优化排序操作
1、PGA
show parameter pga_aggregate_target;
show parameter workarea_size_policy;
setting Initially PGA
For OLTP:
pga_aggregate_target=(total_mem*80%)*20%
For DSS:
pga_aggregate_target=(total_mem*80%)*50%
2、PGA Management Resources
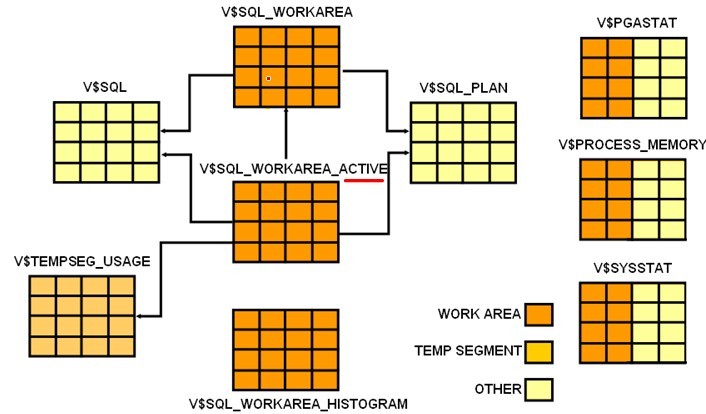
1) Views for monitoring the PGA work area include:
-- v$sql_workarea_histogram
-- v$pagstat
-- v$sql_workarea_active
-- v$sql_workarea
-- v$tempseg_usage
2) Views to assist in sizing the PGA work area are:
-- v$pga_target_advice
-- v$pga_target_advice_histogram
select * from v$pgastat;
select * from v$sql_workarea_histogram;
select low_optimal_size/1024 "Low_kb",(high_optimal_size+1)/1024 "High_kb",
round(100*optimal_executions/total_executions) "Optimal",
round(100*onepass_executions/total_executions) "One Pass",
round(100*multipasses_executions/total_executions) "Multi Pass"
from v$sql_workarea_histogram
where total_executions != 0
order by "Low_kb";
select to_number(decode(sid,65535,null,sid)) sid,
operation_type Oper,
trunc(expected_size/1024) esize,
trunc(actual_mem_used/1024) mem,
trunc(max_mem_used/1024) "Max Mem",
number_passes pass
from v$sql_workarea_active
order by 1,2;
select sql_text,
sum(onepass_executions) onepass_cnt,
sum(multipasses_executions) mpass_cnt
from v$sql s, v$sql_workarea wa
where s.address = wa.address
group by sql_text
having sum(onepass_executions + multipasses_executions)>0;
3、PGA Target Advice Statistics
--v$pga_target_advice
select * from v$pga_target_advice;
v$sql_workarea_histogram;
show parameter sort_area_size;
4、Requiring Sorts
select * from v$sysstat where name like '%sort%';
Avoiding Sort

