如ehcache,guava cache,redis
也有将ehcache,guava cache分级为单机缓存
将redis分为分布式缓存
ehcache官网:https://www.ehcache.org/
这里主要说下ehcache和guava cache
单独使用ehcache(当然真正企业开发并不会单独使用ehcache,而是会和Spring或者SpringBoot集成使用)
ehcache依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>2.10.6</version>
</dependency>
注意ehcache的原生API在实际开发中一般不使用,而是和Spring或者SpringBoot集成使用,但是原理还是ehcache,只不过在Spring和SpringBoot中对它进行了包装,学习ehcache原生API可以帮助理解
这里是建了个Maven工程,引入的依赖,包含了Spring,SpringBoot
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!--springboot web-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--spring aop + aspectj starter-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--引入spring的 cache 支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--缓存实现-->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--jsr107缓存规范-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.cache</groupId>
<artifactId>cache-api</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--lombok,springboot中已定义版本-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>29.0-jre</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.78</version>
</dependency>
<!--redisson的一部分代码是实现了jsr107的,分布式锁-->
<!-- <dependency>-->
<!-- <groupId>org.redisson</groupId>-->
<!-- <artifactId>redisson</artifactId>-->
<!-- <version>3.16.2</version>-->
<!-- </dependency>-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>使用原生ehcache的API
ehcache.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<ehcache
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="https://www.ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd">
