魔塔是一款经典的策略益智游戏,自问世以来一直受部分玩家的追捧,各个魔塔爱好者不仅将这个玩法作为基准推陈出新造出了一系列的同人创作并发展出了自己的游戏社区,而且其内里蕴含的算法与策略也被诸多玩家开发利用。今天笔者就用算法来介绍一下魔塔社区中发现的“全蓝宝石转化理论”。
原作者的数学推理与证明在:【图片】全蓝宝石转换理论【h5魔塔吧】_百度贴吧
对应的教程塔可以在https://h5mota.com/tower/?name=lanbaoshi 中玩到
如果觉得原作者的话过于晦涩难懂,B站上有一个教学视频,更便于理解,笔者也是从这里面理解的: 【新人向】手把手教你过蓝宝石理论_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
一、理论简述
基本原理
最初的魔塔游戏规则是,怪物对勇者的伤害为:
我们把其中怪物的生命值,攻击,防御均视为固定值(有些塔会给你特殊的技能让他们也成为变量),在全蓝宝石理论中,由于勇者只能吃蓝宝石(只能提升防御),那么勇者的攻击也可以看作是固定值。
所以公式中,只有勇者的防御值这一项变量;它的系数是:
这个值可以看做是勇者和怪物经历的战斗回合数的倒数。勇者每增加一点防御就会减少战斗时回合数的损失值。
那么,我们假设有n组怪物,1单位的防御对于每组怪物的减伤效果为a1 a2 a3 …… an;每组怪物都守护着一组宝石b1 b2 b3 …… bn。我们希望能够找到一个打怪顺序,使得勇者受到的伤害最小。而对于如下图那样多个怪物/宝石的情况,可以将怪物合并视作一个大怪物,宝石合并视作大宝石。
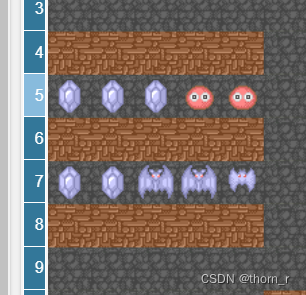
现在我们假设我们的编号顺序本身就已经是最佳打怪顺序,那么每组蓝宝石的减伤效果就是: 。由于W已经是最大的了,所以当我们将其中的某一个顺序调换后,W的值一定不会变大,即
,即
这里的就是原作者所写的特征值,我们希望找到一个从小到大的特征值,这个顺序能够使得宝石减伤效果最大化。
当然,上面的数学公式看不懂也不要紧,其实你可以理解为:
如果有一个怪物守着一系列蓝宝石,那么这些蓝宝石的减伤带来的收益在这个怪物身上一定是“无法体现”的(因为必须打败这个怪物才能获得蓝宝石),那么对于这些蓝宝石而言,每1防御就损失了怪物战斗回合数的收益,可以看作是“获得这些蓝宝石所要付出的边际损失”。可以更加形象地理解“怪物1防减伤/蓝宝石防御力和”的公式含义。
当然,对于这一特征值的公式,还有很多限制:
1、不考虑“怪物特技”对于防御的影响(即怪物即使有特技,怪物对勇者的伤害也依然是关于勇者防御的线性函数),如2连击3连击不受影响,而像是破甲(按勇者防御比例在战斗前给出额外伤害)这样的特技则会让这个理论不再适用。
2、不考虑“0伤负伤”的情况。怪物对玩家造成的伤害一定是一个正值。
3、勇者一定能够找到一条路,获得所有宝石(一开始血量和攻击一定够)
4、地图中没有红宝石(增加勇者攻击力)的干扰。
怪物与宝石交替出现的情况(八爪鱼结构)
对于下图这种,怪物与蓝宝石交替的情况,原作者将其称为“八爪鱼结构”。

对于外面那一层“特征值”更小,而里面那一层特征值更大的情况,实际上是不会影响上面结论的,还是只要更具特征值从小到大一个个打过去就可以了。但是,当外面的特征值更大,而里面的特征值更小时,无法直接先打里面的怪物,这一情况被原作者称为“坏点”,需要拿出来特殊讨论一下。
原作者在这里的证明较为难懂,我这边简单地用自己的理解讲一下:
假设出现了“外部特征值比内部特征值大”的情况,那么必然是打完外部怪物就直接打内部的怪物。
假设外部节点为A,内部节点为B,还有其他的节点C,节点A的特征值比节点B的特征值大;如果C比外部特征值大,那么它应该比A和B打得都要晚。
如果节点C的特征值比节点B的特征值还要小,那么它应该比A和B打得都要早。
如果节点C的特征值比A小,但是比B的特征值大,那么依然应该是先打C节点,再打A节点。
综上,无论其他节点如何,如果外部节点的特征值小于内部特征值,那么必然是“打完外部节点之后直接打内部节点”。所以,这种情况下,内外部节点可以被同一合成为1个大节点。
原作者还单独列举了树结构,描述相对复杂,这里就不展开了,而B站的那位老哥认为可以把树结构看作是一种特殊的八爪鱼结构,我在下面的代码中,也这么认为了。效果可以做到找到最终答案。
二、代码复现
此处是使用代码根据作者的原理,搜索到在https://h5mota.com/tower/?name=lanbaoshi 中可以走通一层的路径。原本在H5mota中的塔是使用JS写出来的,无奈笔者JS能力有限,只能将工程文件下载下来使用python进行读取。
同时,笔者需要在此声明,我在写代码前从未学过图论,数据结构也是快毕业时在Leetcode上补的,没有系统性地学过,所以代码会有很多的不规范之处,希望读者可以海涵,如果能够指出不足之处或者给出更好地思路,实在感激不尽。
0、读取塔信息与地图信息
H5mota中的地图信息、塔设置信息等均记录在js文件中,需要读取。
