这个缓冲机制规定,只有收到回车键,才会将所有输入的数据一次过提交到输入处理函数(就是 cin 或者 scanf 了)
而这个输入过程,在按下回车键之前,是不受到 cin 和 scanf 控制的…..
cin缓冲机制如下:
1)可以看作流输入,是双缓冲的,一个是键盘缓冲,这个存储用户的输入,一个流缓冲;
这个存储流的数据。
2)遇到回车,流缓冲,就从键盘缓冲里读取数据,流输入,从流缓冲里取数据输入到变量中去。
当数据不够用时,流输入就会等待,用户输入回车,然后刷新流缓冲;
3)然后流输入,再从流缓冲里取数据,够用时,数据输入到变量中,多余的数据存储在,流缓冲中,供下次使用。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int Limit=255;
int main()
{
char input[Limit];
cout<<"Enter a string for getline():\n";
cin.getline(input,Limit,'#');
cout<<"Here is your input:\n";
cout<<input<<"\nDone with phase 1\n";
char ch;
cin.get(ch);
cout<<"The next input char is "<<ch<<endl;
if(ch!='\n')
cin.ignore(Limit,'\n');
cout<<"Enter a string for get():\n";
cin.get(input,Limit,'#');
cout<<"Here is your input:\n";
cout<<input<<"\nDone with phase 2\n";
cin.get(ch);
cout<<"The next input char is "<<ch<<endl;
return 0;
}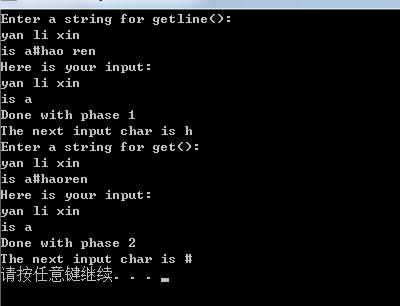
cin.getline()会读取结束符号并丢弃它。而cin.get()不会读取结束符,而是将它留在输入流中。
2.文件的输入和输出
三部曲:1.定义对象fin,fout 2.对象和文件关联3.进行fin和fout。
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char *filename;
//string filename;
double num;
cout<<"Enter the filename:\n";
//cin>>filename;
cin.getline(filename,50); //用getline()不能传string类型的 要char*
ofstream fout;
fout.open(filename);
fout<<"For your eyes only!\n";
cout<<"Enter your secret number:";
cin>>num;
fout<<"your secret num is:"<<num<<endl;
fout.close();
ifstream fin;
fin.open(filename);
cout<<"The content of "<<filename<<" is:\n";
char ch;
while(fin.get(ch))
cout<<ch;
cout<<"Done\n";
fin.close();
return 0;
}3.命令行处理技术
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])//参数个数 和 命令行参数
{
if(argc==1)
{
cerr<<"Usage:"<<argv[0]<<" filename[s]\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
long count;
long total=0;
char ch;
ifstream fin;
for(int file=1;file<argc;file++)//依次处理命令行中的文件
{
fin.open(argv[file]);
if(!fin.is_open())
{
cerr<<"Could not open "<<argv[file]<<endl;
fin.clear();
continue;
}
count=0;
while(fin.get(ch))
count++;
cout<<count<<" characters in "<<argv[file]<<endl;
total+=count;
fin.clear();
fin.close();
}
cout<<total<<" characters in all files\n";
return 0;
}4.追加内容:
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char *filename="guest";
char ch;
string name;
ifstream fin;
fin.open(filename);
if(!fin.is_open())
{
cout<<"File can not be opened!\n";
}
else
{
cout<<"The content of "<<filename<<" is:\n";
while(fin.get(ch))
cout<<ch;
fin.clear();
fin.close();
}
ofstream fout;
fout.open(filename,ios::out|ios::app);//想要追加文件内容打开时以此模式打开就可以了
if(!fout.is_open())
{
cout<<"File can not be opened!\n";
}
else
{
cout<<"Enter the name of guest:";
while(getline(cin,name)&&name.size()>0)
fout<<name<<endl;
fout.clear();
fout.close();
}
//ifstream fin; 不需要再定义对象
fin.open(filename);
if(!fin.is_open())
{
cout<<"File can not be opened!\n";
}
else
{
cout<<"The content of "<<filename<<" is:\n";
while(fin.get(ch))
cout<<ch;
fin.clear();
fin.close();
}
return 0;
}






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