<!--
path:默认写到磁盘的路径:C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Temp\ -->
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/>
<!--
对应类:net.sf.ehcache.config.CacheConfiguration
maxEntriesLocalHeap:内存中最多放多少个元素
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:驱逐策略,net.sf.ehcache.store.MemoryStoreEvictionPolicy.fromString
eternal:true:不过期
timeToIdleSeconds:eternal=false时有效,可以闲置多长时间,单位s
timeToLiveSeconds:eternal=false时有效,从创建开始计算可以存活多长时间,单位s
maxElementsOnDisk:localTempSwap时有效,表示最多可以往磁盘写多少个
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:localTempSwap时有效,检查磁盘元素是否失效的时间间隔
persistence:当cache中的元素个数=maxEntriesLocalHeap时,
localTempSwap:写到磁盘,其他值: net.sf.ehcache.config.PersistenceConfiguration.Strategy
statistics:开启统计
-->
<cache
name="user_cache"
maxEntriesLocalHeap="1000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="600"
timeToLiveSeconds="600"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"
statistics="true"
>
<persistence strategy="localTempSwap"/>
</cache>
</ehcache>Test
相对路径:
String absPath="./src/main/resources/ehcache.xml";
@Test
public void test2(){
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir"));
}
/**
* 单独使用ehcache的api进行编程
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
String absPath = "D:\\cache-demo\\src\\main\\resources\\ehcache.xml";
/*
用来管理多个Cache,user_cache、item_cache、store_cache...
*/
CacheManager cacheManager = CacheManager.create(absPath);
/*
获取到CacheManager管理的所有的cache
*/
String[] cacheNames = cacheManager.getCacheNames();
