全文概要
本文将介绍java.util.concurrent包下一个重要的接口BlockingQueue,主要内容如下:
- 介绍BlockingQueue常见的API以及他们之间的区别;
- 比较几个常见的BlockingQueue的实现类;
- 阻塞队列经常用于生产者/消费者的场景,通过一个案例来实现。
BlockingQueue常见API
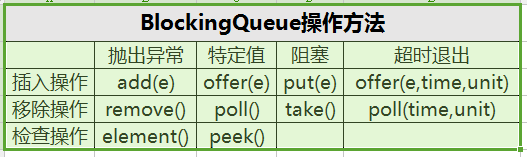
BlockingQueue常见的API如下图所示:
- 抛出异常
是指当阻塞队列满的时候,再添加元素,会抛出IllegalStateException异常;当阻塞队列为空时,从队列中获取元素会抛出NoSuchElementException异常;
- 特定值
是指向阻塞队列中添加元素成功,返回true,失败返回false;当成功移除队列中的元素时返回移除的元素,否则返回null;
- 阻塞
是指当阻塞队列满时,再添加元素,该线程会阻塞;当阻塞队列为空时,从队列移除元素时该线程会阻塞;
- 超时退出
是指当阻塞队列满时添加元素,该线程会阻塞一段时间,若超过该时间队列还是处于满额状态则会退出;
当阻塞队列空时移除元素,该线程会阻塞一段时间,若超过该时间队列还是处于空状态则会退出。
常见BlockingQueue的实现类
- ArrayBlockingQueue 一个由数组组成的有界阻塞队列
- LinkedBlockingQueue 一个由链表组成的有界阻塞队列
- SynchronousQueue 一个不存储元素的阻塞队列,数据是在生产者和消费者之间传递
生产者-消费者场景的实现
前面已经通过synchronized实现消费者模型和使用Lock-Condition实现消费者模型,读者可以三篇对比阅读。
仓库模型代码:
package com.tml.javaCore.concurrent.blockQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingDeque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
/**
* <p>
* 多线程 生产者-消费者仓库模型
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Repository {
/*
* 仓库的容量
*/
private int capacity;
/*
* 仓库的实际容量
*/
private int size;
/*
* 阻塞队列
* 消费者从队列中消费数据,若队列中没有数据,则调用take()时,会阻塞
* 生产者向队列中生产数据,若队列中已经满了,则调用put()时,会阻塞
*/
private BlockingDeque<Integer> blockingDeque ;
public Repository(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.size = 0;
blockingDeque = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Integer>();
}
/**
* <p>
* 生产者生产资源
*
* @param produceAmount
* 生产者预生产量
*/
public void produce(int produceAmount) {
while (produceAmount > 0) {
try {
while(this.size >= this.capacity){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":is fulled!");
return;
}
blockingDeque.put(produceAmount);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/*
* 获取实际的生产量
*/
int actAmount = (size + produceAmount) > capacity ? capacity - size : produceAmount;
size += actAmount;
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":has + :" + actAmount + ",the actual size is:" + size);
produceAmount -= actAmount;
}
}
/**
* <p>
* 消费者消费资源
*
* @param consumeAmount
* 消费者预消费量
*/
public void consume(int consumeAmount) {
while (consumeAmount > 0) {
try {
while(size<=0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":empty!");
return;
}
blockingDeque.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/*
* 获取实际的消费量
*/
int actAmount = (size < consumeAmount) ? size : consumeAmount;
size -= actAmount;
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":has - :" + actAmount + ",the actual size is:" + size);
consumeAmount -= actAmount;
// 通知生产者来生产
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Repository [capacity=" + capacity + ", size=" + size + "]";
}
}测试案例代码:
package com.tml.javaCore.concurrent.blockQueue;
/**
* <p>生产者-消费者
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//新建一个容量为100的仓库
Repository repository =new Repository(100);
//模拟生产者,每隔1000毫秒生产23个产品
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
repository.produce(23);
}
}
},"producer1").start();
//模拟消费者1,每隔2500毫秒消费产品25
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(2500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
repository.consume(25);
}
}
},"consumer1").start();
//模拟消费者2,每隔1500毫秒消费产品10
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
repository.consume(10);
}
}
},"consumer2").start();
}
}- 结果输出
下面是某一次的部分输出结果:
producer1:has + :23,the actual size is:23
consumer2:has - :10,the actual size is:13
producer1:has + :23,the actual size is:36
consumer1:has - :25,the actual size is:11
producer1:has + :23,the actual size is:34
consumer2:has - :10,the actual size is:24
producer1:has + :23,the actual size is:47
consumer2:has - :10,the actual size is:37
producer1:has + :23,the actual size is:60
consumer1:has - :25,the actual size is:35
producer1:has + :23,the actual size is:58
consumer2:has - :10,the actual size is:48
producer1:has + :23,the actual size is:71
consumer1:has - :25,the actual size is:46
producer1:has + :23,the actual size is:69
consumer2:has - :10,the actual size is:59
producer1:has + :23,the actual size is:82
consumer2:has - :10,the actual size is:72
producer1:has + :23,the actual size is:95
consumer1:has - :25,the actual size is:70
producer1:has + :23,the actual size is:93
consumer2:has - :10,the actual size is:83
producer1:has + :17,the actual size is:100
producer1:is fulled!
consumer1:has - :25,the actual size is:75
producer1:has + :23,the actual size is:98
consumer2:has - :10,the actual size is:88
producer1:has + :12,the actual size is:100
producer1:is fulled!consumer2:has - :10,the actual size is:90
- 结果说明
- 在Repository中定义了一个阻塞队列,当队列满时,生产者再添加数据会阻塞,当队列为空时,消费者再消费数据,消费者会阻塞;
- 生产者生产数据时,当仓库的实际值大于等于仓库的最大容量时,直接return,调用put()方法可能会使生产者阻塞;
- 消费者消费数据时,当仓库的实际值小于等于0时,直接return,调用take()方法可能会使消费者阻塞;
- 测试案例代码和之前一样,模拟一个生产者两个消费者,整个体系能有条不紊的运行。






















 115
115

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








