Android开发–UI之Bundle的使用
最近,把之前学过的东西大体的整理了以下,并且想把学过的心得分享给大家。我自己做了一个小小的demo,以便说明具体的应用。

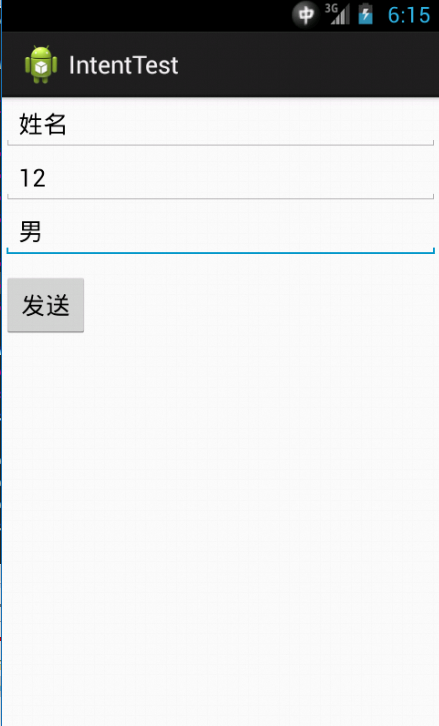
这里的两个界面是通过第一个界面输入,然后,第二个界面输出结果的。
废话少说,直接进入正题。
第一个界面的代码:
package com.example.intenttest;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private EditText edtname;
private EditText edtage;
private EditText edtsex;
private Button send;
private String name;
private String age;
private String sex;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
edtname = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.edt1);
edtage = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.edt2);
edtsex = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.edt3);
send = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn);
send.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
startTransmitData();
}
});
}
private void startTransmitData(){
name = edtname.getText().toString(); //将edtname强制转换为String类型
age = edtage.getText().toString();
sex = edtsex.getText().toString(); //将edtsex强制转换为String类型
Intent mIntent = new Intent();
mIntent.setClass(getApplicationContext(),ShowActivity.class);
Bundle mBundle = new Bundle();
//通过key--valuse进行记录
mBundle.putString("name", name);
mBundle.putString("age", age);
mBundle.putString("sex", sex);
//将整个的数据进行封装到intent中,等待传递
mIntent.putExtras(mBundle);
startActivity(mIntent);
}
}
第一个界面的xml代码:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/LinearLayout1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edt1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10" >
</EditText>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edt2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10" >
</EditText>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edt3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10" >
</EditText>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="发送" />
</LinearLayout>
第二个界面的代码:
package com.example.intenttest;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class ShowActivity extends Activity{
private TextView txtname;
private TextView txtage;
private TextView txtsex;
private Button cal;
private String name;
private String age;
private String sex;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.showactivity);
txtname = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt1);
txtage = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt2);
txtsex = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt3);
Intent inten = getIntent();
Bundle bundle = inten.getExtras();
//通过key值进行获取所对应的valuse值
name = bundle.getString("name");
age = bundle.getString("age");
sex = bundle.getString("sex");
//将内容显示在控件中
txtname.setText(name);
txtage.setText(age);
txtsex.setText(sex);
cal = (Button)findViewById(R.id.cal);
cal.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
finish();
}
});
}
}
第二个界面的xml代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#000"
android:text="测试1" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt2"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#000"
android:text="测试2" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt3"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#000"
android:text="测试3" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/cal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="返回" />
</LinearLayout>
代码到这里已经完成了大部分的功能,只是需要在配置文件中进行以下配置就可以了。
上面的解释很简单也很明了,我相信,你看过之后一定会有很大帮助吧。
你学会了吗??





 本文详细介绍了Android开发中Bundle的使用方法,通过创建简单的demo,展示如何在两个界面间传递数据。包括界面布局设计、代码实现及配置文件调整,确保读者能够清晰掌握Bundle在实际开发中的应用。
本文详细介绍了Android开发中Bundle的使用方法,通过创建简单的demo,展示如何在两个界面间传递数据。包括界面布局设计、代码实现及配置文件调整,确保读者能够清晰掌握Bundle在实际开发中的应用。
















 650
650

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








