
MapperScannerConfigurer介绍
MapperScannerConfigurer是spring和mybatis整合的mybatis-spring jar包中提供的一个类。
想要了解该类的作用,就得先了解MapperFactoryBean。
MapperFactoryBean的出现为了代替手工使用SqlSessionDaoSupport或SqlSessionTemplate编写数据访问对象(DAO)的代码,使用动态代理实现。
比如下面这个官方文档中的配置:
<bean id="userMapper" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean">
<property name="mapperInterface" value="org.mybatis.spring.sample.mapper.UserMapper" />
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory" />
</bean>org.mybatis.spring.sample.mapper.UserMapper是一个接口,我们创建一个MapperFactoryBean实例,然后注入这个接口和sqlSessionFactory(mybatis中提供的SqlSessionFactory接口,MapperFactoryBean会使用SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession)这两个属性。
之后想使用这个UserMapper接口的话,直接通过spring注入这个bean,然后就可以直接使用了,spring内部会创建一个这个接口的动态代理。
当发现要使用多个MapperFactoryBean的时候,一个一个定义肯定非常麻烦,于是mybatis-spring提供了MapperScannerConfigurer这个类,它将会查找类路径下的映射器并自动将它们创建成MapperFactoryBean。
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="org.mybatis.spring.sample.mapper" />
</bean>这段配置会扫描org.mybatis.spring.sample.mapper下的所有接口,然后创建各自接口的动态代理类。
MapperScannerConfigurer底层代码分析
以以下代码为示例进行讲解(部分代码,其他代码及配置省略):
package org.format.dynamicproxy.mybatis.dao;
public interface UserDao {
public User getById(int id);
public int add(User user);
public int update(User user);
public int delete(User user);
public List<User> getAll();
}
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="org.format.dynamicproxy.mybatis.dao"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>我们先通过测试用例debug查看userDao的实现类到底是什么。
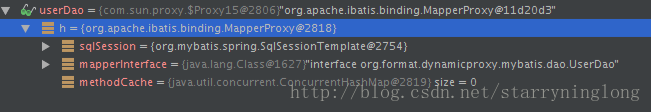
我们可以看到,userDao是1个MapperProxy类的实例。
看下MapperProxy的源码,没错,实现了InvocationHandler,说明使用了jdk自带的动态代理。
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
}下面开始分析MapperScannerConfigurer的源码
MapperScannerConfigurer实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口是一个可以修改spring工长中已定义的bean的接口,该接口有个postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法。
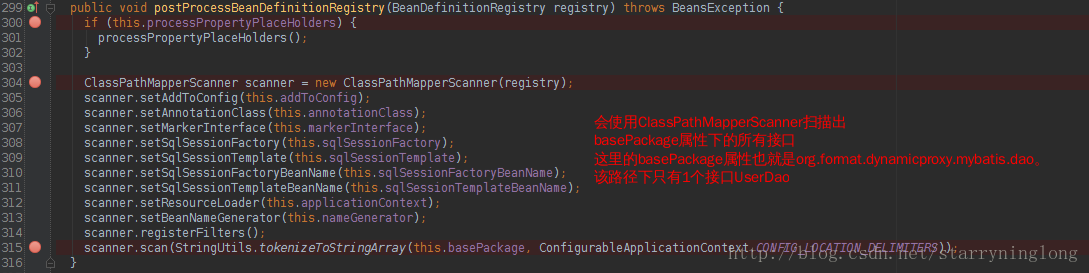
然后我们看下ClassPathMapperScanner中的关键是如何扫描对应package下的接口的。
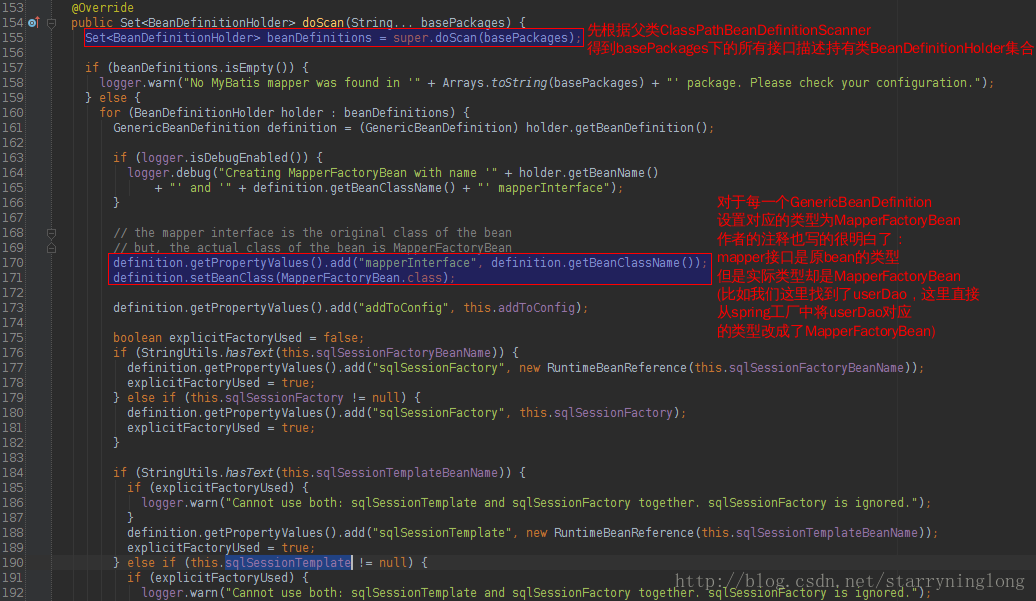
其实MapperScannerConfigurer的作用也就是将对应的接口的类型改造为MapperFactoryBean,而这个MapperFactoryBean的属性mapperInterface是原类型。MapperFactoryBean本文开头已分析过。
所以最终我们还是要分析MapperFactoryBean的实现原理!