塔的每层信息都会保存在MTx.js的文件中,我们只需要读取其map信息就可以了:
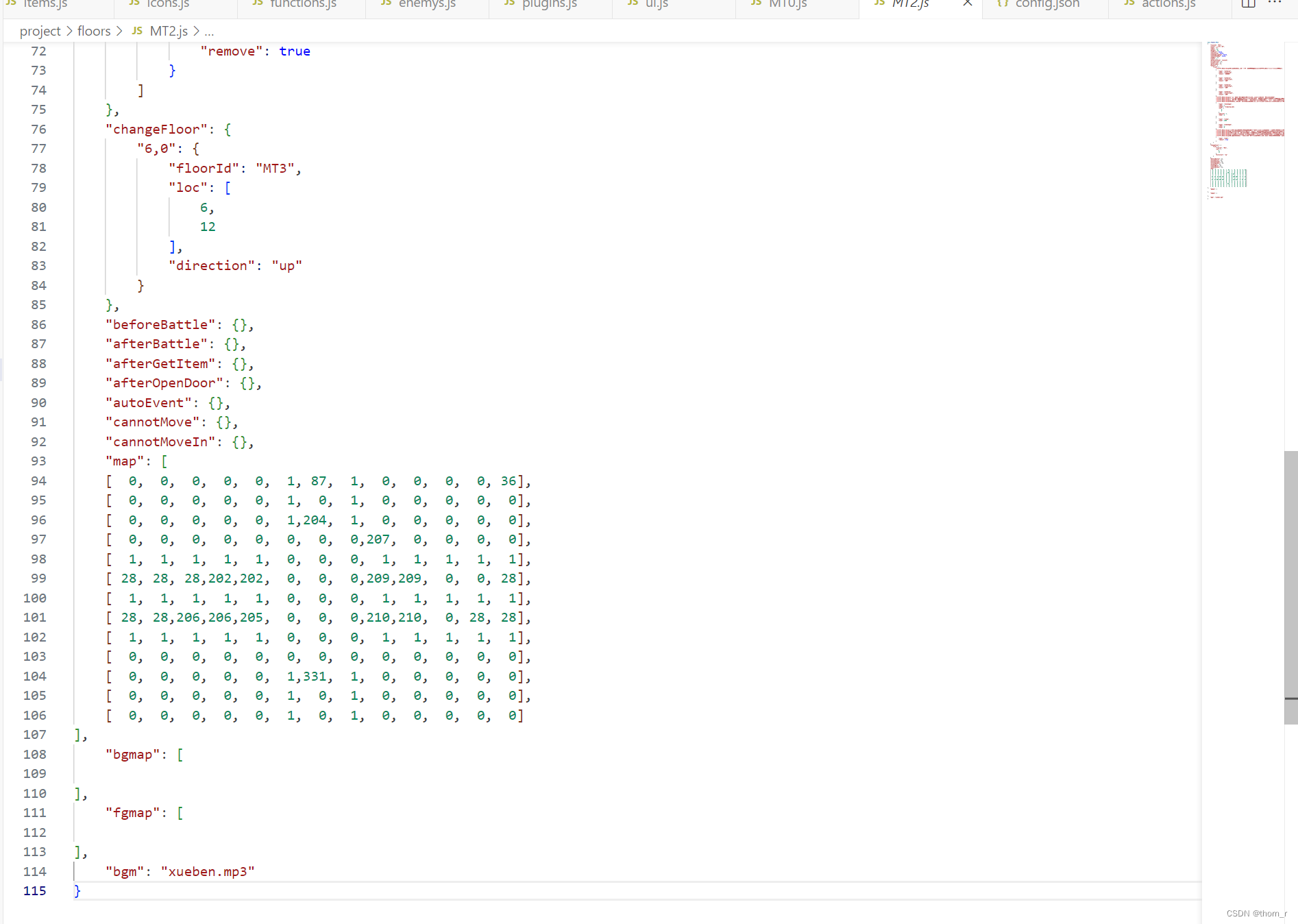
对于地图中每一个数字,每座塔都会有自己的信息字典:

最后,对于怪物的攻防以及特技信息,我们还需要参考工程文件中的敌人信息字典:

当然,其中的特技对应的函数也有个对应字典;只是这座塔里影响我们的实际上只有n连击类的特技,故而没有我读入。

base_path = "lanbaoshi/教程塔ex:蓝宝石转换理论2.9/"
#base_path = "C:/Users/bianshe/jupyter notebook/MT"
maps = base_path+"project/floors/"
configs = base_path+"_server/config.json"
enemys = base_path+"project/enemys.js"
items = base_path+"project/items.js"
datas = base_path+"project/data.js"
map_config = base_path+"project/maps.js"
def get_MAP(filename):
with open(maps+filename,encoding="utf-8") as f:
MAP_str = f.read()
MAP_str = re.findall('"map":(.*?),\s+"',MAP_str,re.S)[0]
exec(f"MAP_tmp={MAP_str}",globals())
MAP = np.array(MAP_tmp)
return MAP
def get_config(filename):
with open(filename,encoding="utf-8") as f:
MAP_str = f.read()
MAP_str = MAP_str[MAP_str.find("\n")+1:].replace("true","True").replace("false","False")
exec(f"MAP_tmp={MAP_str}",globals())
MAP = {int(k):v for k,v in MAP_tmp.items()}#np.array(MAP_tmp)
return MAP
info_dict = get_config(map_config)
def get_enemy_infos(filename):
with open(filename,encoding="utf-8") as f:
MAP_str = f.read()
MAP_str = MAP_str[MAP_str.find("\n")+1:].replace("true","True").replace("false","False").replace("null","None")
exec(f"MAP_tmp={MAP_str}",globals())
MAP = MAP_tmp#np.array(MAP_tmp)
return MAP
enemy_info = get_enemy_infos(enemys)
由于笔者在写代码时尚未学习图论知识,此处使用树状结构来维护房间内的信息。
其中,Room类代表该层塔中的一个子节点,一开始是每个怪物/宝石都单独放一个节点,到了后期会将可以合并的Room节点合并。
class Room:
def __init__(self,coors,room_type,child=[],father = None):
self.coors = coors #坐标
self.room_type = room_type #节点类型
self.child = child #子节点
self.is_cyclic = False #有环图特殊处理
self.father = father #父节点
self.defense_sum = 0 #该点能获取防御值的和
self.atk_times = 0 #该点所有怪物1防减伤之和
self.seq_coor = [] #假设要融合多个子节点,会在此处存放其子节点顺序在Floor类中,保存这一楼层中所有节点的信息并对其进行处理。使用搜索算法将所有的Room都找到并保存其中(广度和深度优先都可以)
class Floor:
def __init__(self,MAP,info_dict,enemy_info,hero_atk = 100,hero_location = [12,6]):
self.head = Room([hero_location],"init")
self.MAP = MAP.copy()
self.info_dict = info_dict
self.visited = np.zeros_like(MAP)
self.cyclic_nodes = []
self.enemy_infos = enemy_info
self.hero_atk = hero_atk
