最近接到了一个需求,里面需要对文件进行md5摘要.从网上搜索到了两个还可以的代码片段,为了更好的判断该使用哪个,这里对这两种摘要方式做了时间和内存的测试.
一 测试环境
1.四种大小的文件:1m,10,20m,30m
3.工具:xcode8
4.设备:iphone4s,ios8;iphone5,ios10;iphone6,ios9;iphone6s,ios10
二. 两种方法代码
使用filehandle
+ (NSString *)md5WithFilePath:(NSString *)path {
NSFileHandle *handle = [NSFileHandle fileHandleForReadingAtPath:path];
if( handle== nil ) {
return nil;
}
CC_MD5_CTX md5;
CC_MD5_Init(&md5);
BOOL done = NO;
while(!done)
{
NSData* fileData = [handle readDataOfLength: 256 ];
CC_MD5_Update(&md5, [fileData bytes], (CC_LONG)[fileData length]);
if( [fileData length] == 0 ) done = YES;
}
unsigned char digest[CC_MD5_DIGEST_LENGTH];
CC_MD5_Final(digest, &md5);
NSString* s = [NSString stringWithFormat: @"%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x",
digest[0], digest[1],
digest[2], digest[3],
digest[4], digest[5],
digest[6], digest[7],
digest[8], digest[9],
digest[10], digest[11],
digest[12], digest[13],
digest[14], digest[15]];
return s;
}
使用readstream
// In bytes
#define FileHashDefaultChunkSizeForReadingData 256
