问题
MyBatis何时把XML或annotation中SQL语句中的参数替换为?
第一阶段:
顺序调用逻辑:
- org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy#invoke
- org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperMethod#execute(根据sql语句的sqlCommandType进对应分支-增删改查)
- org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession#insert(java.lang.String, java.lang.Object)(增删改查进入各自方法)
- org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession#update(java.lang.String, java.lang.Object)(上一步的增删改最后都进入此方法,查询进入select方法,此流程以增删改为例)
思路倒推:
以XML中一条插入语句为例,一路调用至DefaultSqlSession#update
@Override
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) {
try {
dirty = true;
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}调试查看 MappedStatement ms 属性发现其sqlSource.sql语句已经将参数占位替换“?”

也就是说在这之前sql语句已经被替换好,于是往回推理寻找SQL被替换的地方,在DefaultSqlSession#update方法中发现其在调用Executor的update方法之前取出了MappedStatement ,有取出必然有放入,于是我跳转到Configuration#getMappedStatement()类内部一探究竟。
原来这个MappedStatement是存放在Configuration类的属性mappedStatements中,仔细看发现mappedStatements其实只是一个Map集合,定义如下:
Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements第二阶段
接下来我有两个思路:一、这个MappedStatement是何时放进这个Configuration的mappedStatements属性中的;二、MappedStatement中的SQL语句是何时放到其sqlSource.sql中的;答案肯定在这两步中之中;
先来查看第一步,Configuration#addMappedStatement这个方法是向mappedStatements添加MappedStatement,只要找到哪里调用了这个方法就找到第一步的答案。发现只有这里调用了此方法,org.apache.ibatis.builder.MapperBuilderAssistant#addMappedStatement()
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id,
SqlSource sqlSource,
StatementType statementType,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,
Integer fetchSize,
Integer timeout,
String parameterMap,
Class<?> parameterType,
String resultMap,
Class<?> resultType,
ResultSetType resultSetType,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
boolean resultOrdered,
KeyGenerator keyGenerator,
String keyProperty,
String keyColumn,
String databaseId,
LanguageDriver lang,
String resultSets) {
if (unresolvedCacheRef) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
}
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType)
.resource(resource)
.fetchSize(fetchSize)
.timeout(timeout)
.statementType(statementType)
.keyGenerator(keyGenerator)
.keyProperty(keyProperty)
.keyColumn(keyColumn)
.databaseId(databaseId)
.lang(lang)
.resultOrdered(resultOrdered)
.resultSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id))
.resultSetType(resultSetType)
.flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect))
.cache(currentCache);
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}打断点到此处,发现到这里是sql语句已被替换成“?”,不过也发现所有的SQL都是这里被装进去的。
继续向上追溯,发现下面类中调用了MapperBuilderAssistant#addMappedStatement()方法:
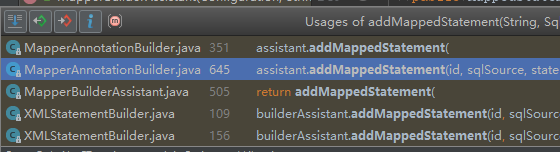
先找个XMLStatementBuilder的进去看看,其中有两个方法调用了addMappedStatement
- XMLStatementBuilder#parseStatementNode(共有方法)
- XMLStatementBuilder#parseSelectKeyNode(私有方法)
先来看第一个方法
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
这个方法重点关注下面两行:
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);第一行代码先调用了processSelectKeyNodes,接着processSelectKeyNodes又调用了parseSelectKeyNodes,再接着parseSelectKeyNodes调用了parseSelectKeyNode,这就回到刚才的问题,XMLStatementBuilder中有两个方法调用了addMappedStatement,实际上都是在parseStatementNode中调用的。
进入到parseStatementNode方法中,关注如下代码:
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, nodeToHandle, parameterTypeClass);
进入langDriver.createSqlSource中一探究竟,发现会弹出选择进入XMLLanguageDriver还是进入RawLanguageDriver;这两个类是父子关系,我们先进入父类XMLLanguageDriver
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) {
XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);
return builder.parseScriptNode();
}发现其调用了XMLScriptBuilder#parseScriptNode方法;
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
List<SqlNode> contents = parseDynamicTags(context);
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = new MixedSqlNode(contents);
SqlSource sqlSource = null;
if (isDynamic) {
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}这里就是构造SqlSource的地方了,调试如图:
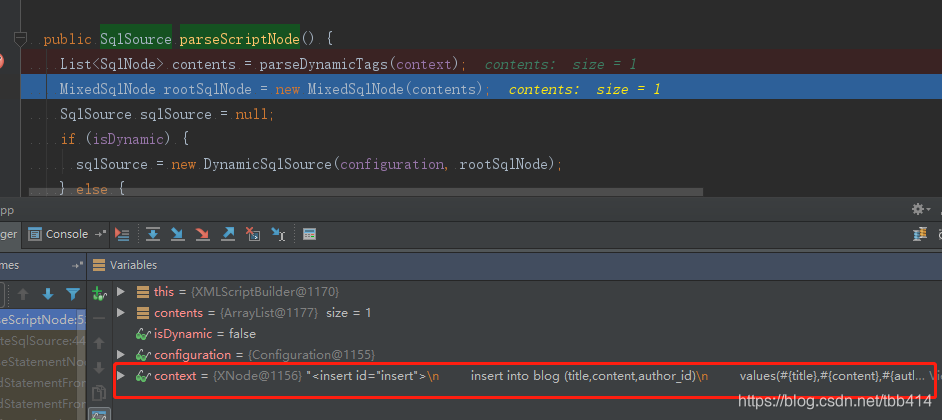
发现到这里Sql语句还是XML中定义的那样没有替换成?
继续往下执行,发现断点进入了else分支里,执行了
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);之后,SQL中参数就被替换为“?”了