self.item_info = {"shield1":10,"blueGem":1}#在js中,宝石和盾牌的处理不一样,此处直接将他们写死
self.item_nodes = []
self.cyclic_item_nodes = []
self.branch = set()
def find_next_node(self,head,find_type,mode="include"):
q = queue.Queue()
q.put(head.coors[0])#每个节点只有1个坐标,后期再合并
childs = []
while not q.empty():
curr_coor = q.get()
x = curr_coor[0]
y = curr_coor[1]
if self.visited[x][y]==0 or curr_coor == head.coors[0]:
self.visited[x][y]=1
if self.MAP[x][y] != 0:
curr_type = self.info_dict[self.MAP[x][y]]["cls"]
if curr_type == "animates": #遇到墙了
continue
if ((curr_type in find_type and mode=="include") or (curr_type not in find_type and mode=="exclude")) and curr_coor != head.coors[0]:
child = Room([curr_coor],curr_type,father=head)
childs.append(child)
continue
for offset in [[x+1,y],[x-1,y],[x,y+1],[x,y-1]]:
if offset[0] in (-1,13) or offset[1] in (-1,13):
continue
q.put(offset)
for node in childs:
node.child = self.find_next_node(node,find_type,mode)
return childs1、标记“闭环”线路
当出现“闭环线路”时,必然有一个怪物是不用打的,然而,当一个怪物不用打时,这个怪物本身对你的减伤就不再仅仅依赖于防御值了,所以不再适用“全蓝宝石转化理论”了。在魔塔中,作者告诉也是我们,根据蓝宝石理论和有限次数的存读档以过包含“闭环”的线路。
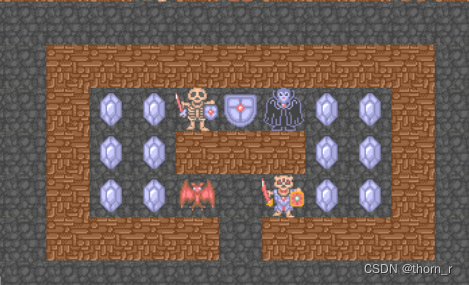
对于有闭环的那些分支,需要后续特殊处理,和其他节点处理方式不同,故而需要先标记一下。
我们对以及保存的树结构进行深度优先搜索,当某一个分支下的最终节点A不是宝石而是怪物时,从那个怪物出发遍历地图,看看周围有没有宝石,有的话从宝石处开始向上遍历树,直到找到与节点A相同父节点的另一个敌人节点B,他们分别是闭环的尾部和头部,将A节点移到B节点所在分支的最后。
def set_node_cyclic(self):
# 当一条路上没有宝石时,判别这条路的终点是不是别的通路的起点
# 只考虑“怪物作为终点”的情况
# 因为相邻分支的宝石最后会被融合为一个节点
# 而且由于深度优先,应该不会存在“一个宝石堆被2个怪物瓜分”的情况
maybe_cyclic = []
q = queue.Queue()
q.put(self.head)
while not q.empty():
node = q.get()
if len(node.child) == 0 and node.room_type == "enemys":
maybe_cyclic.append(node)
for i in node.child:
q.put(i)
for node in maybe_cyclic:
visited_cp = np.zeros_like(MAP)
coor = node.coors[0]
q_coor = queue.Queue()
q_coor.put(coor)
while not q_coor.empty():
curr_coor = q_coor.get()
x = curr_coor[0]
y = curr_coor[1]
if visited_cp[x][y]==0:
visited_cp[x][y]=1
if self.MAP[x][y] != 0:
curr_type = self.info_dict[self.MAP[x][y]]["cls"]
if curr_type in ("animates","enemys") and [x,y] != coor: #此处怪物和墙视为相同
continue
if curr_type == "items":
#找到宝石,此时需要从这个宝石开始一直找父节点
#直到找到与起始节点相同父节点的那个节点
father_enemy = node.father
brother_node = self.search_in_tree(curr_coor)