Diagnostic Tools
-- v$sort_usage
-- v$sort_segment
-- v$tempfile
-- dba_temp_file
十一、Using Resource Manager --使用资源管理器
1、Create Simple Resource Plan
-- dbms_resource_manager
begin
dbms_resource_manager.create_simple_plan('linplan','grp1',80,'grp2',20);
end;
2、Assigning Privilege
-- dbms_resource_manager_privs
dbms_resource_manager_privs.grant_system_privilege
( grantee_name => 'OE',
privilege_name => 'ADMINISTER_RESOURCE_MANAGER',
admin_option => False);
3、Creating Complex RP
1) create a pending area
2) create,modify or delete consumer groups
3) create the resource plan
4) create resource plan directives
5) validate the pending area
6) submit the pending area
begin
dbms_resource_manager.create_pending_area();
end;
begin
dbms_resource_manager.create_consumer_group('my_oltp','this is my group');
end;
begin
dbms_resource_manager.create_plan('my_plan','this is my plan');
end;
begin
dbms_resource_manager.create_plan_directive('my_plan','my_oltp','xxxx',75);
end;
begin
dbms_resource_manager.create_plan_directive('my_plan','other_groups','xxxx',15);
end;
begin
dbms_resource_manager.validate_pending_area();
end;
begin
dbms_resource_manager.submit_pending_area();
end;
Assigning Users
4、Views and DDs
-- dba_rsrc_plans
-- dba_rsrc_plan_directives
-- dba_rsrc_consumer_groups
-- dba_rsrc_consumer_group_privs
-- dba_users中的INITIAL_RSRC_CONSUMER_GROUP列
-- dba_rsrc_manager_system_privs
-- v$session 中的resource_consumer_group列
-- v$rsrc_plan
-- v$rsrc_consumer_group
十一、SQL Statement Tuning --SQL语句调优
1、Using Hints in SQL
select /*+ INDEX(customers gen_idx) */ cust_last_name,cust_street_address,cust_postal_code
from sh.customers where uper(cust_gender) = 'M';
2、Diagnostic Tools
* Statspack
* explain plan
* sql trace and tkprof
* sqlplus autotrace feature
* oracle sql analyze
3、Explain plan
SQL> @?/rdbms/admin/utlxplan.sql
SQL> explain plan for
2 select employee_id,last_name,salary
3 from hr.employees where employee_id=120;
Explained.
SQL> select count(*) from plan_table;
COUNT(*)
----------
3
* Use script utlxpls.sql (hide Parallel Query information)
* Use script utlxplp.sql (show Parallel Query information)
* Use the dbms_xplan package
SQL> @?/rdbms/admin/utlxpls.sql;
SQL> select * from table(dbms_xplan.display);
4、Using SQL Trace & TKPROF Formatting the Trace File
1. cd [ORACLE_HOME]/rdbms/admin
2. log into SQL*Plus as SYSTEM
3. Run @utlxplan
4. Run CREATE PUBLIC SYNONYM PLAN_TABLE FOR PLAN_TABLE;
5. Run GRANT ALL ON PLAN_TABLE TO PUBLIC;
1. cd [ORACLE_HOME]/sqlplus/admin
2. Log in to SQL*Plus as SYS or as SYSDBA
3. Run @plustrce
4. Run GRANT PLUSTRACE TO PUBLIC;
set autot on;
十二、Managing Statistics --管理统计数据
1、 Managing Statistics

Use the dbms_stats package
* gather_table_stats
* gather_index_stats
* gather_schema_stats
* gather_database_stats
* gather_stale_stats
-- all_tables
-- all_indexes
-- user_tab_col_statistics
-- v$segstat_name
-- v$segstat
-- v$segment_statistics
| SQL> select object_id from dba_objects where owner='HR' and object_name='T'; OBJECT_ID ---------- 58134 SQL> select * from v$segstat where dataobj#=58134; TS# OBJ# DATAOBJ# STATISTIC_NAME STATISTIC# VALUE ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------------------------------------------------------------- ---------- ---------- 4 58134 58134 logical reads 0 64 4 58134 58134 buffer busy waits 1 0 4 58134 58134 gc buffer busy 2 0 4 58134 58134 db block changes 3 12704 4 58134 58134 physical reads 4 411 4 58134 58134 physical writes 5 373 4 58134 58134 physical reads direct 6 0 4 58134 58134 physical writes direct 7 0 4 58134 58134 gc cr blocks received 9 0 4 58134 58134 gc current blocks received 10 0 4 58134 58134 ITL waits 11 0 4 58134 58134 row lock waits 12 0 4 58134 58134 space used 14 0 4 58134 58134 space allocated 15 0 4 58134 58134 segment scans 17 0 15 rows selected SQL> |
Enabling Dynamic Sampling
-- show parameter optimizer_dynamic_sampling
Histograms
-- dbms_stats.gather_table_stats
-- dba_histograms
-- dba_tab_histograms
exec dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('HR','T',method_opt=>'FOR COLUMNS SIZE 10 id');
Gathering System Statistics (dbms_stats)
-- gather_system_stats
-- set_system_stats
-- get_system_stats
Collect statistics for OLTP:
execute dbms_stats.gather_system_stats(interval =>120,stattab=>'mystats',statid='OLTP')
Collect statistics for OLAP:
execute dbms_stats.gather_system_stats(interval =>120,stattab=>'mystats',statid='OLAP')
2、Copy Statistics Between DBs
example
1) create the table to hold the statistics:
dbms_stats.create_stat_table
('SH',STATS','SAMPLE');
exec dbms_stats.create_stat_table('HR','MYSTATS');
2) Copy the statistics to a table
dbms_stats.export_table_stats
('SH','SALES',NULL,'STATS','CRS990601',TRUE);
3)Export the stats table and import it into the second database
4)Copy the statistics into the data dictionary
dbms_stats.import_table_stats
('SH','SALES',NULL,'STATS','CR990601',TRUE);
























 2009
2009

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








