ReentrantLock有两种实现方式,一种是公平锁,一种非公平锁。默认为非公平锁。
Lock的不同实现
不允许打断的Lock实现
非公平锁的lock实现
java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock.NonfairSync#lock
final void lock() {
// 如果state是0,表示当前没有人获取锁,通过CAS的方式设置state
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
// 如果获取锁成功了,设置当前支持锁的线程
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
// 如果锁被其它线程持有,则执行该方法
acquire(1);
}
公平锁的lock实现
java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock.FairSync#lock
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
两者都调用了java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer#acquire,所以我们看下该方法的具体实现。
public final void acquire(int arg) {
// 先尝试获取锁
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
// 构建双端队列,且是独占式的
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
// 中断指令
selfInterrupt();
}
这就是一个模板模式,具体实现还得看各自子类的实现。
先看tryAcquire的两种不同实现方式
非公平锁tryAcquire
java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock.NonfairSync#tryAcquire
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// 这里和非公平锁的首次尝试获取是一致的,通过CAS进行设置state状态
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 如果当前锁时当前线程持有,则更新state状态
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
// 否则获取锁失败
return false;
}
公平锁的tryAcquire
java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock.FairSync#tryAcquire
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
// hasQueuedPredecessors为false: 队列为空或者当前线程为头节点
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 如果是当前锁持有,则更新state的状态
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
addWaiter的实现
java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer#addWaiter构建双端队列,依次被唤醒。
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
// 如果当前的尾节点不为空,则将当前线程对应的节点,添加至尾结点
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
// 如果是首次,则构建队列。
enq(node);
// 返回当前节点
return node;
}
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
// 如果是首次添加,则添加一个空节点,我称之为哑节点
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
// 当前节点指向尾结点
node.prev = t;
// 把当前节点赋值于尾结点
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
// 返回的是当前添加前的尾节点。如当前链表是node1、node2,新添加的node3,这里返回node2
return t;
}
}
}
}
acquireQueued的实现
java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer#acquireQueued
通过代码中可以看到,即使中断也不会将获取锁的流程中断,仅是增加一次循环,将interrupted设置为TRUE,虽然获取锁不会被中断,但是在获取锁后,仍然会触发一次中断,如果在获取锁后,仍有中断指令判断,则会触发。
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// 如果当前节点的前置节点是head,则尝试再次获取锁
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
// 将waitstatus设置为signal(-1)
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
// park,阻塞线程执行,等待unpark后继续执行
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
执行park,等待unpark
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
// 先park住了,需要中断指令或者unpark才会继续执行
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
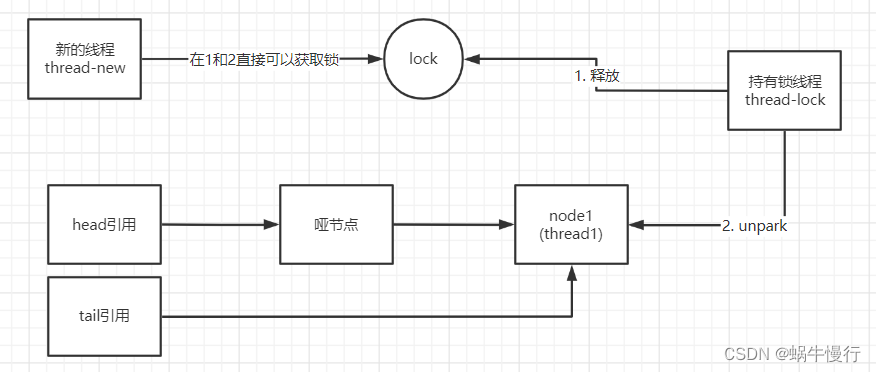
主要流程如下:

允许打断的Lock实现
java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock#lockInterruptibly
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer#acquireInterruptibly允许打断获取锁实现,与不允许打断的lock的区别是,在获取锁之前,先判断当前线程是否被打断。其中tryAcquire与前文所述一致。
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
// 先判断线程是否被打断
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
// 尝试获取锁
if (!tryAcquire(arg))
doAcquireInterruptibly(arg);
}
关于java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer#doAcquireInterruptibly的实现,有一点不同的,具体看逻辑实现
private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
// 这里是抛出一个中断异常,不允许打断锁,这里仅是设置一下中断的状态。
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
尝试获取锁tryLock
及时判断方式
该方式与lock的区别在于仅当state为0或者当前线程持有锁时才返回true,否则返回false。而不会将当前线程构造node进行排队等候。关于nonfairTryAcquire的实现,前文已经有所述,此处不再重述。
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.nonfairTryAcquire(1);
}
带过期时间的方式
java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock#tryLock(long, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit)可以执行过期时间
public boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
public final boolean tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
// 会判断当前线程是否中断
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
// 先尝试获取锁,如果获取成功,则不进行带过期时间的判断了
return tryAcquire(arg) ||
doAcquireNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}
private boolean doAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
// 超时时间为小于0的数,直接结束
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
// 计算超时截止时间
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
// 添加至等待队列
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// 如果当前节点是队首节点,则进行尝试获取锁
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return true;
}
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
// 如果当前已经达到过期时间或者超过,则结束
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
// 如果超时时间大于1000ns, 则进行park等待,否则再次循环判断
nanosTimeout > spinForTimeoutThreshold)
// 通过LockSupport进行超时判断
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
// 如果超时,则将状态设置为取消
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
unlock的实现
加锁方式分为允许中断、不允许中断、带超时等多种方式,但是释放锁仅有一种。
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
// 这里首节点状态应该为-1,signal状态
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// 当前状态减去释放次数,因为Reentrantlock是可重入的,当前线程获取几次锁,得释放几次
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
// 当状态为0,则表明该线程释放了锁
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
唤醒下一个等待锁的线程继续执行java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer#unparkSuccessor
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
// 首节点为哑节点,所以需要唤醒的为head的节点的下一个节点
Node s = node.next;
// 大于0为取消的线程,不需要执行了,超时时就把node的状态设置了cancelled。
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
// 逆向找第一个状态小于0的,也就是第一个状态为-1的
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
// 唤醒对应的线程继续执行。
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
相关问题
- ReentrantLock是否是可重入的,怎么实现可重入的?
是可重入锁,通过exclusiveOwnerThread记录当前获取锁线程,当再次获取锁时,更新state的值实现可重入的。 - ReentrantLock在无锁状态下,state是几?有锁状态下又是多少?
无锁状态下为0,大于0为持有锁,如果为2,则表明持有锁两次 - ReentrantLock超时获取锁时怎么实现的?
基于LockSupport.parkNanos实现的 - 公平锁与非公平锁的体现在哪里?
非公平锁是在获取锁时先尝试获取锁,如果获取失败,则构建FIFO队列,然后等待唤醒。
公平锁是直接通过FIFO队列,等待唤醒






















 7764
7764











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








