一.水仙花数的判断
1)含义
水仙花数(Narcissistic number)也被称为自恋数、阿姆斯特朗数,是指一个n位数,它的每个位上的数字的n次幂之和等于它本身。例如,三位数的水仙花数有153(1^3 + 5^3 + 3^3 = 153)、370(3^3 + 7^3 + 0^3 = 370)等。
2)核心思想
水仙花数的判断本质上是拆数问题,即将数字分离出来
3)步骤
-
将这个数转换成字符串,以获取其位数。
-
遍历每一位数字,计算其n次幂之和。
-
判断该和是否等于原数。
4)具体例子
a.输入一个数,判断是否为水仙花数
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个数来判断是否为水仙花数:");
int inputNumber = scanner.nextInt();
if (isNarcissistic(inputNumber)) {
System.out.println(inputNumber + " 是水仙花数。");
} else {
System.out.println(inputNumber + " 不是水仙花数。");
}
scanner.close();
}
// 方法用于判断给定的数是否为水仙花数
public static boolean isNarcissistic(int num) {
// 将数字转换为字符串,以便获取位数
String numStr = Integer.toString(num);
int length = numStr.length(); // 获取位数
int sum = 0;
// 遍历每一位数字并计算n次幂之和
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int digit = Character.getNumericValue(numStr.charAt(i)); // 获取当前位的数字
sum += Math.pow(digit, length); // 计算该位数字的n次幂并累加
}
// 判断累加和是否等于原数
return sum == num;
}
}


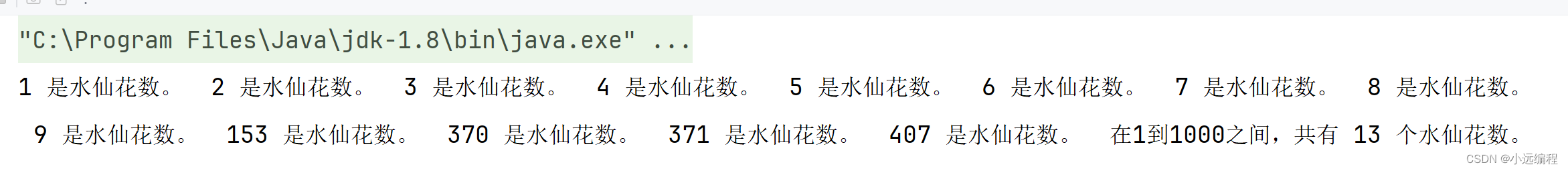
b.在1-1000中,有水仙花数的个数
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0; // 用于计数水仙花数的个数
// 遍历1到1000之间的所有数
for (int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++) {
if (isNarcissistic(i)) {
count++;
System.out.println(i + " 是水仙花数。");
}
}
System.out.println("在1到1000之间,共有 " + count + " 个水仙花数。");
}
// 方法用于判断给定的数是否为水仙花数
public static boolean isNarcissistic(int num) {
String numStr = Integer.toString(num);
int length = numStr.length();
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int digit = Character.getNumericValue(numStr.charAt(i));
sum += Math.pow(digit, length);
}
return sum == num;
}
}
二.闰年的判断
1)闰年的标准:
-
如果年份能被4整除但不能被100整除,则是闰年。
-
或者,如果年份能被400整除,则也是闰年
2)代码实现
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args){
//提示语
System.out.println("请输入一个年份:");
//输入一个年份
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = sc.nextInt();
//异常处理
if(year<0){
System.out.println("年份有误!");
} else if (isLeapYear(year)) {
System.out.println(year + " 是闰年。");
} else {
System.out.println(year + " 不是闰年。");
}
sc.close();
}
//isLeapYear方法来判断这个年份是否为闰年
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year){
return (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0);
}
}
3)具体呈现



三.个位数字统计
1)题目详情
给定一个整数n,统计每种不同的个位数字出现的次数。例如,给定n=100811,则有2个0,3个1,1个8。
输入格式:
输入一个不超过长整型范围的整数n。
输出格式:
对n中每一种不同的各位数字,以 D:M 的格式在一行中输出该位数字 D 及其在 n 中出现的次数 M。要求按 D 的升序输出。
输入样例:
100811
输出样例:
0:2 1:3 8:1
2)代码实现
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个整数: ");