MapperFactoryBean继承了SqlSessionDaoSupport类,SqlSessionDaoSupport类继承DaoSupport抽象类,DaoSupport抽象类实现了InitializingBean接口,因此实例个MapperFactoryBean的时候,都会调用InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet方法。
DaoSupport的afterPropertiesSet方法:
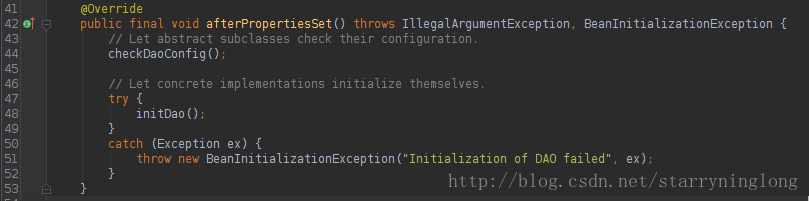
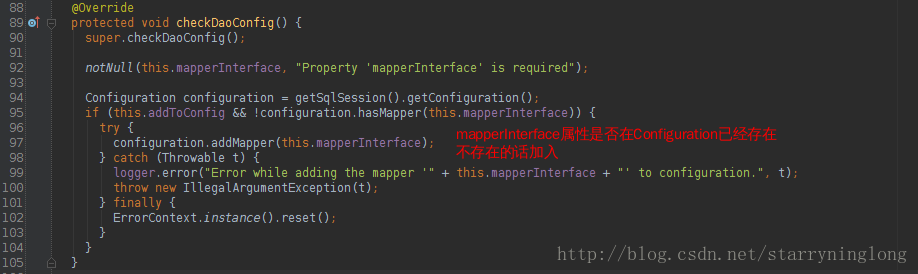
MapperFactoryBean重写了checkDaoConfig方法:
然后通过spring工厂拿对应的bean的时候:

这里的SqlSession是SqlSessionTemplate,SqlSessionTemplate的getMapper方法:

Configuration的getMapper方法,会使用MapperRegistry的getMapper方法:

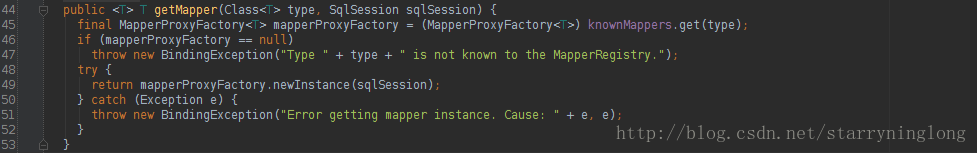
MapperRegistry的getMapper方法:
MapperProxyFactory构造MapperProxy:

没错! MapperProxyFactory就是使用了jdk组带的Proxy完成动态代理。
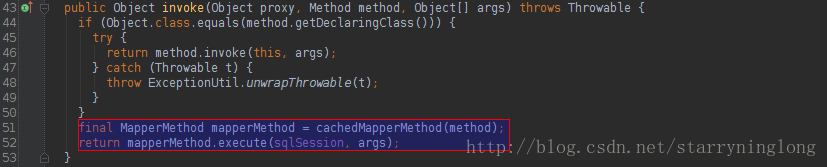
MapperProxy本来一开始已经提到。MapperProxy内部使用了MapperMethod类完成方法的调用:
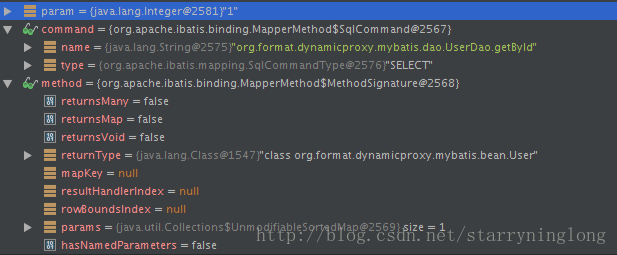
下面,我们以UserDao的getById方法来debug看看MapperMethod的execute方法是如何走的。
@Test
public void testGet() {
int id = 1;
System.out.println(userDao.getById(id));
}
<select id="getById" parameterType="int" resultType="org.format.dynamicproxy.mybatis.bean.User">
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = #{id}
</select>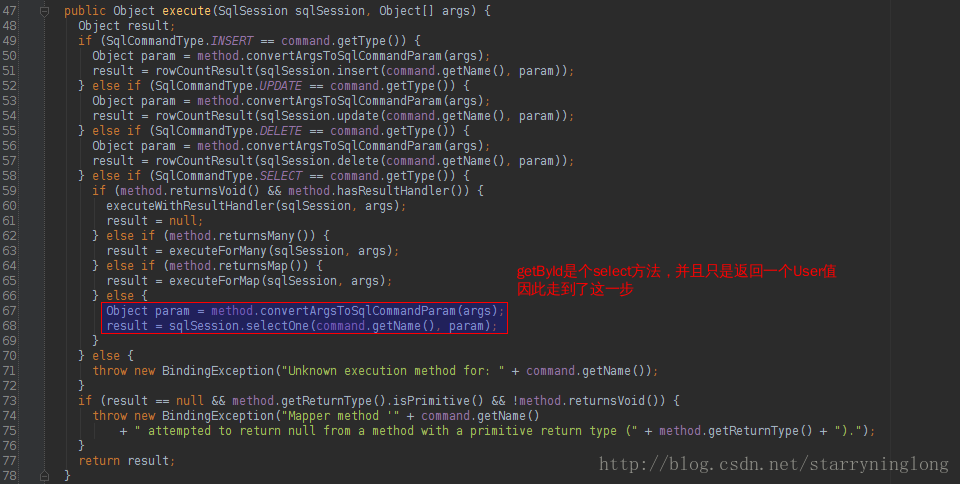
以上转载于http://www.cnblogs.com/fangjian0423/p/spring-mybatis-MapperScannerConfigurer-analysis.html
java动态代理浅析
最近在公司看到了mybatis与spring整合中MapperScannerConfigurer的使用,该类通过反向代理自动生成基于接口的动态代理类。
于是想起了java的动态代理,然后就有了这篇文章。
本文使用动态代理模拟处理事务的拦截器。
接口:
public interface UserService {
public void addUser();
public void removeUser();
public void searchUser();
}实现类:
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
public void addUser() {
System.out.println("add user");
}
public void removeUser() {
System.out.println("remove user");
}
public void searchUser() {
System.out.println("search user");
}
}java动态代理的实现有2种方式
1.jdk自带的动态代理
使用jdk自带的动态代理需要了解InvocationHandler接口和Proxy类,他们都是在java.lang.reflect包下。
InvocationHandler介绍:
InvocationHandler是代理实例的调用处理程序实现的接口。
每个代理实例都具有一个关联的InvocationHandler。对代理实例调用方法时,这个方法会调用InvocationHandler的invoke方法。
Proxy介绍:
Proxy 提供静态方法用于创建动态代理类和实例。
实例(模拟AOP处理事务):
public class TransactionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
private Object target;
public void setTarget(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("start Transaction");
method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("end Transaction");
return null;
}
}测试代码:
public class TestDynamicProxy {
@Test
public void testJDK() {
TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
transactionInterceptor.setTarget(userService);
UserService userServiceProxy =
(UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
userService.getClass().getClassLoader(),
userService.getClass().getInterfaces(),
transactionInterceptor);
userServiceProxy.addUser();
}
}测试结果:
start Transaction
add user
end Transaction很明显,我们通过userServiceProxy这个代理类进行方法调用的时候,会在方法调用前后进行事务的开启和关闭。
2. 第三方库cglib
CGLIB是一个功能强大的,高性能、高质量的代码生成库,用于在运行期扩展Java类和实现Java接口。
它与JDK的动态代理的之间最大的区别就是:
JDK动态代理是针对接口的,而cglib是针对类来实现代理的,cglib的原理是对指定的目标类生成一个子类,并覆盖其中方法实现增强,但因为采用的是继承,所以不能对final修饰的类进行代理。
实例:
public class UserServiceCallBack implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("start Transaction by cglib");
methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, args);
System.out.println("end Transaction by cglib");
return null;
}
}测试代码:
public class TestDynamicProxy {
@Test
public void testCGLIB() {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(UserServiceImpl.class);
enhancer.setCallback(new UserServiceCallBack());
UserServiceImpl proxy = (UserServiceImpl)enhancer.create();
proxy.addUser();
}
}测试结果:
start Transaction by cglib
add user