gem_node = brother_node
while brother_node.father != father_enemy:
brother_node = brother_node.father
self.change_tree_cyclic_nodes(brother_node,node,gem_node)
break
for offset in [[x+1,y],[x-1,y],[x,y+1],[x,y-1]]:
if offset[0] in (-1,13) or offset[1] in (-1,13):
continue
q_coor.put(offset)
def change_tree_cyclic_nodes(self,begin,end,gem):
#直接把那个独立的节点放到最后就行了,反正最后蓝宝石都要合并的;起始节点需要设置is_cyclic属性
#最后删除原本的节点
begin.is_cyclic = True
self.cyclic_nodes.append(begin)
end.father = gem
gem.child.append(end)
father = begin.father
father.child = [i for i in father.child if i != end]
def search_in_tree(self,coor):
q = queue.Queue()
q.put(self.head)
while not q.empty():
curr_node = q.get()
if curr_node.coors[0] == coor:
return curr_node
for i in curr_node.child:
q.put(i)忽略下图这种“最后一个敌人没有任何收益”的意义不明的情况。

2、合并相邻的蓝宝石
首先将所有相邻的宝石合并。由于是根据坐标遍历绘制的树,有些相邻树的节点会成为兄弟节点,有些则是父子节点,针对这2种情况,分别对他们做合并。
def merge_brother_gems(self):
#同一层的树,相邻的2个宝石合并(需要有同一个父节点),child也合并
s = [[self.head]]
while len(s)> 0:
nodes = s[0]
s.pop()
new_nodes = []
item_nodes_dict = {}
#last_Node = None
for node in nodes:
if node is None:
continue
else:
for child in node.child:
if child.room_type == "items":
if node in item_nodes_dict.keys():
item_nodes_dict[node].append(child)
else:
item_nodes_dict[node] = [child]
else:
new_nodes.append(child)
for father,item_nodes in item_nodes_dict.items():
if len(item_nodes) == 1:
new_nodes += item_nodes
if len(item_nodes)>1:
final_item_node = item_nodes[0]
#father = final_item_node.father
for i in range(1,len(item_nodes)):
item_node = item_nodes[i]
final_item_node.coors += item_node.coors
final_item_node.child += item_node.child
for child in item_node.child:
child.father = final_item_node
father.child = [i for i in father.child if i != item_node]
del item_node
new_nodes.append(final_item_node)
if len(new_nodes)>0:
s.append(new_nodes)
def merge_chain_gems(self,father,node,target_type = "items"):
#父子关系的宝石融合,父宝石合并子宝石的child
#需要从下往上遍历节点
#怪物暂时不能这么合并
if father is None:
for child in node.child:
self.merge_chain_gems(node,child,target_type)
elif node is None:
return
else:
if father.room_type != target_type and node.room_type == target_type:
if len(node.child) == 0 or target_type not in [i.room_type for i in node.child]:
self.item_nodes.append(node)
if father.room_type != target_type or node.room_type != target_type or node.is_cyclic:
for child in node.child:
self.merge_chain_gems(node,child,target_type)
else:
if father.father.room_type != target_type:
self.item_nodes.append(father)
if len(node.child)>0:
for child in node.child:
self.merge_chain_gems(node,child,target_type)
father.child = [i for i in father.child if i!=node]
father.coors = father.coors + node.coors
for child in node.child:
child.father = father
father.child.append(child)
del node3、计算房间内的1防减伤/蓝宝石防御总和
def calc_room_values(self):
q = queue.Queue()
q.put(self.head)
while not q.empty():
node = q.get()
if node.room_type == "items":
for x,y in node.coors:
name = self.info_dict[self.MAP[x][y]]['id']
node.defense_sum += self.item_info[name]
elif node.room_type == "enemys":
for x,y in node.coors:
name = self.info_dict[self.MAP[x][y]]['id']
monster = self.enemy_infos[name]
monster_defense = int(monster["def"])
monster_hp = int(monster["hp"])
monster_atk = int(monster["atk"])
monster_atk_times = math.ceil(monster_hp/(self.hero_atk-monster_defense))-1
if monster_atk_times == 0:
continue
if monster["special"] is not None and type(monster["special"])==list:# 此处的special具体规律没看懂,有时是一个单独int变量,有时是数组;但是n连击的特性都是数组,不是单个整型变量
if 6 in monster["special"]:
n = monster["n"]
elif 4 in monster["special"]:
n = 2
elif 5 in monster["special"]:
n = 3
else:
n = 1
monster_atk_times *= n #n连击
node.atk_times += monster_atk_times
for child in node.child:
q.put(child)4、融合怪物与“坏点”
首先,忽略那些“闭环”节点,根据每个宝石的父节点来看怪物,将那些怪物合并
def mix_rooms(self):
for node in self.cyclic_nodes:
q = queue.Queue()
q.put(node)
while not q.empty():
node_tmp = q.get()
if node_tmp.room_type == "items":
self.cyclic_item_nodes.append(node_tmp)
for child in node_tmp.child:
q.put(child)
#新策略:根据每个宝石的节点来看父节点
for i in self.item_nodes:
if i not in self.cyclic_item_nodes:
father = i.father
father.child = [n for n in father.child if n != i]+i.child
for child in i.child:
child.father = father
father.coors += i.coors
father.defense_sum += i.defense_sum
#将同一个支路上单个怪物合并
node = father