System.out.println("CacheManager管理的所有的cache的名字"+ Arrays.toString(cacheNames));
/*
获取cache的名字(我们指定的)获取具体的cache
*/
Cache userCache = cacheManager.getCache("user_cache");
/*
往userCache放入一个user
*/
User user = new User();
user.setId(1001L);
user.setName("劈里啪啦");
Element element = new Element(user.getId(),user);
userCache.put(element);
/*
通过key取出缓存的对象
*/
Element resultEle = userCache.get(1001L);
System.out.println("获取到的resultEle:" +resultEle);
System.out.println("获取Element的value:" + resultEle.getObjectValue());
}
关于jsr107缓存规范
依赖
<!-- JCACHE-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.cache</groupId>
<artifactId>cache-api</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
-
jcp介绍: The Java Community Process(SM) Program - JSRs: Java Specification Requests - detail JSR# 107
-
项目地址: GitHub - jsr107/jsr107spec: JSR107 Cache Specification
api结构
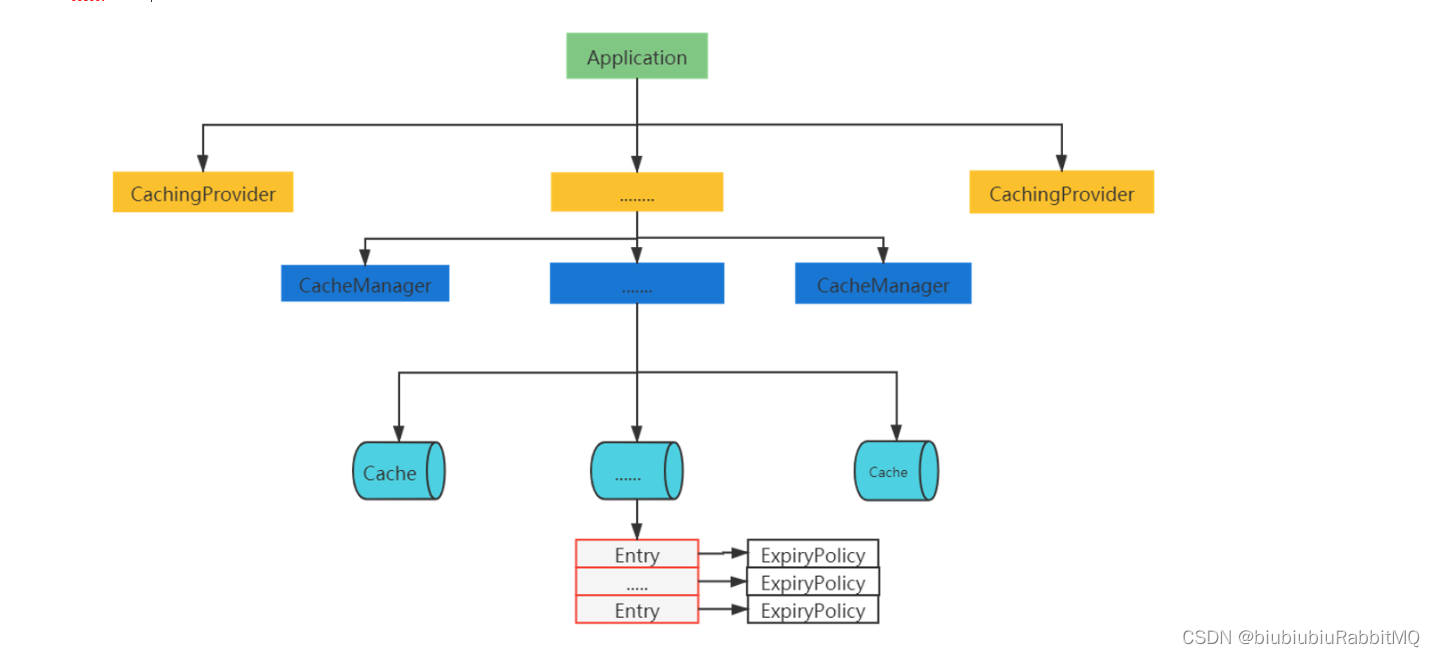
如何理解上面这张图:就是说一个应用程序下面,有很多个CahingProvider,每个CachingProvider里又包含很多CacheManager,每个CacheManager里有包含很多Cache
对于jsr107缓存规范只做了解,过于复杂
下面是Spring的缓存抽象,设计就相对简单了
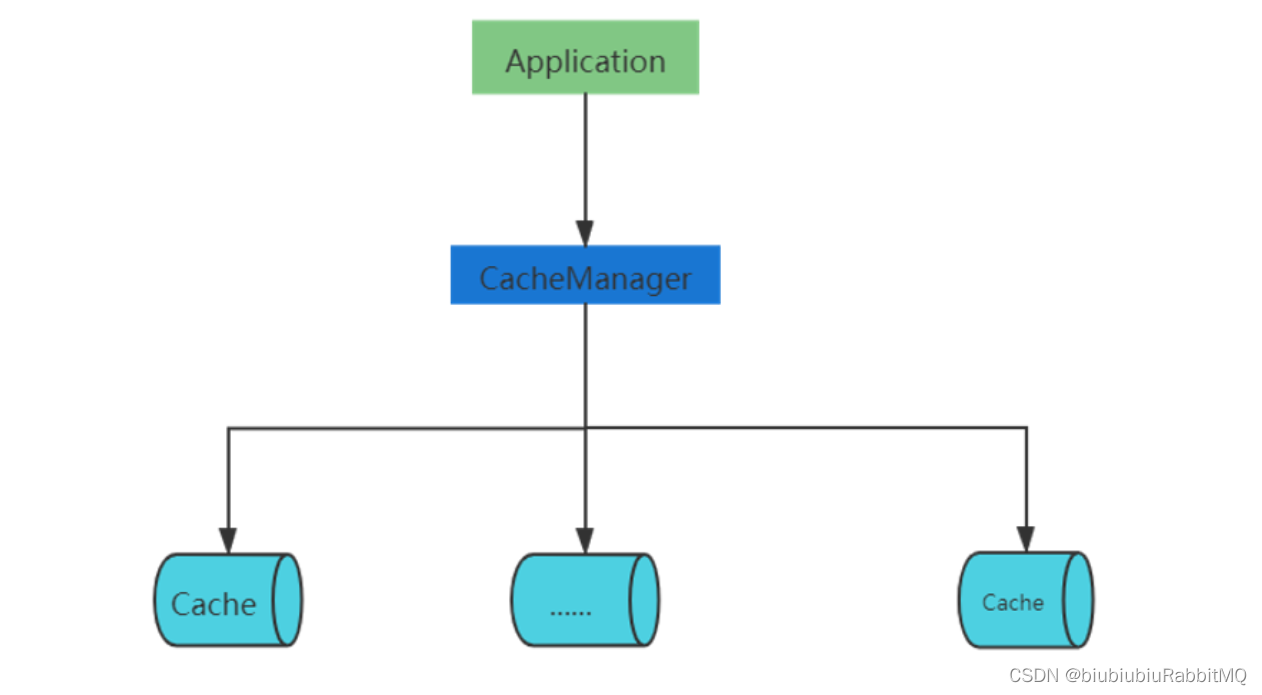
就是说一个应用里面有一个CacheManager,管理着多个Cache
ehcache与Spring集成以及编程式操作缓存
Spring依赖一开始就已经引入了
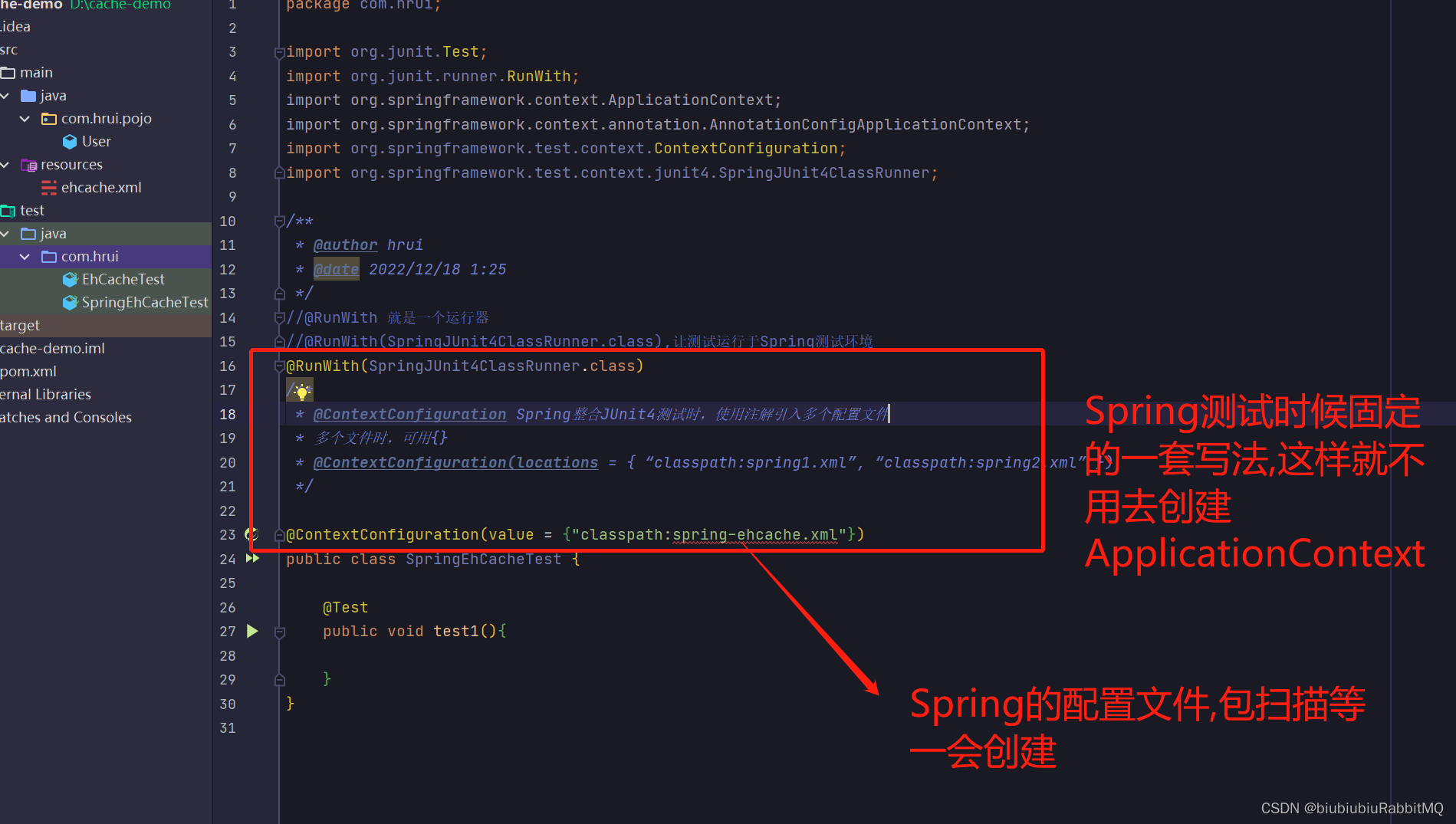
Spring集成ehCache两种方式:
1.编程式使用
2.注解方式使用
注意在Spring集成ehcache的这张图
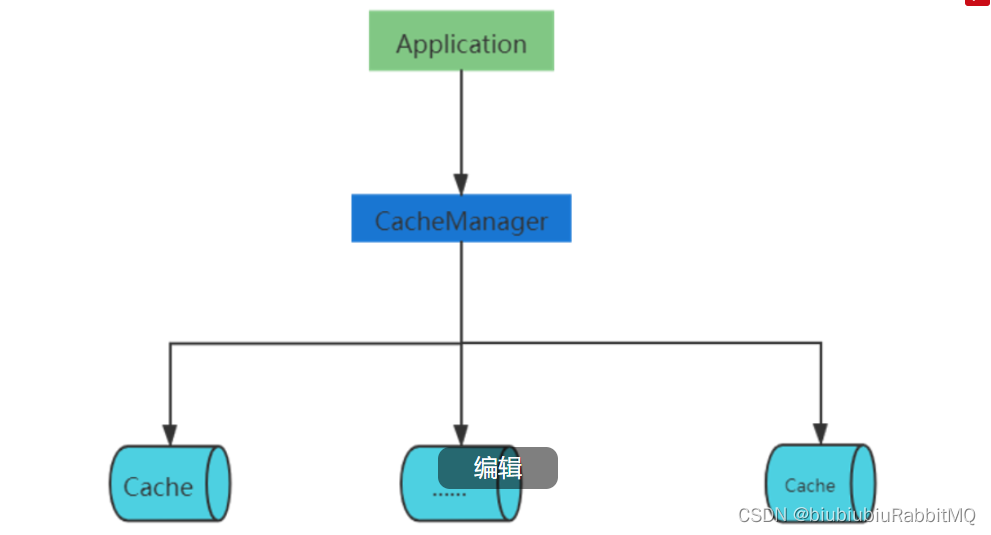
新建一个测试类
1.编程式使用
spring-ehcache.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache-4.0.xsd">
<!--相当于CacheManager cacheManager = CacheManager.create(absPath);-->
<bean
id="ehCacheManager"