end Transaction by cglib以上转载于http://www.cnblogs.com/fangjian0423/p/java-dynamic-proxy.html
mybatis如何根据mapper接口生成其实现类
mybatis里头给sqlSession指定执行哪条sql的时候,有两种方式,一种是写mapper的xml的namespace+statementId,如下:
public Student findStudentById(Integer studId) {
logger.debug(“Select Student By ID :{}”, studId);
SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisSqlSessionFactory.getSqlSession();
try {
return sqlSession.selectOne(“com.mybatis3.StudentMapper.findStudentById”, studId);
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
另外一种方法是指定mapper的接口:
public Student findStudentById(Integer studId) {
logger.debug(“Select Student By ID :{}”, studId);
SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisSqlSessionFactory.getSqlSession();
try {
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
return studentMapper.findStudentById(studId);
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
一般的话,比较推荐第二种方法,因为手工写namespace和statementId极大增加了犯错误的概率,而且也降低了开发的效率。
问题
mapper的实现类如何生成
如果使用mapper接口的方式,问题来了,这个是个接口,通过sqlSession对象get出来的一定是个实现类,问题是,我们并没有手工去写 实现类,那么谁去干了这件事情呢?答案是mybatis通过JDK的动态代理方式,在启动加载配置文件时,根据配置mapper的xml去生成。
mybatis-spring帮忙做了什么
自动open和close session
一、mapper代理类是如何生成的
启动时加载解析mapper的xml
如果不是集成spring的,会去读取节点,去加载mapper的xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="useColumnLabel" value="true"/>
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="false"/>
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="SIMPLE"/>
<setting name="defaultStatementTimeout" value="2"/>
</settings>
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="CommentInfo" type="com.xixicat.domain.CommentInfo"/>
</typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value=""/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/xixicat/dao/CommentMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>如果是集成spring的,会去读spring的sqlSessionFactory的xml配置中的mapperLocations,然后去解析mapper的xml
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!-- 配置mybatis配置文件的位置 -->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/>
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.xixicat.domain"/>
<!-- 配置扫描Mapper XML的位置 -->
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:com/xixicat/dao/*.xml"/>
</bean>然后绑定namespace(XMLMapperBuilder)
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//ignore, bound type is not required
}
if (boundType != null) {
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag
// to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface
// look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
}这里先去判断该namespace能不能找到对应的class,若可以则调用
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
configuration委托给MapperRegistry:
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
mapperRegistry.addMapper(type);
}生成该mapper的代理工厂(MapperRegistry)
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}这里的重点就是MapperProxyFactory类:
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}getMapper的时候生成mapper代理类
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}new出来MapperProxy
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
这里给代理类注入了sqlSessionMapperProxy实现InvocationHandler接口进行拦截代理
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
}这里的代理拦截,主要是寻找到MapperMethod,通过它去执行SQL。
MapperMethod委托给SqlSession去执行sql
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.UPDATE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.DELETE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.SELECT == command.getType()) {
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
} else if (SqlCommandType.FLUSH == command.getType()) {
