转:
http://blog.csdn.net/zen99t/article/details/49512411



(三)解析注解
1. 注解处理器
何为解析注解?即通过反射获取类、函数或成员上的
运行时注解信息,从而实现动态控制程序运行的逻辑。
解析注解主要用到两个类库:
1.1. java.lang.annotation.Annotation
Java使用Annotation接口来代表程序元素前面的注解,该接口是所有Annotation类型的父接口。
1.2. java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement
AnnotatedElement 接口代表程序中可以接受注解的程序元素,是所有程序元素(Class、Method
、Field、Package和Constructor)的父接口。获取该接口对象之后,即可以调用对象方法来访问Annotation信息,常用有如下几个:
1. getAnnotations():返回该程序元素上存在的所有注解。
2. isAnnotationPresent(annotation.class):判断该程序元素上是否包含指定类型的注解
3. getDeclaredAnnotations():返回直接存在于此元素上的所有注释。与此接口中的其他方法不同,该方法将忽略继承的注释。
2. 解析注解的代码例子
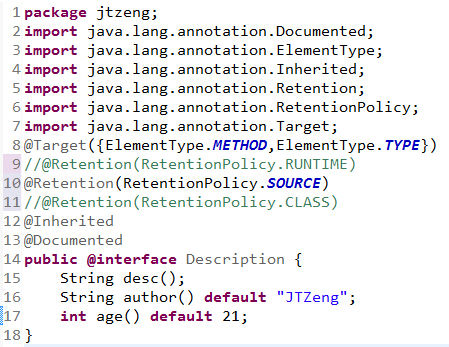
定义一个注解如下:
- package jtzeng;
- import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
- import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
- import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
- import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
- import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
- import java.lang.annotation.Target;
- @Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- @Inherited
- @Documented
- public @interface Description {
- String desc();
- String author() default “JTZeng”;
- int age() default 21;
- }
package jtzeng;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Description {
String desc();
String author() default "JTZeng";
int age() default 21;
}
定义一个使用了注解的Test类:
- package jtzeng;
- @Description(desc=“this is ElementType.TYPE”,author=“JTZeng”,age=21)
- public class Test1 {
- @Description(desc=“this is ElementType.METHOD”,author=“JTZeng”,age=18)
- public void run(){
- System.out.println(”I can run!”);
- }
- }
package jtzeng;
@Description(desc="this is ElementType.TYPE",author="JTZeng",age=21)
public class Test1 {
@Description(desc="this is ElementType.METHOD",author="JTZeng",age=18)
public void run(){
System.out.println("I can run!");
}
}
再编写一个解析类:
- package jtzeng;
- import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
- import java.lang.reflect.Method;
- public class ParseAnno {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- try {
- /*
- * 1.使用类加载器加载类
- * Class.forName(“类名字符串”) (注意:类名字符串必须是全称,包名+类名)
- */
- Class c = Class.forName(”jtzeng.Test1”);
- //2.判断类上是否存在注解,并获取类上面注解的实例
- if(c.isAnnotationPresent(Description.class)){
- Description Description = (Description) c.getAnnotation(Description.class);
- System.out.println(Description.desc());
- System.out.println(Description.author());
- System.out.println(Description.age());
- }
- //3.判断方法上是否存在注解,并获取方法上面注解的实例
- Method[] ms = c.getMethods();
- for (Method method : ms) {
- if(method.isAnnotationPresent(Description.class)){
- Description Description = (Description)method.getAnnotation(Description.class);
- System.out.println(Description.desc());
- System.out.println(Description.author());
- System.out.println(Description.age());
- }
- }
- //另一种获取方法上的注解的解析方法
- for (Method method : ms) {
- Annotation[] as = method.getAnnotations();
- for (Annotation annotation : as) {
- if(annotation instanceof Description){
- System.out.println(((Description) annotation).desc());
- System.out.println(((Description) annotation).author());
- System.out.println(((Description) annotation).age());
- }
- }
- }
- } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- }
package jtzeng;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ParseAnno {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
/*
* 1.使用类加载器加载类
* Class.forName("类名字符串") (注意:类名字符串必须是全称,包名+类名)
*/
Class c = Class.forName("jtzeng.Test1");
//2.判断类上是否存在注解,并获取类上面注解的实例
if(c.isAnnotationPresent(Description.class)){
Description Description = (Description) c.getAnnotation(Description.class);
System.out.println(Description.desc());
System.out.println(Description.author());
System.out.println(Description.age());
}
//3.判断方法上是否存在注解,并获取方法上面注解的实例
Method[] ms = c.getMethods();
for (Method method : ms) {
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(Description.class)){
Description Description = (Description)method.getAnnotation(Description.class);
System.out.println(Description.desc());
System.out.println(Description.author());
System.out.println(Description.age());
}
}
//另一种获取方法上的注解的解析方法
for (Method method : ms) {
Annotation[] as = method.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : as) {
if(annotation instanceof Description){
System.out.println(((Description) annotation).desc());
System.out.println(((Description) annotation).author());
System.out.println(((Description) annotation).age());
}
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行解析类,结果如下,有三部分,第一部分是类上的注解,第二、三部分是不同的方法解析方法上的注解:

3.测试元注解@Retention
如果把@Retention改为SOURCE或者CLASS,再次运行ParseAnno类:


运行结果如下,什么也没有,这进一步说明了,只有设置为RUNTIME,才可以在运行时通过反射机制来获取注解信息,从而实现动态控制程序运行的逻辑。

4. 测试元注解@Inherited
创建一个接口和一个父类,并改写Test1类:
- package jtzeng;
- @Description(desc = “this is Interface”) //因为注解Description中的author和age成员有默认值,所以可以省略
- public interface Invalid {
- @Description(desc = “this is Interface method”)
- public void print();
- }
- package jtzeng;
- @Description(desc = “this is class”)
- public class Valid {
- @Description(desc = “this is class method”)
- public void run(){
- System.out.println(”注解继承只能在子类中有效,不能在接口中继承”);
- }
- }
- package jtzeng;
- public class Test1 extends Valid implements Invalid {
- @Override
- public void run(){
- System.out.println(”覆盖父类的方法”);
- }
- @Override
- public void print() {
- System.out.println(”实现接口的方法”);
- }
- }
package jtzeng;
@Description(desc = "this is Interface") //因为注解Description中的author和age成员有默认值,所以可以省略
public interface Invalid {
@Description(desc = "this is Interface method")
public void print();
}
package jtzeng;
@Description(desc = "this is class")
public class Valid {
@Description(desc = "this is class method")
public void run(){
System.out.println("注解继承只能在子类中有效,不能在接口中继承");
}
}
package jtzeng;
public class Test1 extends Valid implements Invalid {
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("覆盖父类的方法");
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.println("实现接口的方法");
}
}
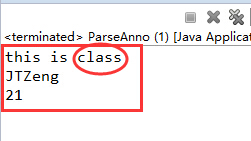
再一次运行ParseAnno解析类,输出结果如下,说明只能继承父类的注解,并且是类上的注解:

5. 知识导图
最后给出一张Java注解的知识导图,觉得总结得不错,这里就直接拿来了,导图来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/peida/archive/2013/04/26/3038503.html























 670
670

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