// Function
CFStringRef FileMD5HashCreateWithPath(CFStringRef filePath,
size_t chunkSizeForReadingData) {
// Declare needed variables
CFStringRef result = NULL;
CFReadStreamRef readStream = NULL;
// Get the file URL
CFURLRef fileURL =
CFURLCreateWithFileSystemPath(kCFAllocatorDefault,
(CFStringRef)filePath,
kCFURLPOSIXPathStyle,
(Boolean)false);
if (!fileURL) goto done;
// Create and open the read stream
readStream = CFReadStreamCreateWithFile(kCFAllocatorDefault,
(CFURLRef)fileURL);
if (!readStream) goto done;
bool didSucceed = (bool)CFReadStreamOpen(readStream);
if (!didSucceed) goto done;
// Initialize the hash object
CC_MD5_CTX hashObject;
CC_MD5_Init(&hashObject);
// Make sure chunkSizeForReadingData is valid
if (!chunkSizeForReadingData) {
chunkSizeForReadingData = FileHashDefaultChunkSizeForReadingData;
}
// Feed the data to the hash object
bool hasMoreData = true;
while (hasMoreData) {
uint8_t buffer[chunkSizeForReadingData];
CFIndex readBytesCount = CFReadStreamRead(readStream,
(UInt8 *)buffer,