接下来我们就来看一下new RawSqlSource()里面都做了些什么。
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode, Class<?> parameterType) {
this(configuration, getSql(configuration, rootSqlNode), parameterType);
}
private static String getSql(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode) {
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, null);
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
return context.getSql();
}
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, Class<?> parameterType) {
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> clazz = parameterType == null ? Object.class : parameterType;
sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(sql, clazz, new HashMap<String, Object>());
}执行了上述三个方法,继续打断点跟踪getSql,getSql只是将Sql取出,再关注如下代码:
sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(sql, clazz, new HashMap<String, Object>());发现又进入SqlSourceBuilder#parse方法:
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType, additionalParameters);
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);
String sql = parser.parse(originalSql);
return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings());
}再到GenericTokenParser#parse方法,走到这里感觉快要破案了,是不是有点小激动,parse方法如下,内容有点长耐心一行行看
public String parse(String text) {
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
//1.将SQL语句转为char数组
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
// search open token
//检查SQL中是否有“#{”,openToken的只是在SqlSourceBuilder#parse中设置的
int start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
if (start == -1) {
return text;
}
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder expression = null;
while (start > -1) {
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
// found open token. let's search close token.
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
offset = start + openToken.length();
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
break;
}
}
if (end == -1) {
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
//重点关注这句话
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
}
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
} //重点关注这句话
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
handler.handleToken点击进去后发现如下:
表明有四个类实现了TokenHandler#handleToken方法,一个个点进去发现
private static class ParameterMappingTokenHandler extends BaseBuilder implements TokenHandler {
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
parameterMappings.add(buildParameterMapping(content));
return "?";
}
}
private static class VariableTokenHandler implements TokenHandler {
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
if (variables != null) {
String key = content;
if (enableDefaultValue) {
final int separatorIndex = content.indexOf(defaultValueSeparator);
String defaultValue = null;
if (separatorIndex >= 0) {
key = content.substring(0, separatorIndex);
defaultValue = content.substring(separatorIndex + defaultValueSeparator.length());
}
if (defaultValue != null) {
return variables.getProperty(key, defaultValue);
}
}
if (variables.containsKey(key)) {
return variables.getProperty(key);
}
}
return "${" + content + "}";
}
}
private static class DynamicCheckerTokenParser implements TokenHandler {
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
this.isDynamic = true;
return null;
}
}这四个内部类的handlerToken方法功能如下:
ParameterMappingTokenHandler:返回“?”
VariableTokenHandler:返回"${" + content + "}"
DynamicCheckerTokenParser:只是设置isDynamic=true
BindingTokenParser:只是设置isDynamic=true
结案
org.apache.ibatis.parsing.GenericTokenParser#parse方法就是替换参数的地方。
调用时序图
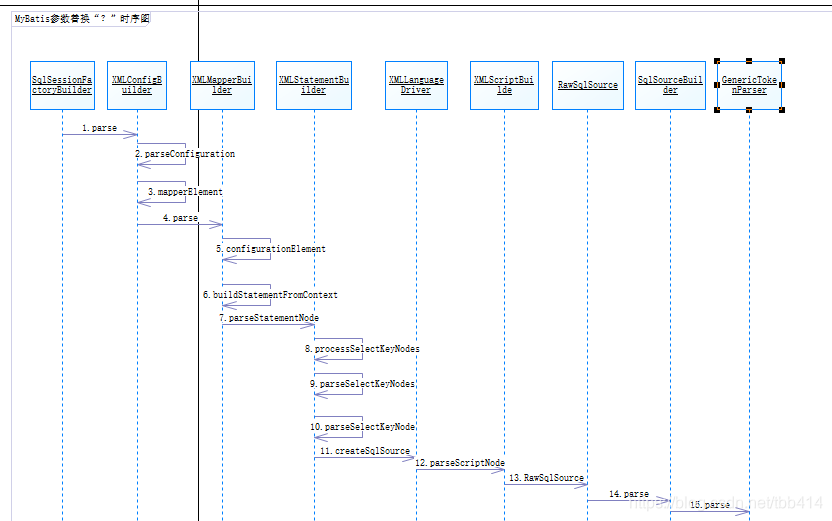
说明
1. 本文中只是通过一条最简单的insert语句进行跟踪来探究SQL中的参数何时被替换为“?”,并不能覆盖所有语句,只是作为一个思路。
2.在探索过程中意外发现了$符号的藏身地。
发散点
- 探索其他复杂SQL(尤其是select)的替换过程
- 探索$符号的替换过程
- 探索annotation的替换过程
- 探索SQL语句是何时被从“?”替换成实际输入参数的。























 6795
6795











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