long n = scanner.nextLong();
scanner.close();
// 初始化一个数组来存储0-9每个数字出现的次数
int[] digitCount = new int[10];
// 遍历n的每一位数字并计数
while (n != 0) {
digitCount[(int) (n % 10)]++;
n /= 10;
}
// 直接遍历0-9,输出每个数字及其出现的次数
for (int digit = 0; digit < digitCount.length; digit++) {
if (digitCount[digit] > 0) {
System.out.print(digit + ":" + digitCount[digit]+" ");
}
}
}
}
3)具体呈现
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个整数: ");
long n = scanner.nextLong();
scanner.close();
// 初始化一个数组来存储0-9每个数字出现的次数
int[] digitCount = new int[10];
// 遍历n的每一位数字并计数
while (n != 0) {
digitCount[(int) (n % 10)]++;
n /= 10;
}
// 直接遍历0-9,输出每个数字及其出现的次数
for (int digit = 0; digit < digitCount.length; digit++) {
if (digitCount[digit] > 0) {
System.out.print(digit + ":" + digitCount[digit]+" ");
}
}
}
}

四.构造方法与toString
1)题目详情
定义一个有关人的Person类,内含属性: String name、int age、boolean gender、int id,所有的变量必须为私有(private)。 注意:属性顺序请严格按照上述顺序依次出现。
1.编写无参构造函数:
-
打印"This is constructor"。
-
将name,age,gender,id按照
name,age,gender,id格式输出
2.编写有参构造函数
依次对name,age,gender赋值。
3.覆盖toString
按照格式:类名 [name=, age=, gender=, id=]输出。建议使用Eclipse自动生成.
4.对每个属性生成setter/getter方法
5.main方法中
-
首先从屏幕读取n,代表要创建的对象个数。
-
然后输入n行name age gender , 调用上面2编写的有参构造函数新建对象。
-
然后将刚才创建的所有对象
逆序输出。 -
接下来使用无参构造函数新建一个Person对象,并直接打印该对象。
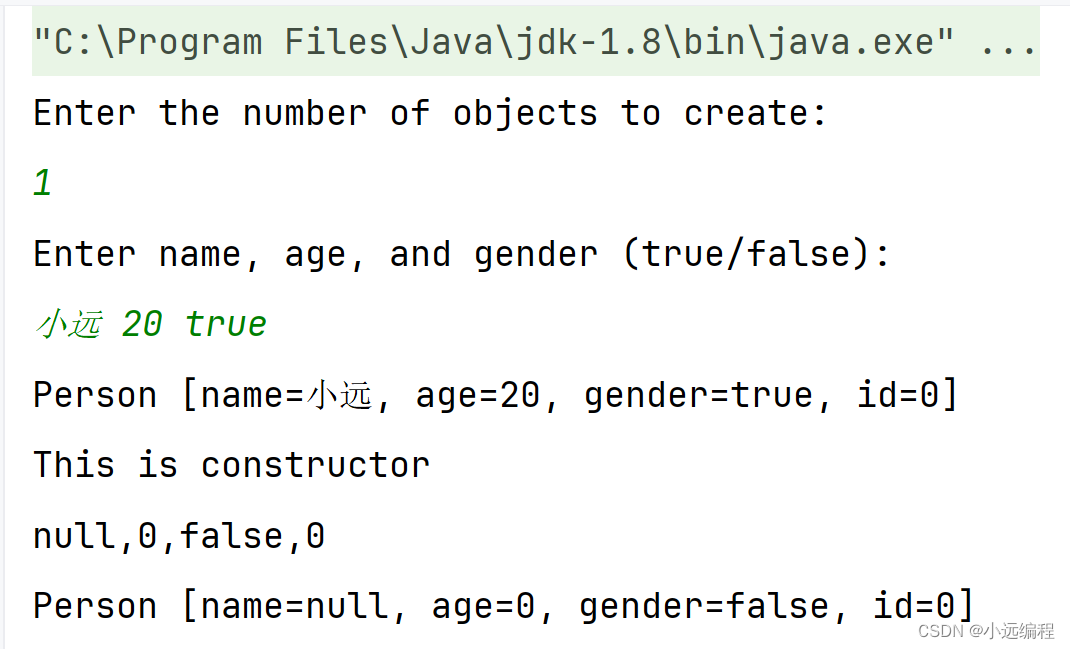
输入样例:
3 a 11 false b 12 true c 10 false
输出样例:
Person [name=c, age=10, gender=false, id=0] Person [name=b, age=12, gender=true, id=0] Person [name=a, age=11, gender=false, id=0] This is constructor null,0,false,0 Person [name=null, age=0, gender=false, id=0]
2)代码实现
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private boolean gender;
private int id;
// 1. 无参构造函数
public Person() {
System.out.println("This is constructor");
System.out.println(this.name + "," + this.age + "," + this.gender + "," + this.id);
}
// 2. 有参构造函数
public Person(String name, int age, boolean gender) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
// 注意:id未在构造函数中初始化,通常id可能由数据库生成或有特定的生成逻辑
}
// toString方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", gender=" + gender + ", id=" + id + "]";
}
// setter和getter方法
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public int getAge() { return age; }
public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; }
public boolean isGender() { return gender; }
public void setGender(boolean gender) { this.gender = gender; }
public int getId() { return id; } // 假设id一旦设定则不变,故不提供setter
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of objects to create:");