(CFIndex)sizeof(buffer));
if (readBytesCount == -1) break;
if (readBytesCount == 0) {
hasMoreData = false;
continue;
}
CC_MD5_Update(&hashObject,
(const void *)buffer,
(CC_LONG)readBytesCount);
}
// Check if the read operation succeeded
didSucceed = !hasMoreData;
// Compute the hash digest
unsigned char digest[CC_MD5_DIGEST_LENGTH];
CC_MD5_Final(digest, &hashObject);
// Abort if the read operation failed
if (!didSucceed) goto done;
// Compute the string result
char hash[2 * sizeof(digest) + 1];
for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(digest); ++i) {
snprintf(hash + (2 * i), 3, "%02x", (int)(digest[i]));
}
result = CFStringCreateWithCString(kCFAllocatorDefault,
(const char *)hash,
kCFStringEncodingUTF8);
done:
if (readStream) {
CFReadStreamClose(readStream);
CFRelease(readStream);
}
if (fileURL) {
CFRelease(fileURL);
}
return result;
}
为方便比较,两个方法每次相同的每次读取大小256k
三 耗时比较
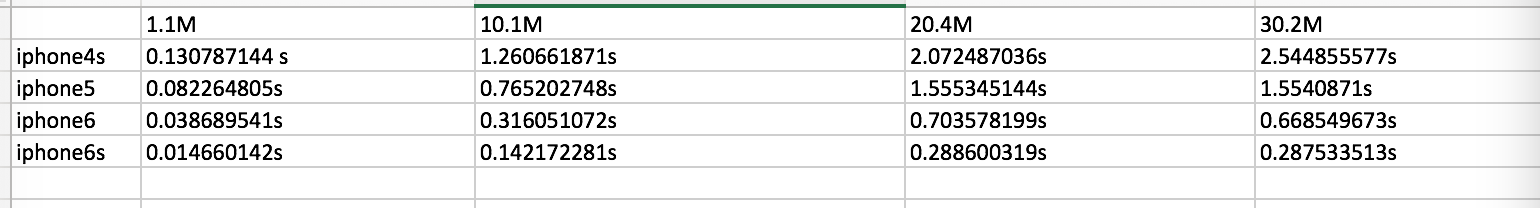
耗时测试方法:
1.采用dispatch_benchmark,对每个文件md5 100次,取平均值
2.示例代码:
“`
- (IBAction)M_md5_10M:(id)sender {