father = father.father
while father.room_type == "enemys":
if len(father.child)>1 and father.defense_sum==0:
self.branch.add(father)
break
if father.defense_sum>0:
break
father.coors += node.coors
father.child = node.child
father.defense_sum = node.defense_sum
father.atk_times += node.atk_times
for child in node.child:
child.father = father
del node
node = father
father = father.father在原塔中4楼有着“多个节点连续坏点”以及“坏点分支下有多个坏点需要合并”的情况,此处坏点从内而外做以下操作:
1、将坏点的外部和内部合并
2、当坏点内部有多个子房间时,需要将它们所有的坏点都融合
3、接2,有多个坏点时,需要在父节点下保存所有坏点的顺序于seq_coor中
这就是Room类中seq_coor的用处
def merge_bad_rooms(self,node):
#“八爪鱼结构”,见https://tieba.baidu.com/p/5871628045
# 对于坏点组,内部和外部血量差一个固定值(内部1防御减伤*外部能获得的宝石数量),因此这样操作后不影响最优路线的选取
#此处需要做以下几件事:
#1、将坏点的外部和内部合并
#2、当坏点内部有多个子房间时,需要将它们所有的坏点都融合
#3、接2,有多个坏点时,需要在父节点下保存所有坏点的顺序
# 必须是从外向内
if len(node.child)==0:
return
curr_feature_value = self.calc_feature(node)
# 对于合并之后还需要再合并的情况,此处设定“只要节点特征值更新就需要重新计算”
flag = True #节点特征值是否重新更新了
while flag and len(node.child)>0:
flag = False
child_dict = {}
for child in node.child:
#self.merge_bad_rooms(child)
feature_child = self.calc_feature(child)
child_dict[child] = feature_child
for child,child_feature in sorted(child_dict.items(),key=lambda x:x[1]):
# merge时应该将seq也merge上
if child_feature<curr_feature_value:
#坏点,融合并记录其顺序
#node.coors += child.coors
node.defense_sum += child.defense_sum
node.atk_times += child.atk_times
node.child = [i for i in node.child if i != child] + child.child
for c in child.child:
c.father = node
node.seq_coor.append(child.coors)
node.seq_coor += child.seq_coor
del child
#更新这个节点的特征值
curr_feature_value = self.calc_feature(node)
flag = True
for child in node.child:
self.merge_bad_rooms(child)5、对于闭环情形,手动“存读档”并打印最终信息
当楼层中没有闭环节点时,只需要简单地将坏点等信息融合后打印打怪顺序即可;但是对于闭环而言,就需要遍历闭环中每一个怪物,假设它不用打。那么剩下的节点就需要翻转,成为原本闭环节点的兄弟节点,以此重新计算特征值。
笔者在此对于每一种情况都作为新的楼层计算,可以说是穷举打印顺序了。
def mix_rooms_with_cyc(self):
# 先消除那些“伪闭环”
if len(self.cyclic_nodes)==0:
self.mix_rooms()
for i in self.head.child:
self.merge_bad_rooms(i)
self.print_node_with_seq()
else:
sub_head = self.cyclic_nodes[0]
node = sub_head
while len(node.child)>0: #最后一个sub_child只要手动剔除就行了
if node.room_type == "enemys":
need_coors = node.coors
floor_cp = deepcopy(self)