int n = scanner.nextInt();
List<Person> people = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println("Enter name, age, and gender (true/false):");
String inputName = scanner.next();
int inputAge = scanner.nextInt();
boolean inputGender = scanner.nextBoolean();
people.add(new Person(inputName, inputAge, inputGender));
}
// 逆序输出创建的对象
Collections.reverse(people);
for (Person person : people) {
System.out.println(person);
}
// 使用无参构造函数创建Person对象并打印
Person defaultPerson = new Person();
System.out.println(defaultPerson);
}
}
3)具体呈现
五.USB接口的定义
1)题目详情
定义一个USB接口,并通过Mouse和U盘类实现它,具体要求是:
1.接口名字为USB,里面包括两个抽象方法:
void work();描述可以工作
void stop(); 描述停止工作
2.完成类Mouse,实现接口USB,实现两个方法:
work方法输出“我点点点”;
stop方法输出 “我不能点了”;
3.完成类UPan,实现接口USB,实现两个方法:
work方法输出“我存存存”;
stop方法输出 “我走了”;
4测试类Main中,main方法中
定义接口变量usb1 ,存放鼠标对象,然后调用work和stop方法
定义接口数组usbs,包含两个元素,第0个元素存放一个Upan对象,第1个元素存放Mouse对象,循环数组,对每一个元素都调用work和stop方法。
输出格式:
输出方法调用的结果
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
我点点点 我不能点了 我存存存 我走了 我点点点 我不能点了
2)代码实现
// 1. 定义USB接口
interface USB{
void work();//描述可以工作
void stop();//描述停止工作
}
// 2. 实现USB接口的Mouse类
class Mouse implements USB{
@Override
public void work() {
System.out.println("我点点点");
}
@Override
public void stop() {
System.out.println("我不能点了");
}
}
// 3. 实现USB接口的UPan类
class UPan implements USB{
@Override
public void work(){
System.out.println("我存存存");
}
@Override
public void stop(){
System.out.println("我走了");
}
}
// 4. 测试类Main
public class Main {
public static void main(String[]args){
// 创建Mouse对象并调用其方法
USB usb1 = new Mouse();
usb1.work();
usb1.stop();
// 创建USB接口数组,存放U盘和鼠标对象,并循环调用它们的方法
USB[] usbs =new USB[2];
usbs[0] = new UPan();
usbs[1] = new Mouse();
for(USB usb:usbs){
usb.work();
usb.stop();
}
}
}
3)具体呈现

六.继承
1)题目详情
1.定义抽象类Shape 属性:不可变静态常量double PI,值为3.14, 抽象方法:public double getPerimeter(),public double getArea()
2.Rectangle与Circle类均继承自Shape类。 Rectangle类(属性:int width,length)、Circle类(属性:int radius)。 带参构造方法为Rectangle(int width,int length),Circle(int radius)。 toString方法(Eclipse自动生成)
3.编写double sumAllArea方法计算并返回传入的形状数组中所有对象的面积和与 double sumAllPerimeter方法计算并返回传入的形状数组中所有对象的周长和。
4.main方法 4.1 输入整型值n,然后建立n个不同的形状。如果输入rect,则依次输入宽、长。如果输入cir,则输入半径。 4.2 然后输出所有的形状的周长之和,面积之和。并将所有的形状信息以样例的格式输出。 提示:使用Arrays.toString。 4.3 最后输出每个形状的类型与父类型.使用类似shape.getClass() //获得类型, shape.getClass().getSuperclass() //获得父类型;
注意:处理输入的时候使用混合使用nextInt与nextLine需注意行尾回车换行问题。
思考
-
你觉得
sumAllArea和sumAllPerimeter方法放在哪个类中更合适? -
是否应该声明为static?