__block NSString *md5 = nil;
uint64_t t2 = dispatch_benchmark(_count, ^{
@autoreleasepool {
NSString *path = [self.paths objectAtIndex:1];
md5 = [self.class md5WithFilePath:path];
}
});
NSLog(@"[md5 10m file:] Avg. Runtime: %llu ns,md5:%@", t2,md5);
}
“`
耗时测试结果
handle耗时:
readstream耗时
结论:从上面两张图片可以看出,使用readsteam方法耗时平均比filehandle少50%左右,在iphone6和iphone6s上表现更为明显
四 . 内存消耗
内存测试方法
采用xcode memory 测试工具
测试结果
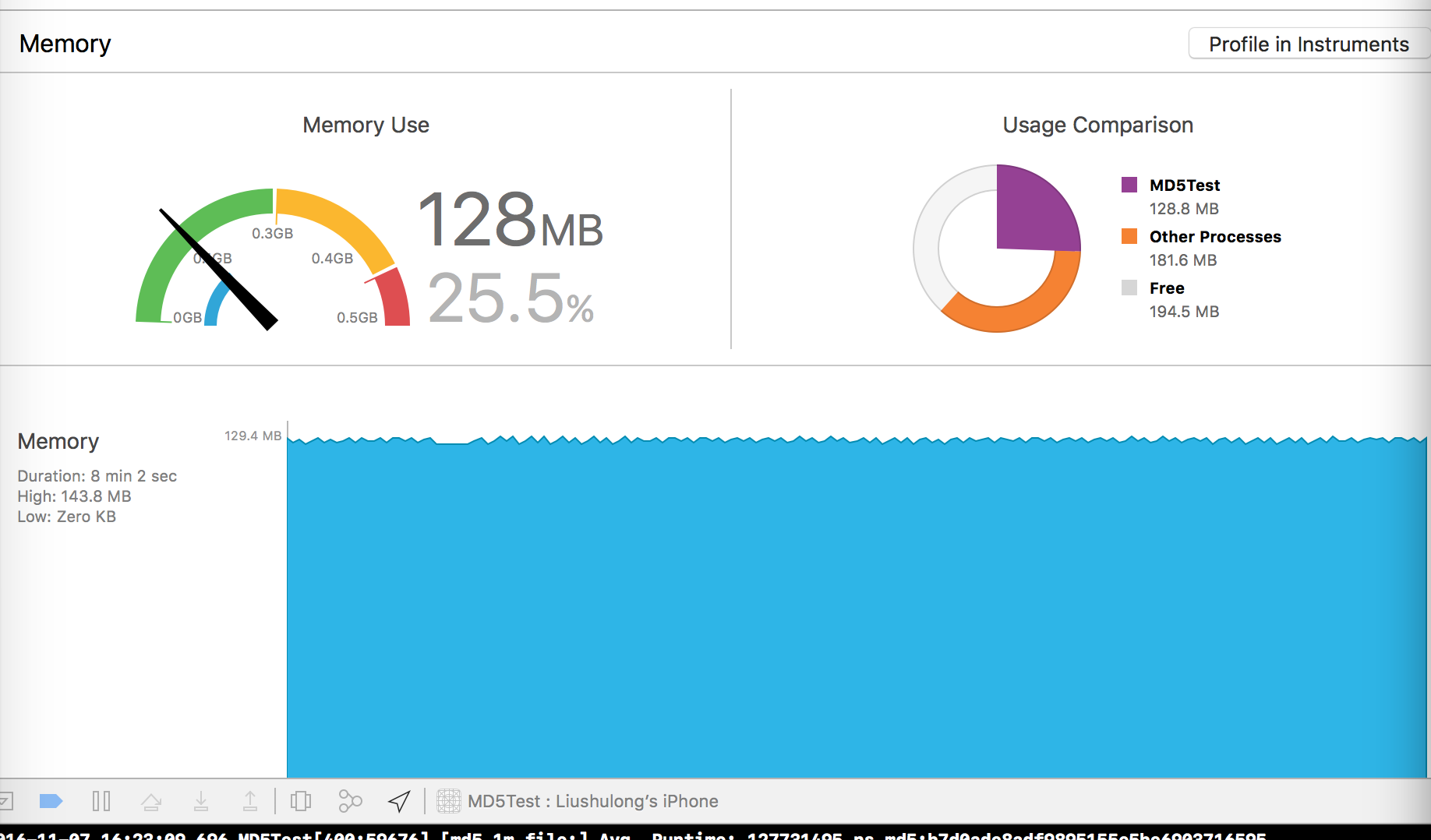
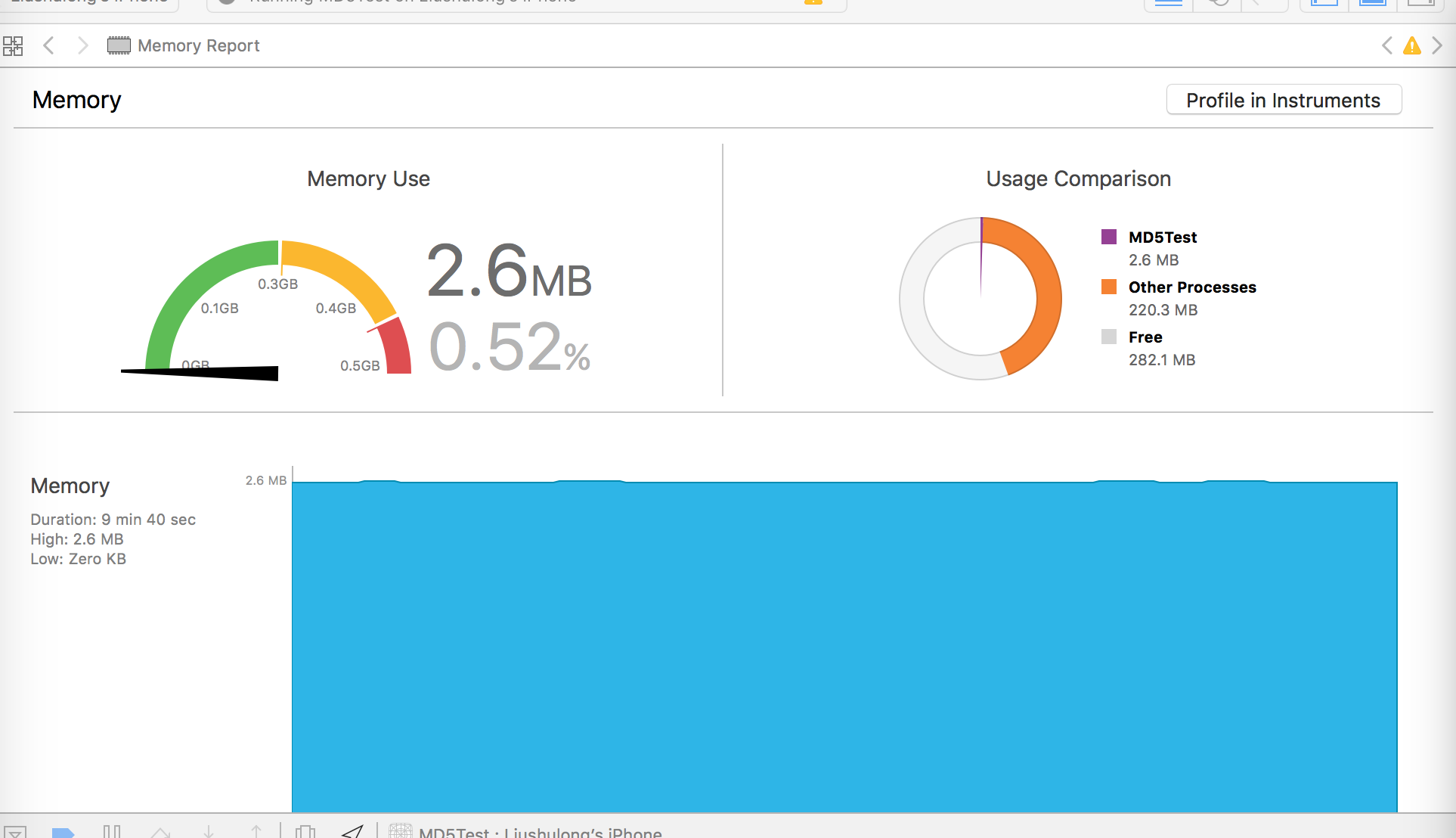