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
} else {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}其实这里就回到了第一种模式,该模式是直接指定了statement的Id(这里是command.getName()),而通过mapper的接口方式,则多了这么步骤,最后通过MapperMethod,给sqlSession传入statement的id。
sqlSession其实自己也不执行sql,它只是mybatis对外公布的一个api入口,具体它委托给了executor去执行sql。
什么时候去getMapper
手工get,比如
public void createStudent(Student student) {
SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisSqlSessionFactory.getSqlSession();
try {
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
studentMapper.insertStudent(student);
sqlSession.commit();
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}- 集成spring的话
在spring容器给指定的bean注入mapper的时候get出来(见MapperFactoryBean的getObject方法)
二、mybatis-spring帮忙做了什么
通过MapperScannerConfigurer将mapper适配成spring bean
<!-- 配置扫描Mapper接口的包路径 -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/>
<property name="basePackage" value="com.xixicat.dao"/>
</bean>这里使用 MapperFactoryBean将Mapper接口配置成 Spring bean 实体同时注入sqlSessionFactory。
MapperScannerConfigurer给每个mapper生成对应的MapperFactoryBean
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) {
processPropertyPlaceHolders();
}
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig);
scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass);
scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName);
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator);
scanner.registerFilters();
scanner.scan(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
}委托给ClassPathMapperScanner去scan
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn("No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages) + "' package. Please check your configuration.");
} else {
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) {
GenericBeanDefinition definition = (GenericBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName()
+ "' and '" + definition.getBeanClassName() + "' mapperInterface");
}
// the mapper interface is the original class of the bean
// but, the actual class of the bean is MapperFactoryBean
definition.getPropertyValues().add("mapperInterface", definition.getBeanClassName());
definition.setBeanClass(MapperFactoryBean.class);
definition.getPropertyValues().add("addToConfig", this.addToConfig);
boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false;
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionFactory != null) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
logger.warn("Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionTemplate != null) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
logger.warn("Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (!explicitFactoryUsed) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Enabling autowire by type for MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "'.");
}
definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}这里出现了MapperFactoryBean的身影,然后判断配置文件是指定注入sqlSessionFactory,还是 sqlTemplate(二者不能同时指定,这里是指定了sqlSessionFactory)。这里通过 sqlSessionFactoryBeanName暂时先注入引用,因为此时还在给spring托管的bean进行create,不确定 sqlSessionFactory是否已经被创建。
关于MapperFactoryBean
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> {
private Class<T> mapperInterface;
private boolean addToConfig = true;
/**
* Sets the mapper interface of the MyBatis mapper
*
* @param mapperInterface class of the interface
*/
public void setMapperInterface(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
/**
* If addToConfig is false the mapper will not be added to MyBatis. This means
* it must have been included in mybatis-config.xml.
* <p>
* If it is true, the mapper will be added to MyBatis in the case it is not already