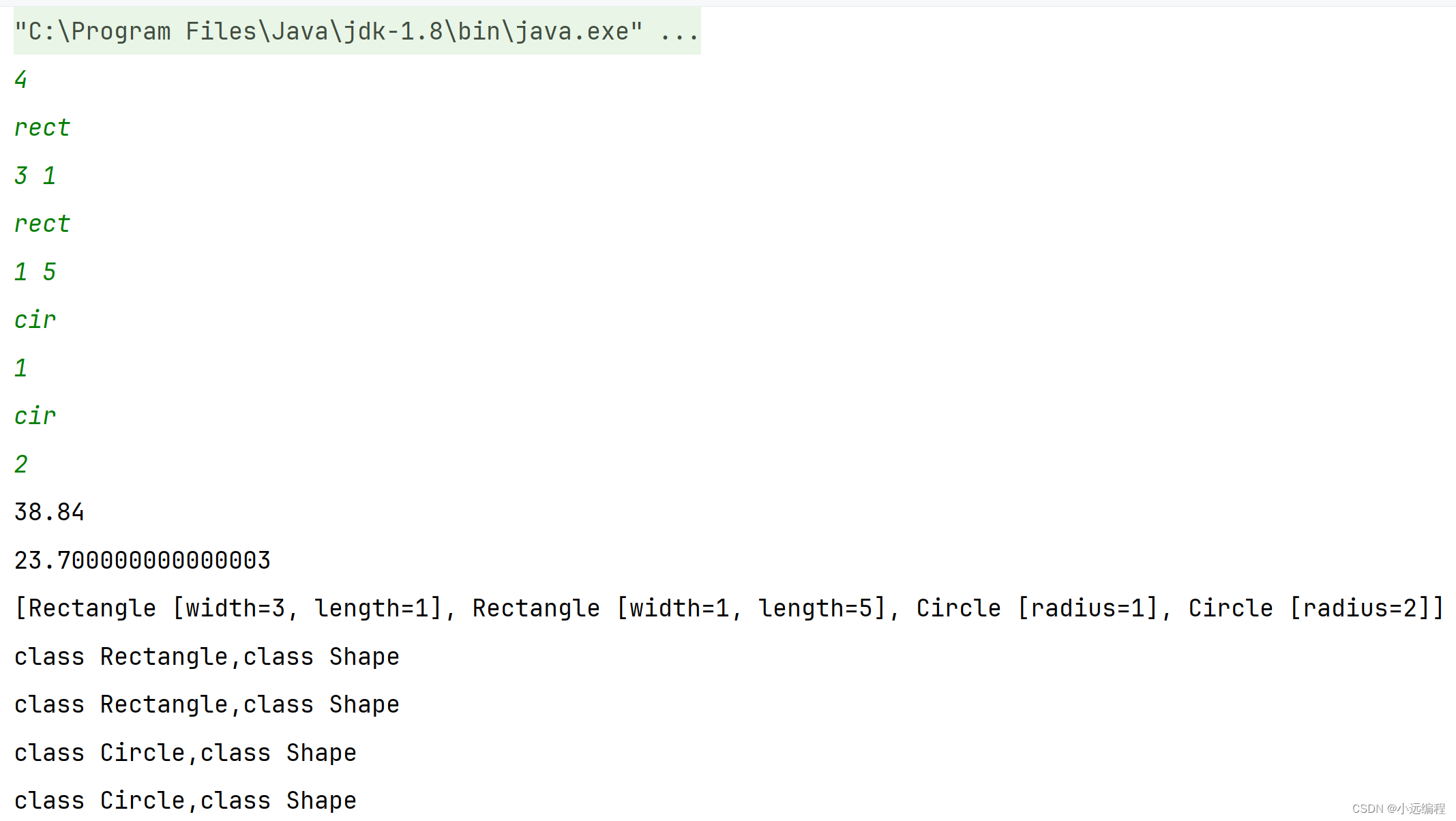
输入样例:
4 rect 3 1 rect 1 5 cir 1 cir 2
输出样例:
38.84 23.700000000000003 [Rectangle [width=3, length=1], Rectangle [width=1, length=5], Circle [radius=1], Circle [radius=2]] class Rectangle,class Shape class Rectangle,class Shape class Circle,class Shape class Circle,class Shape
2)代码实现
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
abstract class Shape {
protected static final double PI = 3.14; // 不可变静态常量
public abstract double getPerimeter();
public abstract double getArea();
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
private final int width;
private final int length;
public Rectangle(int width, int length) {
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
}
@Override
public double getPerimeter() {
return 2 * (width + length);
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return width * length;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Rectangle [width=" + width + ", length=" + length + "]";
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
private final int radius;
public Circle(int radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public double getPerimeter() {
return 2 * PI * radius;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return PI * radius * radius;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Circle [radius=" + radius + "]";
}
}
//考虑将其放置于一个工具类中,因为它们是基于数组的操作,不直接依赖于某个特定的形状实例,因此声明为静态方法较为合适。
class ShapeUtils {
public static double sumAllArea(Shape[] shapes) {
double totalArea = 0;
for (Shape shape : shapes) {
