题目
标题和出处
标题:二叉搜索树的范围和
难度
3 级
题目描述
要求
给定二叉搜索树的根结点 root \texttt{root} root 以及两个整数 low \texttt{low} low 和 high \texttt{high} high,返回值位于范围 [low, high] \texttt{[low, high]} [low, high] 内的所有结点值的和。
示例
示例 1:
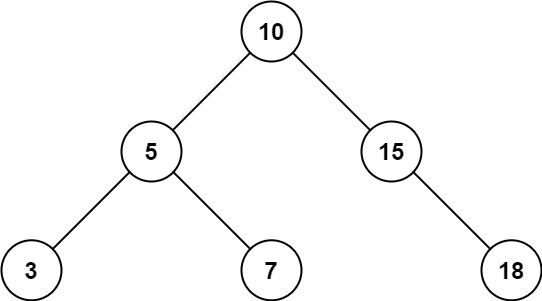
输入:
root
=
[10,5,15,3,7,null,18],
low
=
7,
high
=
15
\texttt{root = [10,5,15,3,7,null,18], low = 7, high = 15}
root = [10,5,15,3,7,null,18], low = 7, high = 15
输出:
32
\texttt{32}
32
解释:结点
7
\texttt{7}
7、
10
\texttt{10}
10 和
15
\texttt{15}
15 在范围
[10,
15]
\texttt{[10, 15]}
[10, 15] 内。
7
+
10
+
15
=
32
\texttt{7} + \texttt{10} + \texttt{15} = \texttt{32}
7+10+15=32。
示例 2:
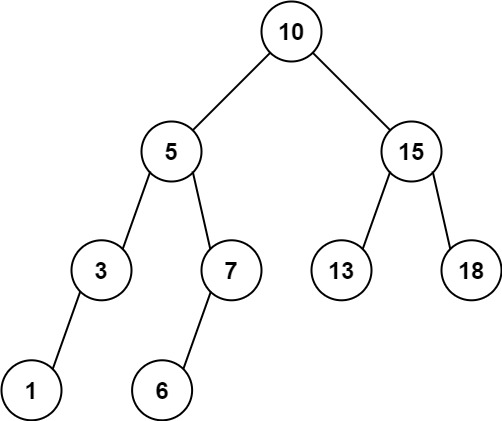
输入:
root
=
[10,5,15,3,7,13,18,1,null,6],
low
=
6,
high
=
10
\texttt{root = [10,5,15,3,7,13,18,1,null,6], low = 6, high = 10}
root = [10,5,15,3,7,13,18,1,null,6], low = 6, high = 10
输出:
23
\texttt{23}
23
解释:结点
6
\texttt{6}
6、
7
\texttt{7}
7 和
10
\texttt{10}
10 在范围
[6,
10]
\texttt{[6, 10]}
[6, 10] 内。
6
+
7
+
10
=
23
\texttt{6} + \texttt{7} + \texttt{10} = \texttt{23}
6+7+10=23。
数据范围
- 树中结点数目在范围 [1, 2 × 10 4 ] \texttt{[1, 2} \times \texttt{10}^\texttt{4}\texttt{]} [1, 2×104] 内
- 1 ≤ Node.val ≤ 10 5 \texttt{1} \le \texttt{Node.val} \le \texttt{10}^\texttt{5} 1≤Node.val≤105
- 1 ≤ low ≤ high ≤ 10 5 \texttt{1} \le \texttt{low} \le \texttt{high} \le \texttt{10}^\texttt{5} 1≤low≤high≤105
- 所有 Node.val \texttt{Node.val} Node.val 各不相同
解法一
思路和算法
如果二叉搜索树为空,则结点值总和为 0 0 0。
如果二叉搜索树不为空,则首先判断根结点值是否在给定的范围内,决定根结点是否计入结点值总和。
-
如果根结点值大于上界,则根结点的右子树中的所有结点值都大于根结点值,因此都大于上界,应该在根结点的左子树中计算结点值总和。
-
如果根结点值小于下界,则根结点的左子树中的所有结点值都小于根结点值,因此都小于下界,应该在根结点的右子树中计算结点值总和。
-
如果根结点值在给定的边界范围内,则根结点计入结点值总和,对左子树和右子树分别结点值总和。得到根结点值、左子树结点值总和与右子树结点值总和之后,即可得到原二叉搜索树的结点值总和。
上述过程是一个递归的过程,递归的终止条件是当前结点为空,此时返回 0 0 0。对于其余情况,首先判断根结点是否计入结点值总和,然后对根结点的左子树和右子树调用递归,计算结点值总和。
代码
class Solution {
public int rangeSumBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
if (root.val > high) {
return rangeSumBST(root.left, low, high);
}
if (root.val < low) {
return rangeSumBST(root.right, low, high);
}
return root.val + rangeSumBST(root.left, low, high) + rangeSumBST(root.right, low, high);
}
}
复杂度分析
-
时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),其中 n n n 是二叉搜索树的结点数。每个结点最多被访问一次。
-
空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),其中 n n n 是二叉搜索树的结点数。空间复杂度主要是递归调用的栈空间,取决于二叉搜索树的高度,最坏情况下二叉搜索树的高度是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
解法二
思路和算法
由于二叉搜索树的中序遍历序列是单调递增的,因此只要得到二叉搜索树的中序遍历序列,即可得到给定的范围在中序遍历序列中对应的连续子序列,计算该连续子序列中的结点值总和,即为给定的范围内的结点值总和。
由于只是计算给定的范围内的结点值总和,因此不需要存储完整的中序遍历序列。
对于中序遍历过程中访问的每个结点,判断该结点值是否在给定的范围内。如果结点值在给定的范围内,则将结点值加到结点值总和中。如果结点值大于上界,则中序遍历序列中的其余结点值一定都大于上界,因此结束遍历。
代码
class Solution {
public int rangeSumBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
int sum = 0;
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<TreeNode>();
TreeNode node = root;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || node != null) {
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
node = stack.pop();
if (node.val >= low && node.val <= high) {
sum += node.val;
} else if (node.val > high) {
break;
}
node = node.right;
}
return sum;
}
}
复杂度分析
-
时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),其中 n n n 是二叉搜索树的结点数。每个结点最多被访问一次。
-
空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),其中 n n n 是二叉搜索树的结点数。空间复杂度主要是栈空间,取决于二叉搜索树的高度,最坏情况下二叉搜索树的高度是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
解法三
思路和算法
莫里斯遍历是使用常数空间遍历二叉树的方法。
使用莫里斯遍历对二叉搜索树中序遍历时,同样判断访问的每个结点值是否在给定的范围内,计算给定的范围内的结点值总和,当遇到一个结点值大于上界时结束遍历。
代码
class Solution {
public int rangeSumBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
int sum = 0;
TreeNode node = root;
boolean inRange = true;
while (node != null && inRange) {
if (node.left == null) {
if (node.val >= low && node.val <= high) {
sum += node.val;
} else if (node.val > high) {
inRange = false;
}
node = node.right;
} else {
TreeNode predecessor = node.left;
while (predecessor.right != null && predecessor.right != node) {
predecessor = predecessor.right;
}
if (predecessor.right == null) {
predecessor.right = node;
node = node.left;
} else {
predecessor.right = null;
if (node.val >= low && node.val <= high) {
sum += node.val;
} else if (node.val > high) {
inRange = false;
break;
}
node = node.right;
}
}
}
return sum;
}
}
复杂度分析
-
时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),其中 n n n 是二叉搜索树的结点数。使用莫里斯遍历,每个结点最多被访问两次。
-
空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)。

























 1573
1573











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