* registered.
* <p>
* By default addToCofig is true.
*
* @param addToConfig
*/
public void setAddToConfig(boolean addToConfig) {
this.addToConfig = addToConfig;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
super.checkDaoConfig();
notNull(this.mapperInterface, "Property 'mapperInterface' is required");
Configuration configuration = getSqlSession().getConfiguration();
if (this.addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this.mapperInterface)) {
try {
configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface);
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Error while adding the mapper '" + this.mapperInterface + "' to configuration.", t);
throw new IllegalArgumentException(t);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public Class<T> getObjectType() {
return this.mapperInterface;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}注意这里继承了SqlSessionDaoSupport,在spring把sqlSessionFactory创建出来后,会去把之前注入的引用改为真的实例,调用SqlSessionDaoSupport的setSqlSessionFactory方法。
public abstract class SqlSessionDaoSupport extends DaoSupport {
private SqlSession sqlSession;
private boolean externalSqlSession;
public void setSqlSessionFactory(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
if (!this.externalSqlSession) {
this.sqlSession = new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
public void setSqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSessionTemplate;
this.externalSqlSession = true;
}
/**
* Users should use this method to get a SqlSession to call its statement methods
* This is SqlSession is managed by spring. Users should not commit/rollback/close it
* because it will be automatically done.
*
* @return Spring managed thread safe SqlSession
*/
public SqlSession getSqlSession() {
return this.sqlSession;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
notNull(this.sqlSession, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' or 'sqlSessionTemplate' are required");
}
}这里值得注意的是setSqlSessionFactory方法new了一个SqlSessionTemplate。
SqlSessionTemplate
它的一个重要的构造器为
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");
notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.executorType = executorType;
this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class },
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}mybatis-srping比传统mybatis方法多做的事情就在于此,生成了一个sqlSessionProxy。这里static import了java.lang.reflect.Proxy.newProxyInstance;也就是使用使用jdk代理进行了 SqlSessionInterceptor拦截。
SqlSessionInterceptor
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(
SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
// force commit even on non-dirty sessions because some databases require
// a commit/rollback before calling close()
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
Throwable unwrapped = unwrapThrowable(t);
if (SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator != null && unwrapped instanceof PersistenceException) {
// release the connection to avoid a deadlock if the translator is no loaded. See issue #22
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
sqlSession = null;
Throwable translated = SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator.translateExceptionIfPossible((PersistenceException) unwrapped);
if (translated != null) {
unwrapped = translated;
}
}
throw unwrapped;
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
}到了这里就明白了mybatis-spring帮忙做了session的open和close。
以上转载于http://www.cnblogs.com/ChenLLang/p/5307590.html

























 121
121

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








