1. LeetCode 530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-absolute-difference-in-bst/description/
文章链接:https://programmercarl.com/0530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差.html
视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1DD4y11779
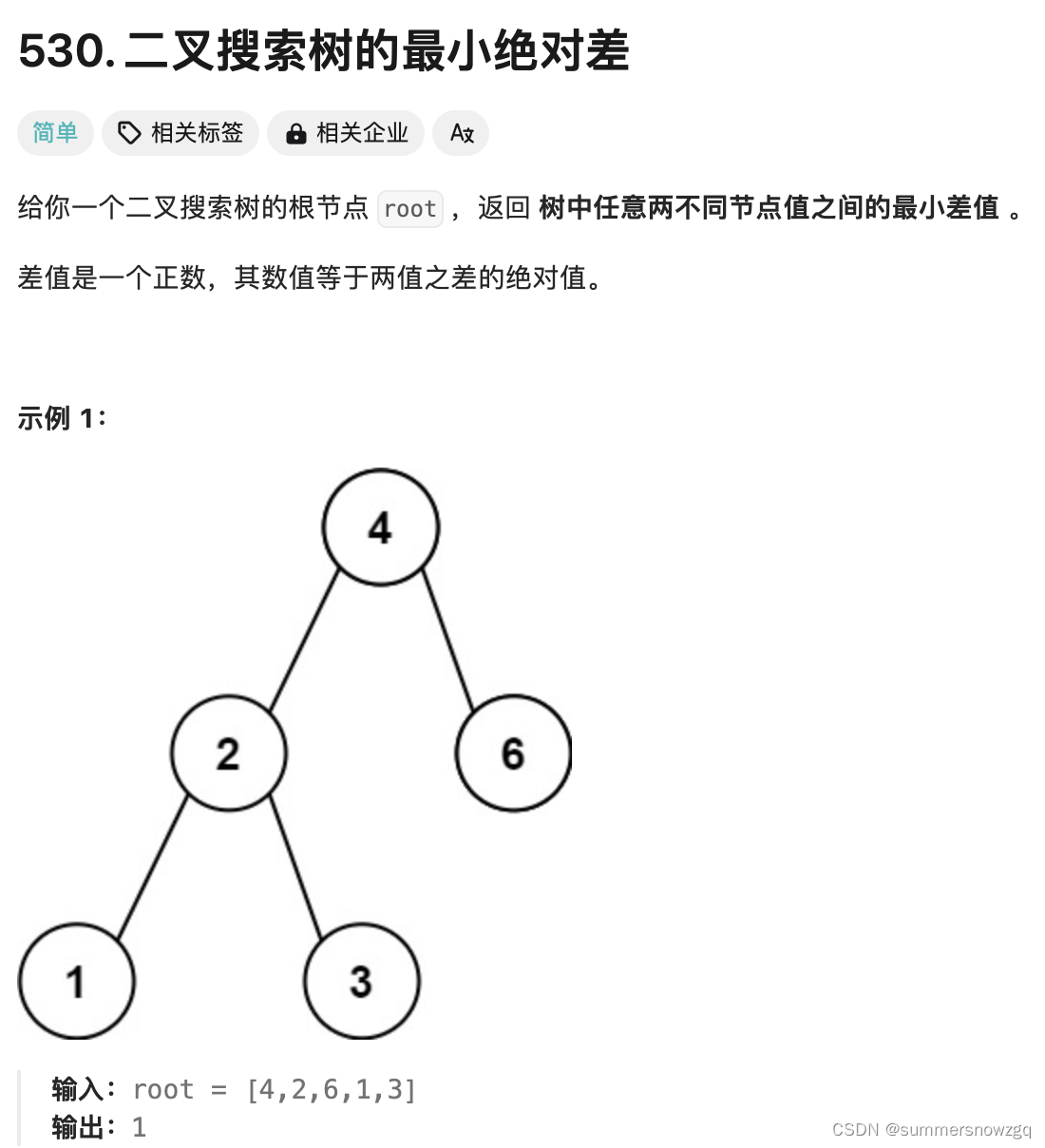
思路:
使用中序遍历。因为二叉搜索树中序遍历是单调递增的,通过前后两个节点的差值与最小值进行比较,找出最终最小值。
解法:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
TreeNode pre = null;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// 中序遍历递归法
// public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
// if(root==null || (root.left==null && root.right==null)) {
// return 0;
// }
// find(root);
// return min;
// }
// // 中序遍历
// public void find(TreeNode root) {
// if (root == null) return;
// // 左
// find(root.left);
// // 中
// if (pre!=null) {
// int curInter = root.val - pre.val;
// if (curInter < min) {
// min = curInter;
// }
// }
// pre = root;
// // 右
// find(root.right);
// }
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
find(root);
return min;
}
// 中序遍历迭代法
public void find(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
if (root == null || (root.left==null && root.right==null)) {
min = 0;
return;
}
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
// 左
cur = cur.left;
} else {
// 中
cur = stack.pop();// 当前节点
if (pre != null) {
if (cur.val-pre.val<min) {
min = cur.val-pre.val;
}
}
pre = cur;
// 右
cur = cur.right;
}
}
}
}
2. LeetCode 501.二叉搜索树中的众数
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree/description/
文章链接:https://programmercarl.com/0501.二叉搜索树中的众数.html
视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fD4y117gp