totalArea += shape.getArea();
}
return totalArea;
}
public static double sumAllPerimeter(Shape[] shapes) {
double totalPerimeter = 0;
for (Shape shape : shapes) {
totalPerimeter += shape.getPerimeter();
}
return totalPerimeter;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//请输入整型值n:建立n个不同的形状
int n = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine(); // 消耗掉换行符
List<Shape> shapes = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
//请输入形状类型(rect/cir)
String type = scanner.nextLine();
if ("rect".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
//请输入宽和长,以空格分隔
int width = scanner.nextInt();
int length = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine(); // 消耗掉换行符
shapes.add(new Rectangle(width, length));
} else if ("cir".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
//请输入半径:
int radius = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine(); // 消耗掉换行符
shapes.add(new Circle(radius));
}
}
double totalPerimeter = ShapeUtils.sumAllPerimeter(shapes.toArray(new Shape[0]));
double totalArea = ShapeUtils.sumAllArea(shapes.toArray(new Shape[0]));
System.out.println(totalPerimeter);
System.out.println(totalArea);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(shapes.toArray()));
for (Shape shape : shapes) {
System.out.println(shape.getClass() + "," + shape.getClass().getSuperclass());
}
}
}
3)具体呈现
七.遍历链表
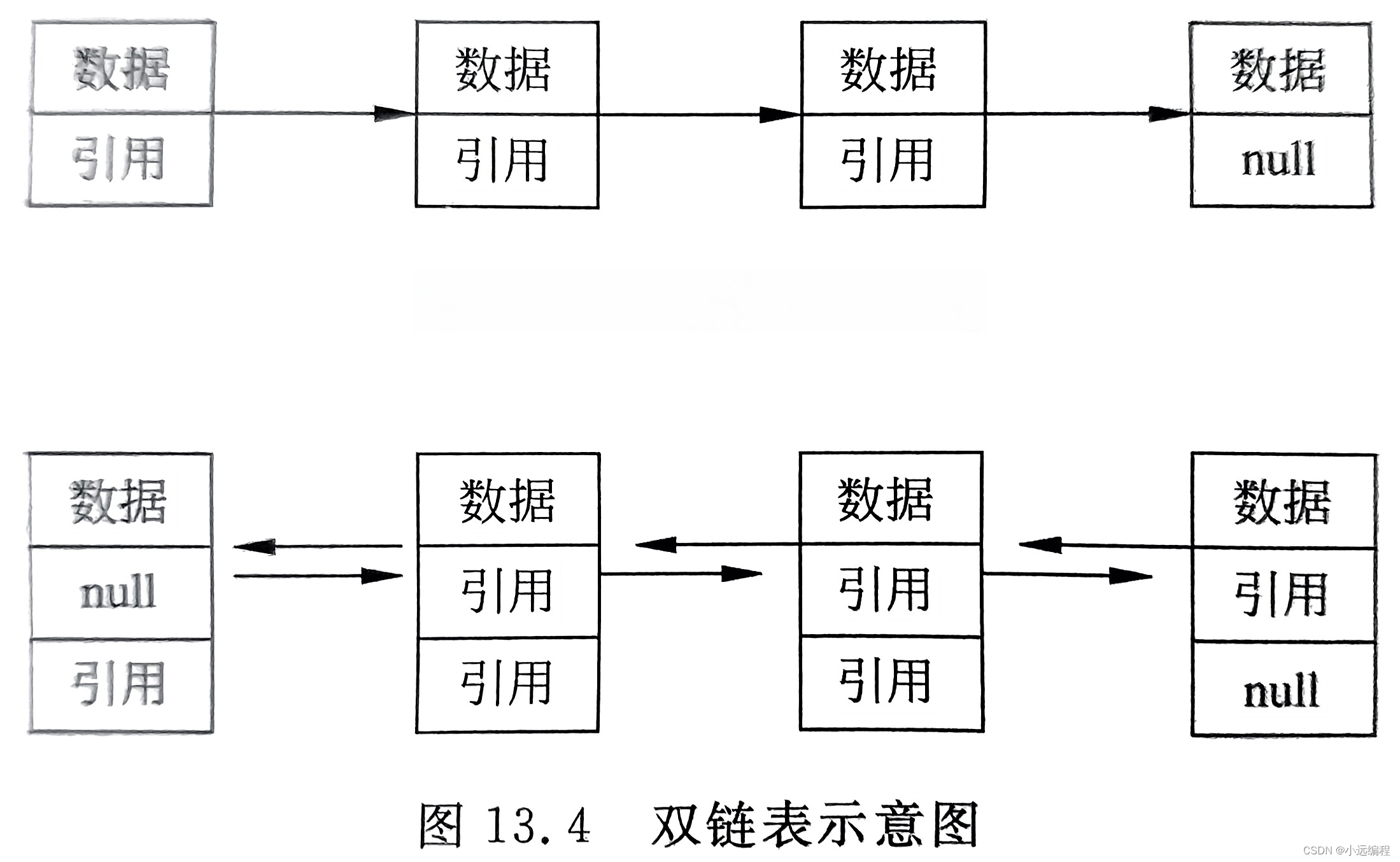
1)链表的定义
链表是由若干个被称为结点的对象组成的一种数据结构,每个结点含有一个数据和下一个结点的引用(单链表),或者有一个数据结构并含有上一个结点的引用和下一个结点的引用(双链表)
2)遍历链表的核心思想
a.使用迭代器遍历集合 b.使用get方法遍历集合
3)例子
A.给定一个单向链表,遍历链表并打印所有节点的值。
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
public class LinkedListTraversal {
Node head; // head of list
void printList() {
Node n = head;
while (n != null) {
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedListTraversal list = new LinkedListTraversal();
list.head = new Node(1);
list.head.next = new Node(2);
list.head.next.next = new Node(3);
System.out.println("Linked list:");
list.printList();
}
}

B.从尾到头打印链表
import java.util.Stack;
public class ReversePrintLinkedList {
public void printReverse(Node head) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
stack.push(current.data);
current = current.next;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(stack.pop() + " ");
}
}
}

C.比较迭代器遍历链表和比较使用get(int index)方法遍历链表所用的时间
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args){
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 60096; i++) {
list.add("speed"+i);
}
Iterator<String> iter= list.iterator();
long starttime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (iter.hasNext()){
String te = iter.next();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long result = endTime-starttime;
System.out.println("使用迭代器遍历集合所用时间:"+result+"ms");
starttime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String te = list.get(i);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
result = endTime-starttime;
System.out.println("使用get方法遍历集合所用时间:"+result+"ms");
}
}






















 388
388











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








