主要是记录个人如何按照Boost程序完全开发一书去学习入门Boost库
书中第一个是date_time库首先我们看一下怎么去用
#include <boost\timer.hpp>
#include <boost\progress.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include "mytimer.h"
using namespace boost;
void main1()
{
boost::timer t;
std::cout<< "max span" << t.elapsed_max() / 3600 << "h" << std::endl;
std::cout << "time espaced" << t.elapsed() << "S" << std::endl;
shao::mytimer mytime;
std::cout << "mytime spend " << mytime.time_spend() << "S" << std::endl;
system("pause");
}
void test()
{
boost::progress_timer time;
}
void main2()
{
test();
std::cin.get();
}
看一下boost::timer的实现还是简单的
// boost timer.hpp header file ---------------------------------------------//
// Copyright Beman Dawes 1994-99. Distributed under the Boost
// Software License, Version 1.0. (See accompanying file
// LICENSE_1_0.txt or copy at http://www.boost.org/LICENSE_1_0.txt)
// See http://www.boost.org/libs/timer for documentation.
// Revision History
// 01 Apr 01 Modified to use new <boost/limits.hpp> header. (JMaddock)
// 12 Jan 01 Change to inline implementation to allow use without library
// builds. See docs for more rationale. (Beman Dawes)
// 25 Sep 99 elapsed_max() and elapsed_min() added (John Maddock)
// 16 Jul 99 Second beta
// 6 Jul 99 Initial boost version
#ifndef BOOST_TIMER_HPP
#define BOOST_TIMER_HPP
#include <boost/config.hpp>
#include <ctime>
#include <boost/limits.hpp>
# ifdef BOOST_NO_STDC_NAMESPACE
namespace std { using ::clock_t; using ::clock; }
# endif
namespace boost {
// timer -------------------------------------------------------------------//
// A timer object measures elapsed time.
// It is recommended that implementations measure wall clock rather than CPU
// time since the intended use is performance measurement on systems where
// total elapsed time is more important than just process or CPU time.
// Warnings: The maximum measurable elapsed time may well be only 596.5+ hours
// due to implementation limitations. The accuracy of timings depends on the
// accuracy of timing information provided by the underlying platform, and
// this varies a great deal from platform to platform.
class timer
{
public:
timer() { _start_time = std::clock(); } // postcondition: elapsed()==0
// timer( const timer& src ); // post: elapsed()==src.elapsed()
// ~timer(){}
// timer& operator=( const timer& src ); // post: elapsed()==src.elapsed()
void restart() { _start_time = std::clock(); } // post: elapsed()==0
double elapsed() const // return elapsed time in seconds
{ return double(std::clock() - _start_time) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; }
double elapsed_max() const // return estimated maximum value for elapsed()
// Portability warning: elapsed_max() may return too high a value on systems
// where std::clock_t overflows or resets at surprising values.
{
return (double((std::numeric_limits<std::clock_t>::max)())
- double(_start_time)) / double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
}
double elapsed_min() const // return minimum value for elapsed()
{ return double(1)/double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC); }
private:
std::clock_t _start_time;
}; // timer
} // namespace boost
#endif // BOOST_TIMER_HPP
下面就是boost::progress_display进度条的显示
使用案例
#include <boost\progress.hpp>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
using namespace boost;
using namespace std;
void main()
{
std::vector<string> myvec(100);
//文件输出流
ofstream outFile("D:\\shao.txt");
progress_display progress(myvec.size(),std::cout);
vector<string>::iterator myit = myvec.begin();
for(;myit != myvec.end();myit++)
{
outFile << *myit << endl;
++progress;
}
std::cin.get();
} 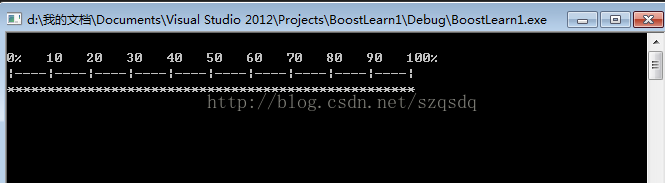
下面我们看一下progress_display的源码呢
class progress_display : private noncopyable
{
public:
//构造函数需要进度条的最大值 和 输出流 默认是控制台
explicit progress_display( unsigned long expected_count,
std::ostream & os = std::cout,
const std::string & s1 = "\n", //leading strings
const std::string & s2 = "",
const std::string & s3 = "" )
: noncopyable(), m_os(os), m_s1(s1), m_s2(s2), m_s3(s3) { restart(expected_count); }
void restart( unsigned long expected_count )
{
_count = _next_tic_count = _tic = 0;
_expected_count = expected_count;
m_os << m_s1 << "0% 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100%\n"
<< m_s2 << "|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|"
<< std::endl // endl implies flush, which ensures display
<< m_s3;
if ( !_expected_count ) _expected_count = 1; // prevent divide by zero
} // restart
//重载+=方法
unsigned long operator+=( unsigned long increment )
{
if ( (_count += increment) >= _next_tic_count ) { display_tic(); }
return _count;
}
//重载 ++方法 进度+1
unsigned long operator++() { return operator+=( 1 ); }
unsigned long count() const { return _count; }
unsigned long expected_count() const { return _expected_count; }
private:
std::ostream & m_os; // may not be present in all imps
const std::string m_s1; // string is more general, safer than
const std::string m_s2; // const char *, and efficiency or size are
const std::string m_s3; // not issues
unsigned long _count, _expected_count, _next_tic_count;
unsigned int _tic;
void display_tic()
{
unsigned int tics_needed =
static_cast<unsigned int>(
(static_cast<double>(_count)/_expected_count)*50.0 );
do { m_os << '*' << std::flush; } while ( ++_tic < tics_needed );
_next_tic_count =
static_cast<unsigned long>((_tic/50.0)*_expected_count);
if ( _count == _expected_count ) {
if ( _tic < 51 ) m_os << '*';
m_os << std::endl;
}
} // display_tic
};到这进度 计时的类库还是比较简单的 算是入门第一篇吧 作者讲解的挺好 有点缺点都会暴露出来






















 287
287

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