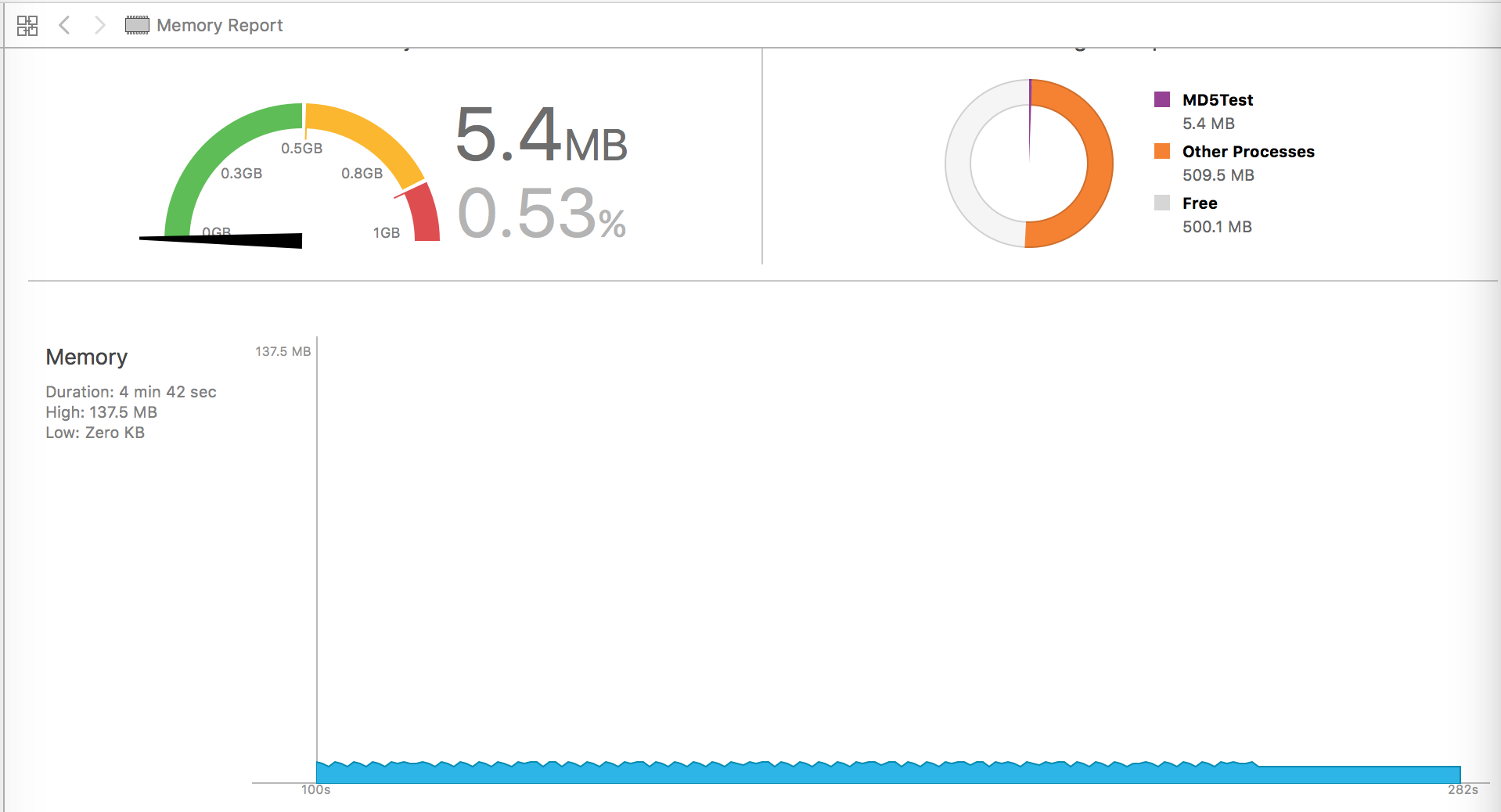
iphone4s, 第一个为handle,第二个为readstream:
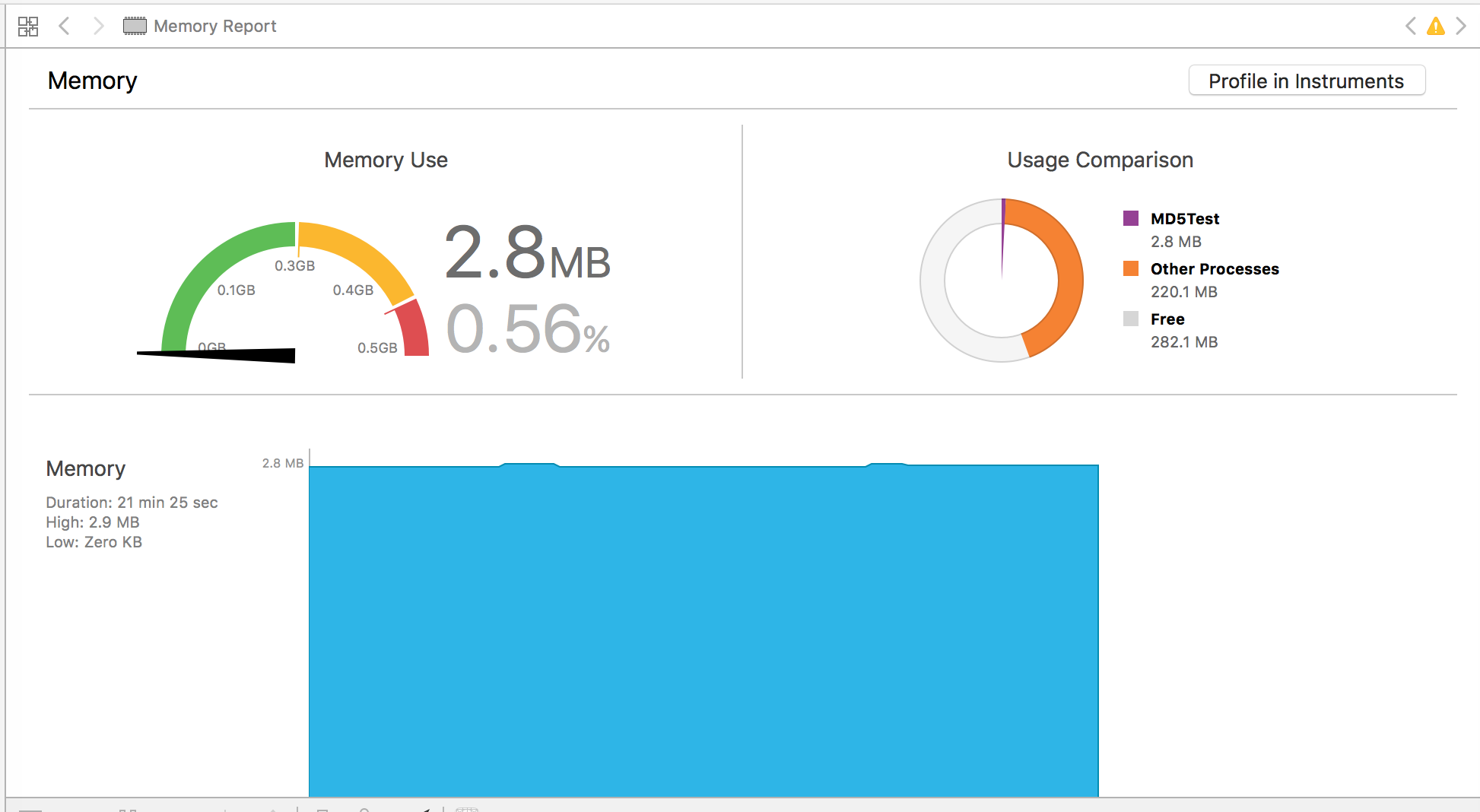
iphone5, 第一个为handle,第二个为readstream:
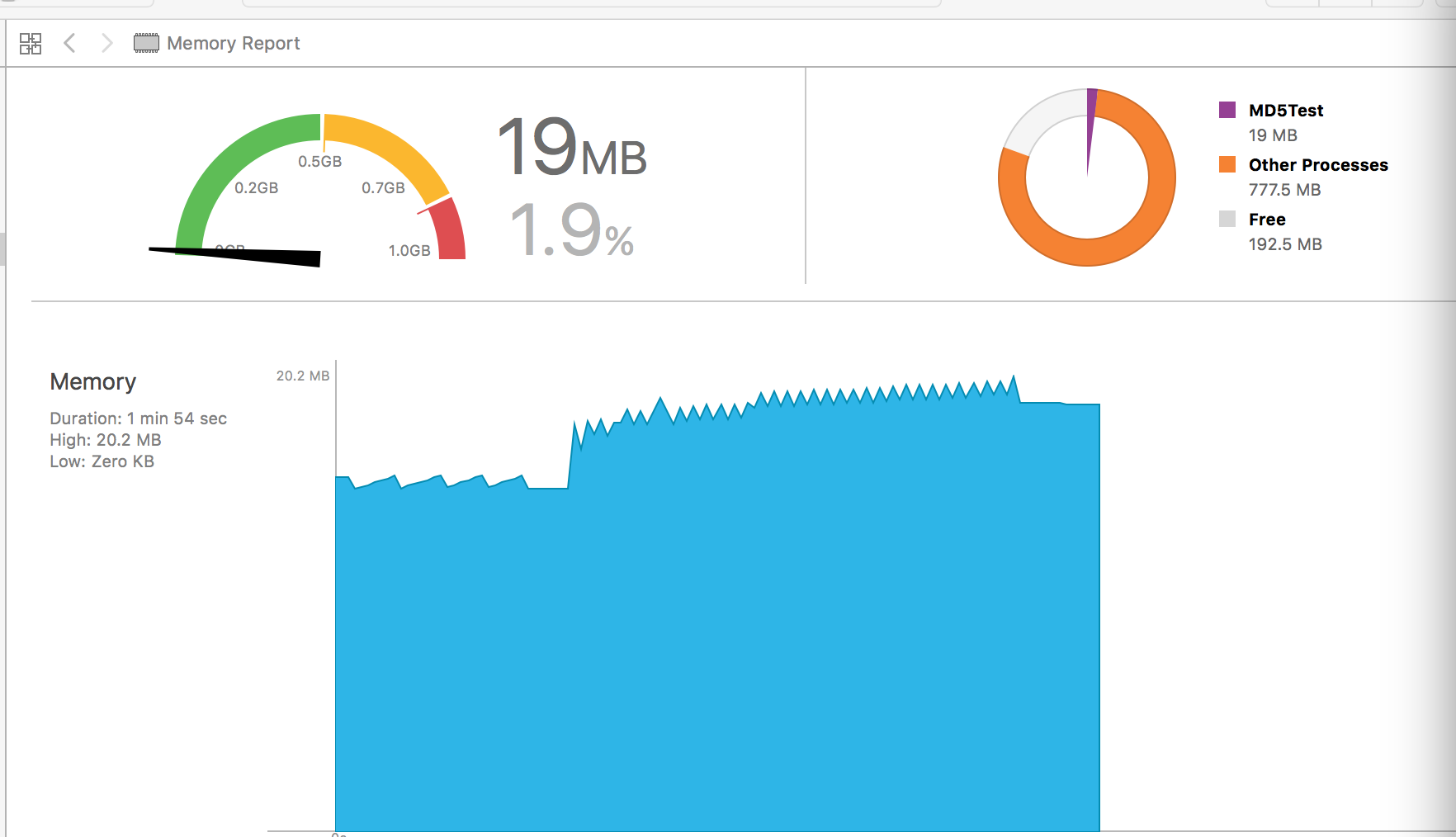
iphone6, 第一个为handle,第二个为readstream:
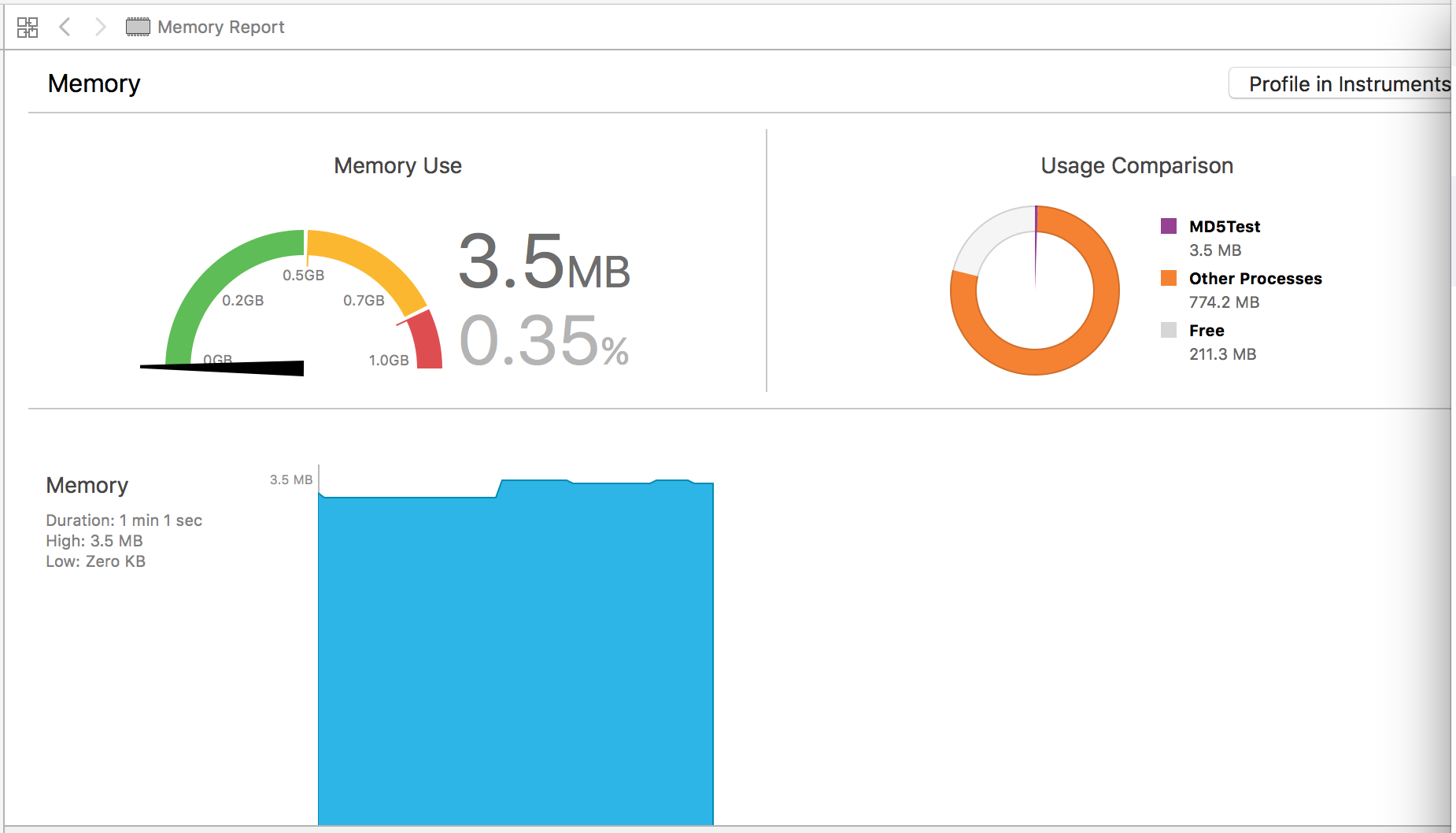
iphone6s, 第一个为handle,第二个为readstream:
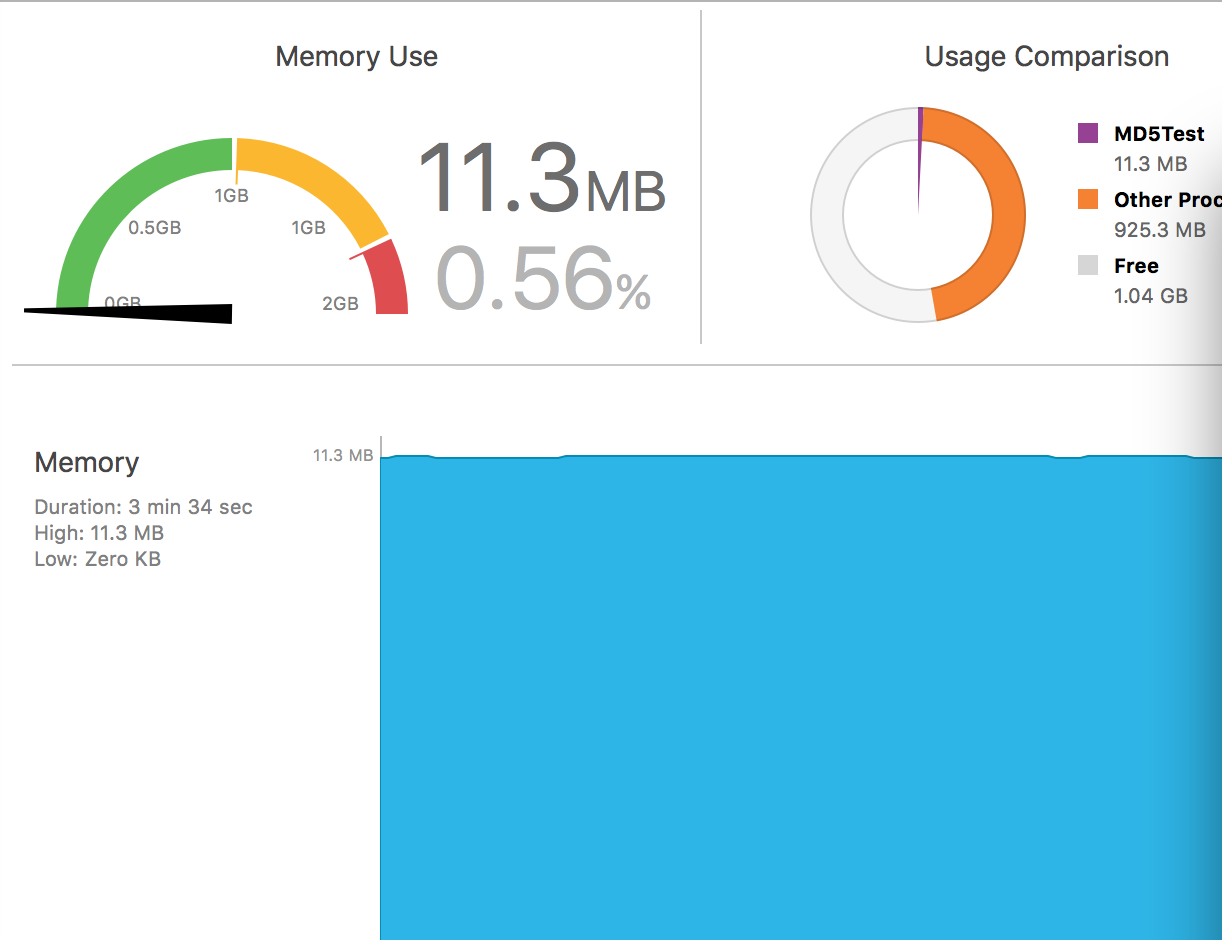
对比结果:readstream在内存上比handle消耗平均也少50%以上.
结论
readstream方法在时间和内存消耗上明显优于filehandle,平均都有50%的性能优势.因此选用readstream方法对大文件进行md5摘要.
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