sub_head_cp = floor_cp.cyclic_nodes[0]
sub_head_cp.is_cyclic = False
node_reverse = floor_cp.search_in_tree(need_coors[0])
floor_cp.reserve_node(node_reverse,sub_head_cp)
floor_cp.cyclic_nodes = floor_cp.cyclic_nodes[1:]
floor_cp.mix_rooms_with_cyc()
node = node.child[0]
if node.room_type == "enemys":
floor_cp = deepcopy(self)
floor_cp.cyclic_nodes[0].is_cyclic = False
floor_cp.cyclic_nodes = floor_cp.cyclic_nodes[1:]
floor_cp.mix_rooms_with_cyc()
def print_node_with_seq(self):
child_dict = {}
nodes = [self.head]
while len(nodes)>0:
tmp = []
for node in nodes:
if node.room_type == "enemys":
child_dict[node] = self.calc_feature(node)
for child in node.child:
tmp.append(child)
nodes = tmp
#print_the_dict
for child,child_feature in sorted(child_dict.items(),key=lambda x:x[1]):
# 先打印节点的怪物坐标,再打印seq的怪物坐标
for x,y in child.coors:
curr_type = self.info_dict[self.MAP[x][y]]["cls"]
if curr_type == "enemys":
print([x,y])
for coors in child.seq_coor:
for x,y in coors:
curr_type = self.info_dict[self.MAP[x][y]]["cls"]
if curr_type == "enemys":
print([x,y])
print("end \r\n")6、实例运行
MAP = get_MAP('MT4.js')
floor5 = Floor(MAP,info_dict,enemy_info)
floor5.head.child = floor5.find_next_node(floor5.head,['enemys', 'items'])
floor5.set_node_cyclic()
floor5.merge_brother_gems()
floor5.merge_chain_gems(None,floor5.head)
floor5.calc_room_values()
floor5.mix_rooms_with_cyc()
最终的结果为:

这座塔的所有楼层都是卡1血通过,此处答案正好能够通过这一楼层。
注意[6,2]位置的蓝宝石,需要站在[7,1]位置,使用空格轻按获取,否则会多吃一次巫师的领域伤害从而无法通过本层。
MAP = get_MAP('MT5.js')
floor5 = Floor(MAP,info_dict,enemy_info)
floor5.head.child = floor5.find_next_node(floor5.head,['enemys', 'items'])
floor5.set_node_cyclic()
floor5.merge_brother_gems()
floor5.merge_chain_gems(None,floor5.head)
floor5.calc_room_values()
floor5.mix_rooms_with_cyc()
而对于第五层而言,出现了闭环的结构(注意除了中间,右上角2个其实也算是闭环结构,只是删去哪个节点都无所谓,因为闭环中只有2个相同的怪物)。
最终会输出2*2*4=16种可能得顺序,实际上只有4种,因为右上角再怎么变都没有实际意义。

经检验,圈出的顺序可以顺利通过本层。
三、总结
这个理论本身的严格证明与作者的论证实际上是包含了许多的图论知识的,同时其证明以及定理推论十分严谨。魔塔无论是作为游戏还是作为数学模型,都有着很多值得推敲的地方,同时也让笔者也领略到数据结构与算法本身的一些魅力。笔者不得不佩服原作者的研究精神与其图论知识的扎实程度。
代码有诸多的不规范之处,还请见谅,如果有更好的实现方法或者是更适合使用的数据结构,还望在评论区多多指教。
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