思路:
使用中序遍历。
首先将当前节点与前一节点进行比较,若相等,则当前节点的计数加1;否则当前节点的计数等于1。
然后比较当前节点的计数与最大计数,若大于,则清空集合,并传入当前节点的值;若相等,则传入当前节点的值;若小于,则不传入集合。
解法:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int count = 1;
int max = 1;
TreeNode pre = null;
List<Integer> modes = new ArrayList<>();
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
find(root);
// 将众数列表转换为数组
return modes.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
private void find(TreeNode cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return;
}
// 左
find(cur.left);
// 中
if (pre != null) {
if (pre.val == cur.val) {
count++;
} else {
count = 1;
}
}
if (count > max) {
max = count;
modes.clear();
modes.add(cur.val);
} else if (count == max) {
modes.add(cur.val);
}
pre = cur;
// 右
find(cur.right);
}
}
3.LeetCode 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/description/
文章链接:https://programmercarl.com/0236.二叉树的最近公共祖先.html
视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1jd4y1B7E2
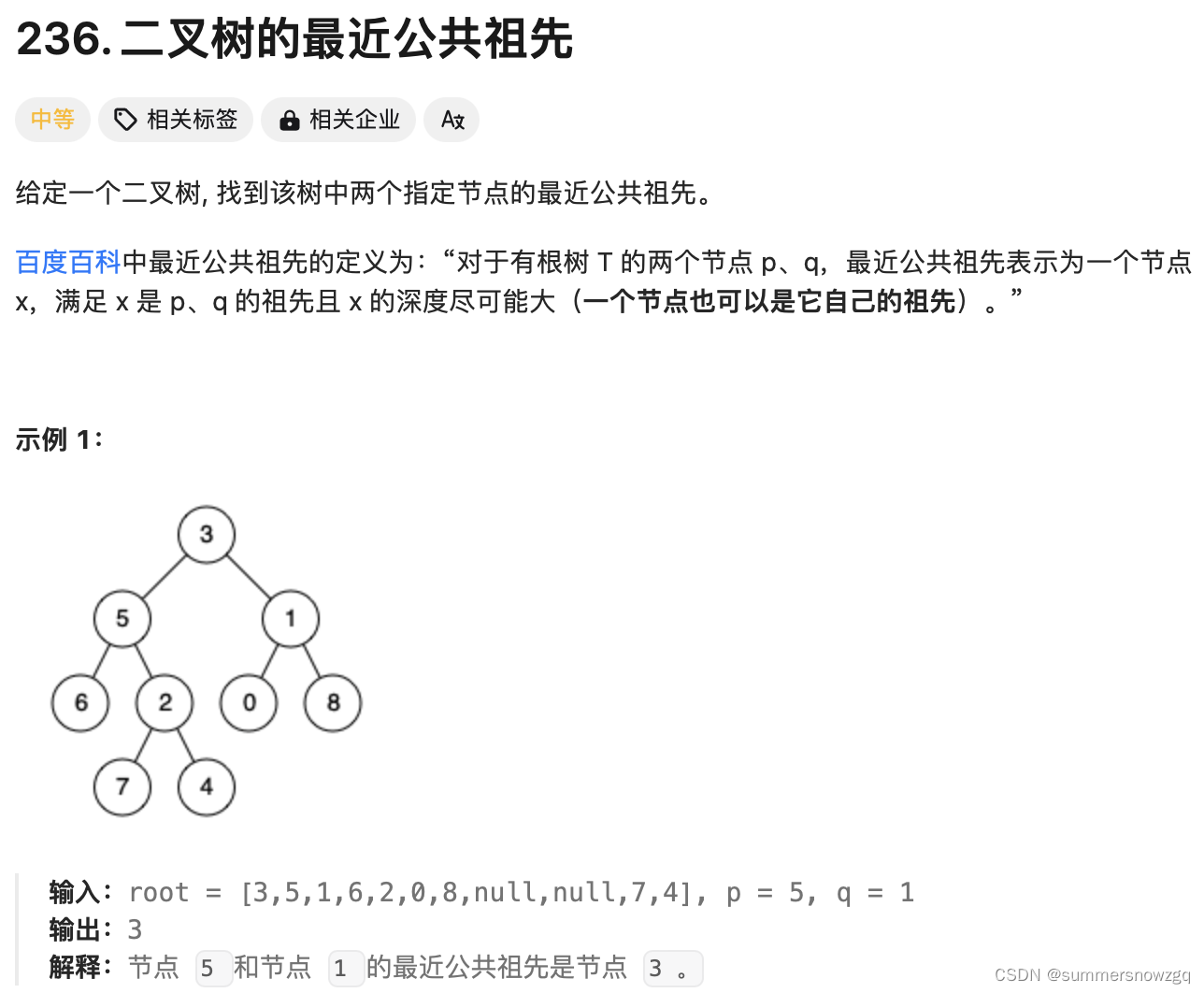
思路:使用后序遍历从底往上递归方式。
解题关键是,只有左右节点返回都不是空时,当前节点才是公共祖先。
若有一个左或右节点为空,说明当前节点不是公共祖先,公共祖先在上面的层上,将不为空的节点继续返回,表示上面的递归中,某个节点的某个子树中含有某一个目标节点,只需找到左右子树都含有目标节点的节点,即公共祖先。
归纳如下三点:
1️⃣求最小公共祖先,需要从底向上遍历,那么二叉树,只能通过后序遍历(即:回溯)实现从底向上的遍历方式。
2️⃣在回溯的过程中,必然要遍历整棵二叉树,即使已经找到结果了,依然要把其他节点遍历完,因为要使用递归函数的返回值(也就是代码中的left和right)做逻辑判断。
3️⃣要理解如果返回值left为空,right不为空为什么要返回right,为什么可以用返回right传给上一层结果。
解法:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null) return null;
// 左
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
// 右
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
// 中
if (root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
if (left != null && right == null) {
return left;
} else if (left == null && right != null) {
return right;
} else if (left == null && right == null) {
return null;
} else {
return root;
}
}
}





















 1121
1121

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