class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean">
<!--配置ehcache.xml的路径-->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:ehcache.xml"/>
</bean>
<!--Spring中对原生的CacheManager进行包装,
org.springframework.cache.CacheManager有多个实现
-->
<bean
id="ehCacheCacheManager"
class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheCacheManager">
<property name="cacheManager" ref="ehCacheManager"/>
<!--事务回滚缓存也回滚-->
<property name="transactionAware" value="true"/>
</bean>
<!--和上面是同级的,指定用哪个实现类-->
<!-- <bean-->
<!-- id="concurrentMapCacheManager"-->
<!-- class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheManager">-->
<!-- <property name="cacheNames">-->
<!-- <list>-->
<!-- <value>item_cache</value>-->
<!-- <value>store_cache</value>-->
<!-- </list>-->
<!-- </property>-->
<!-- </bean>-->
<!--跟org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching一样-->
<cache:annotation-driven proxy-target-class="true"
cache-manager="ehCacheCacheManager"/>
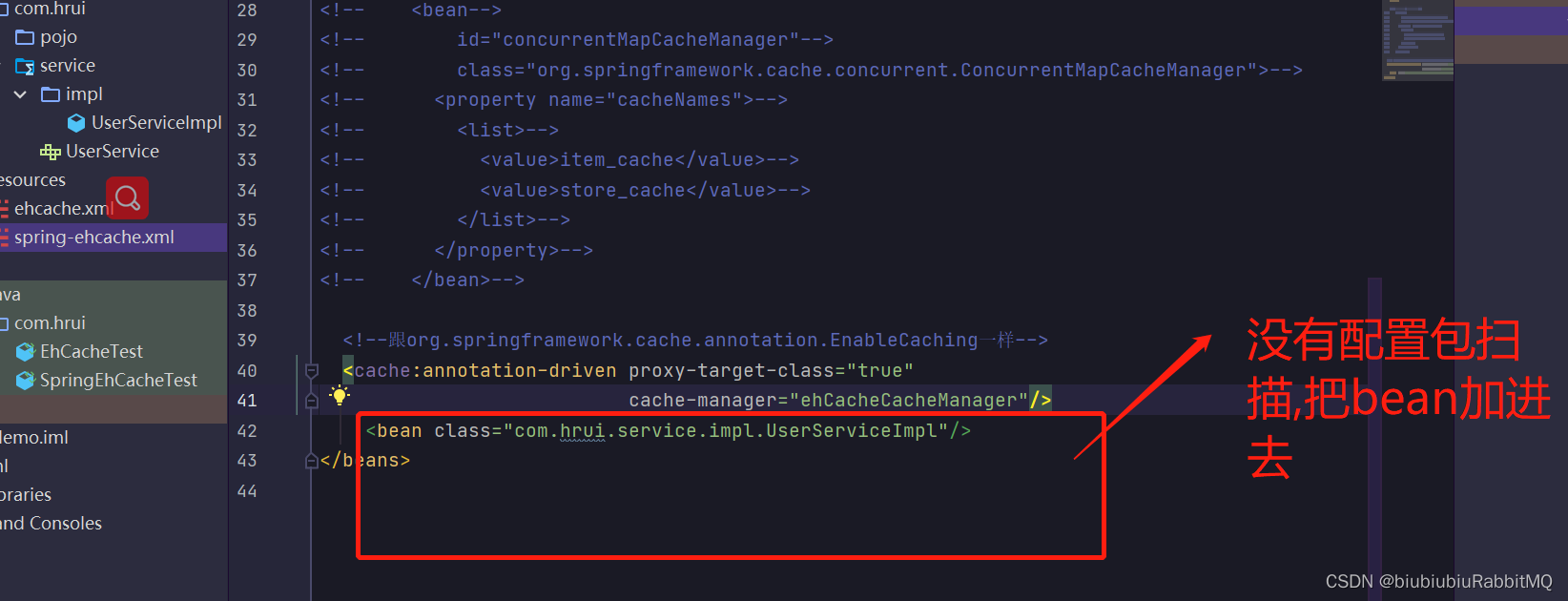
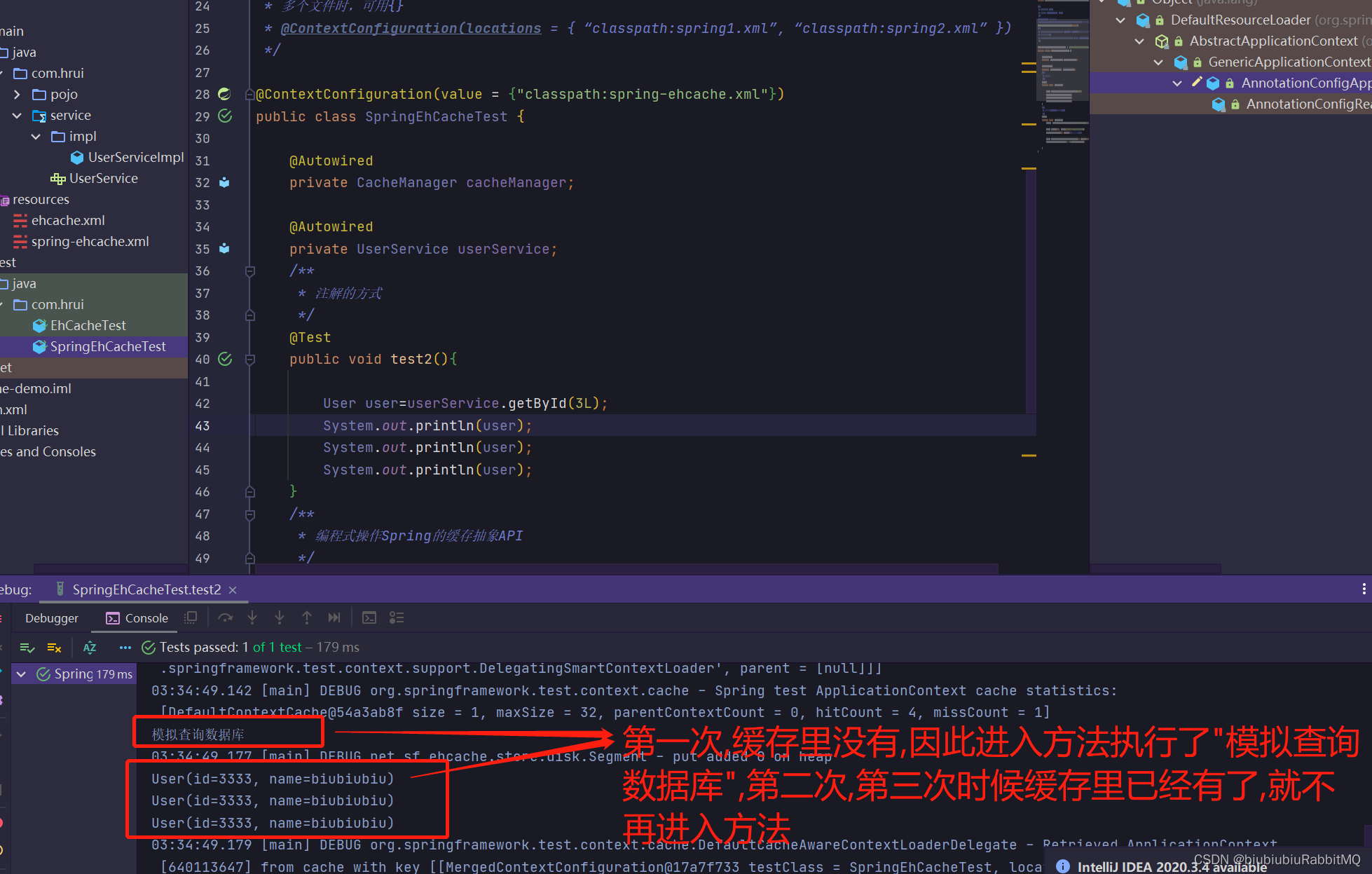
</beans>现在可以开始玩了
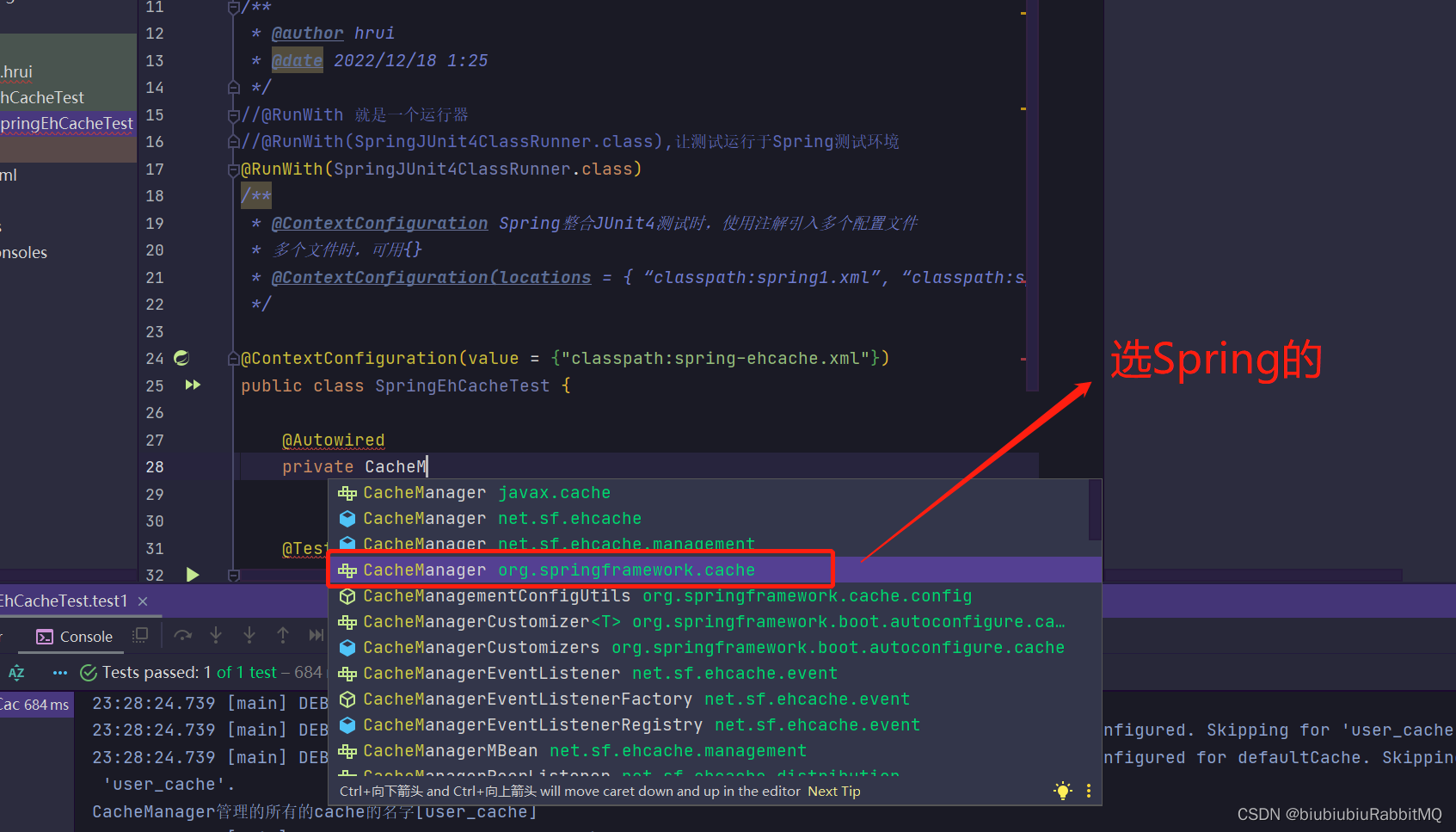
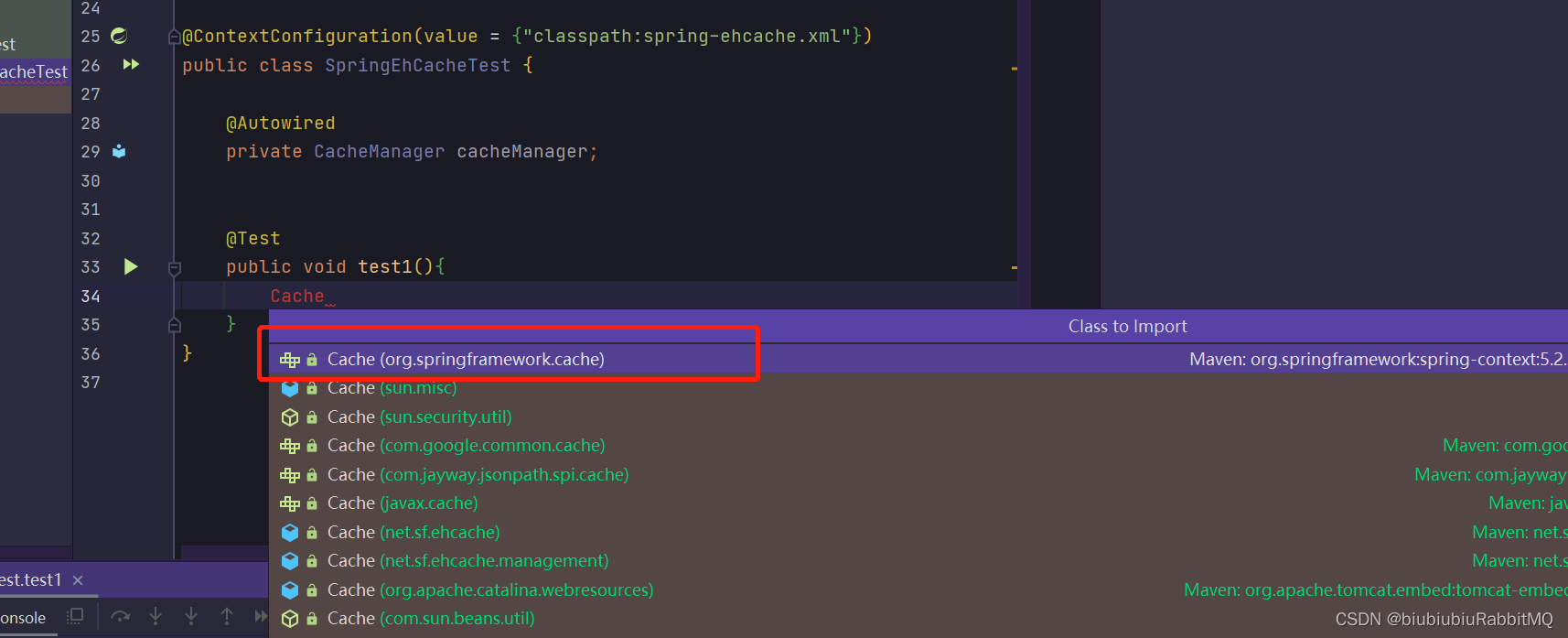
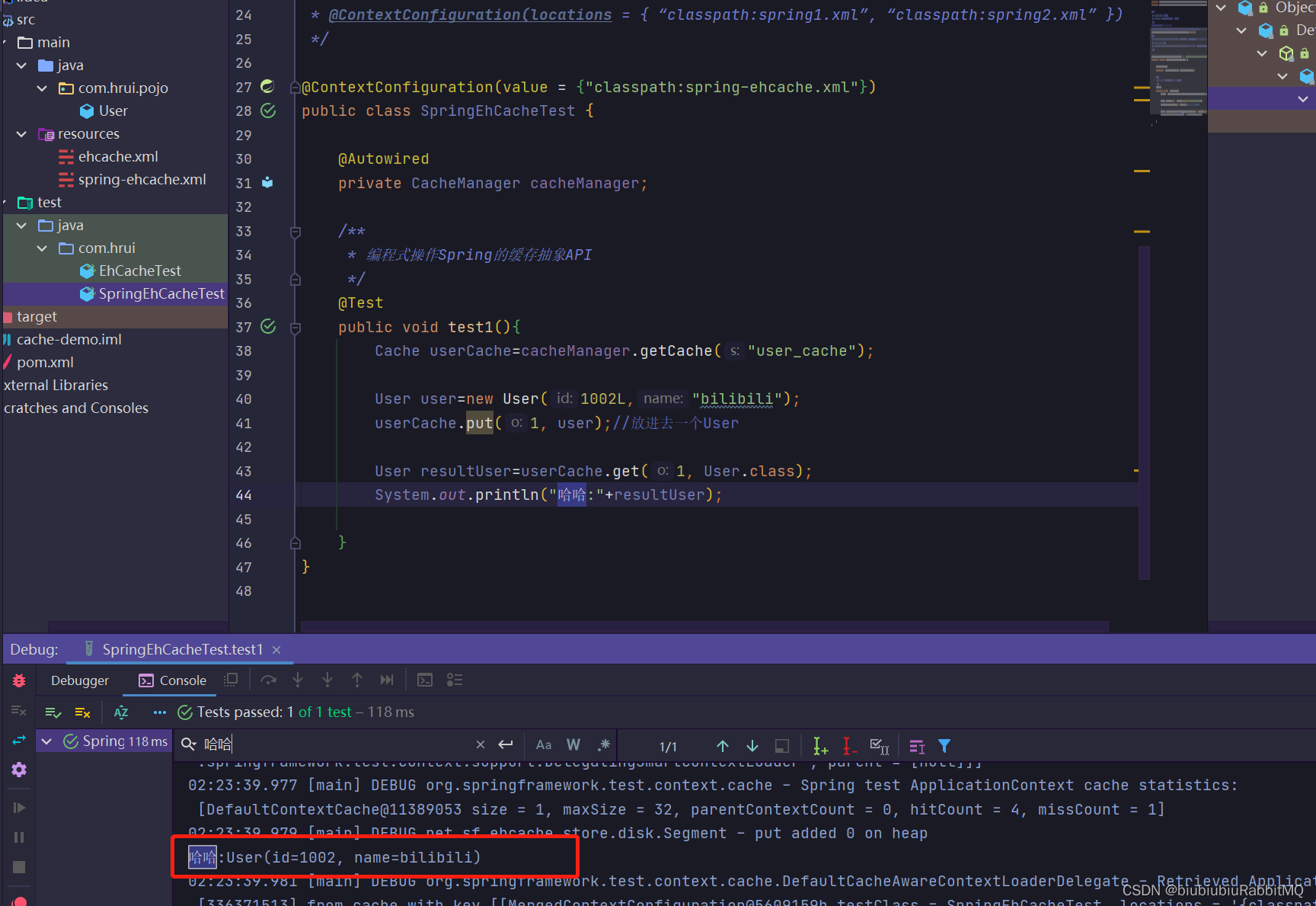
打印了,但是控制台最后也报错了,说没有实现序列化
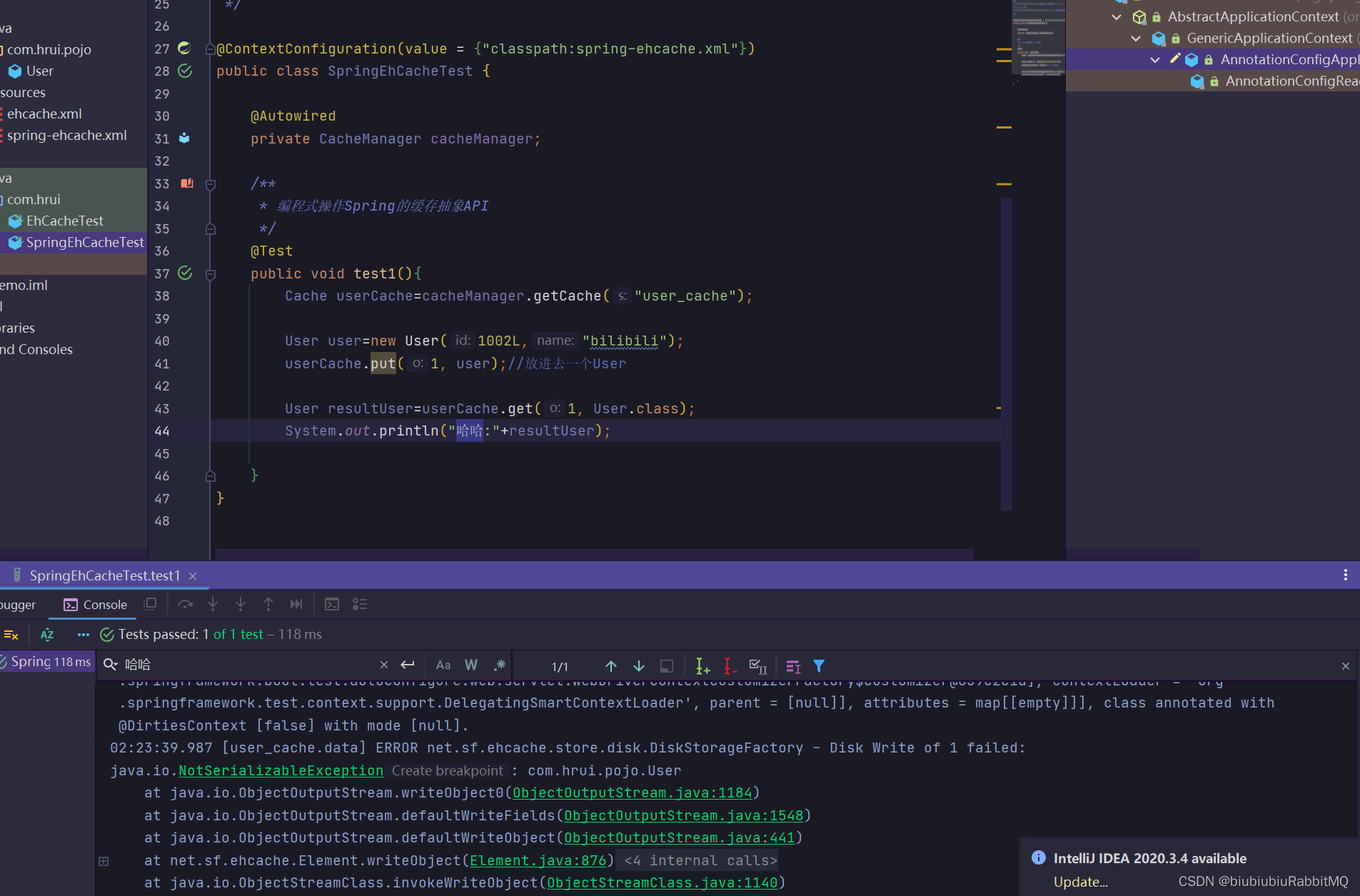
原因是

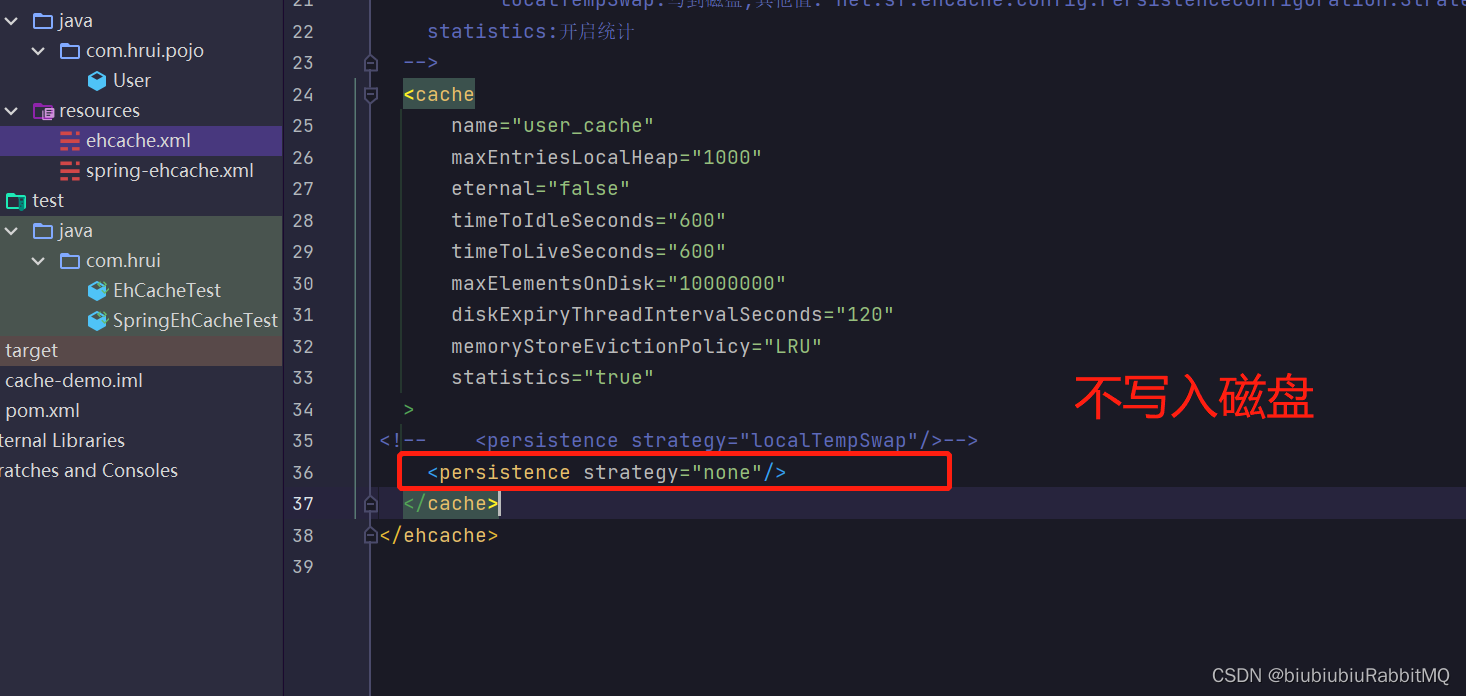
解决方式:1个改成不写入磁盘
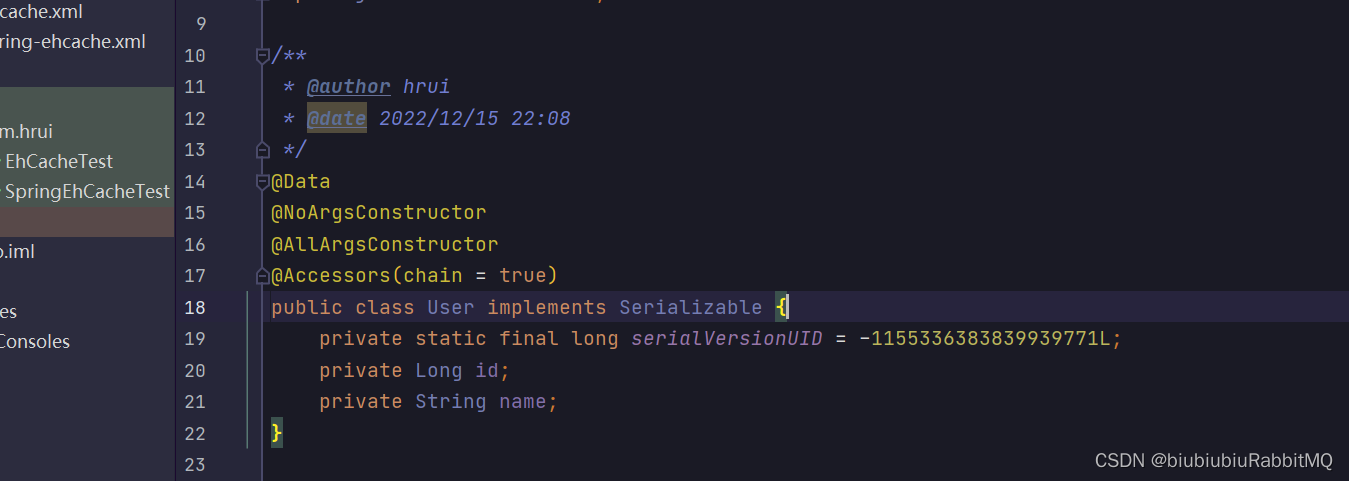
2,那就是实现序列化
2.注解方式使用 使用@Cacheable
比如顶一个接口
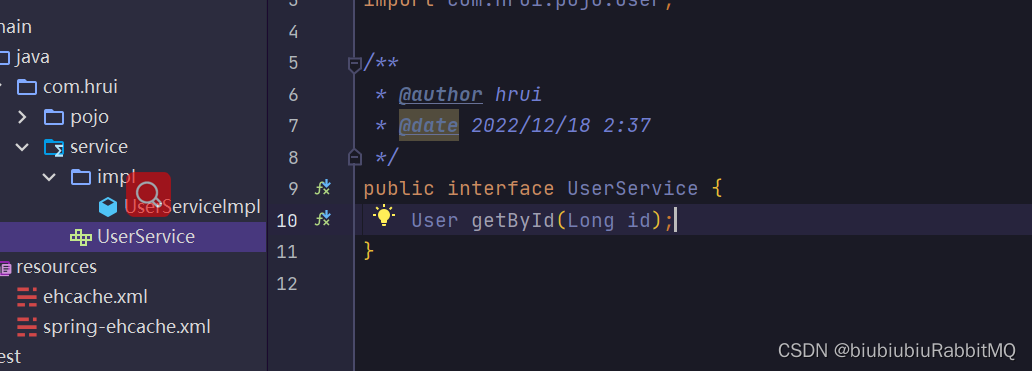
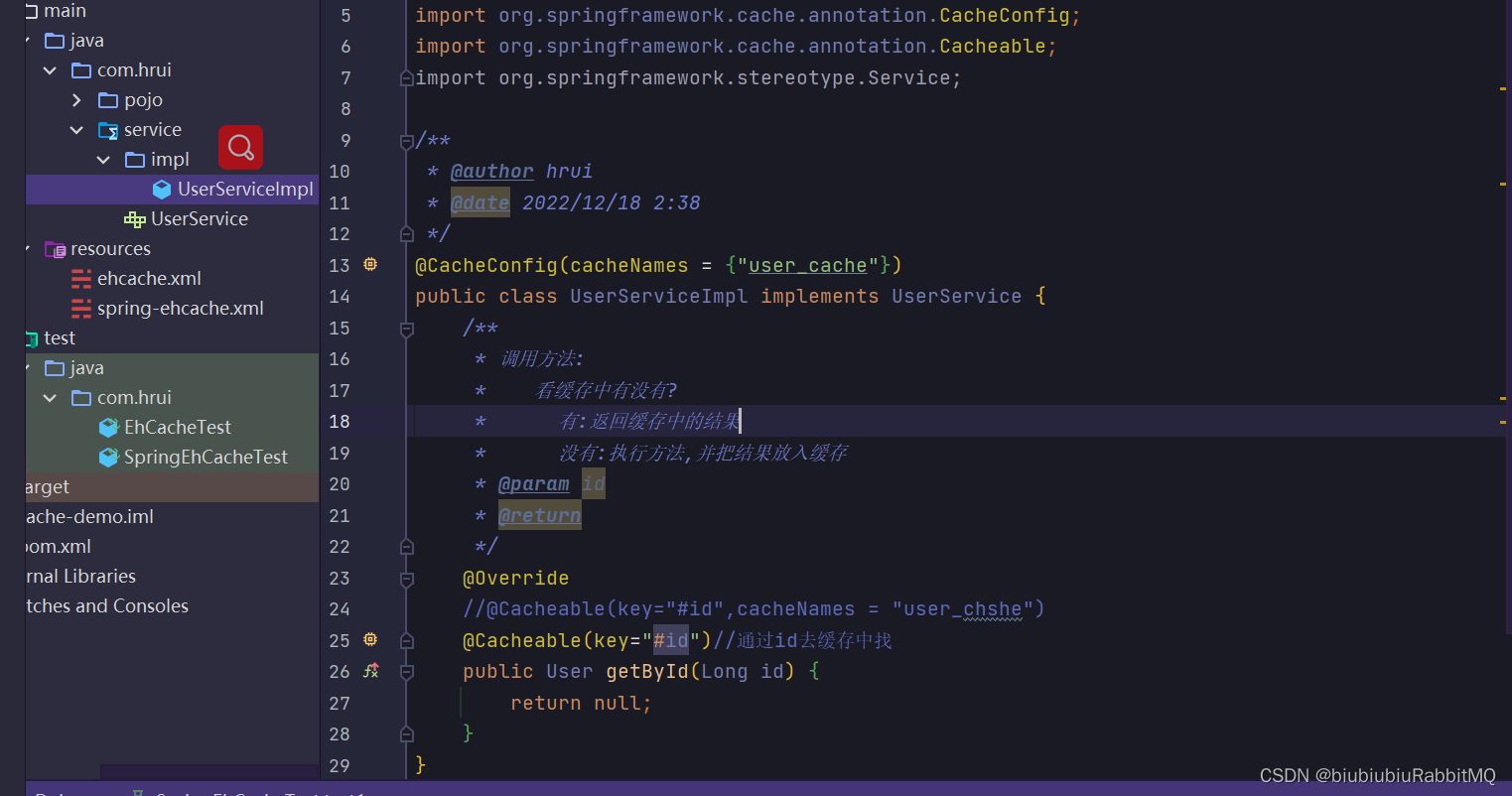
下面就是实际开发中会用到的
SpringBoot集成ehcache
依赖一开始就已引入
直接测试
写个启动类,且加上@EnableCaching注解
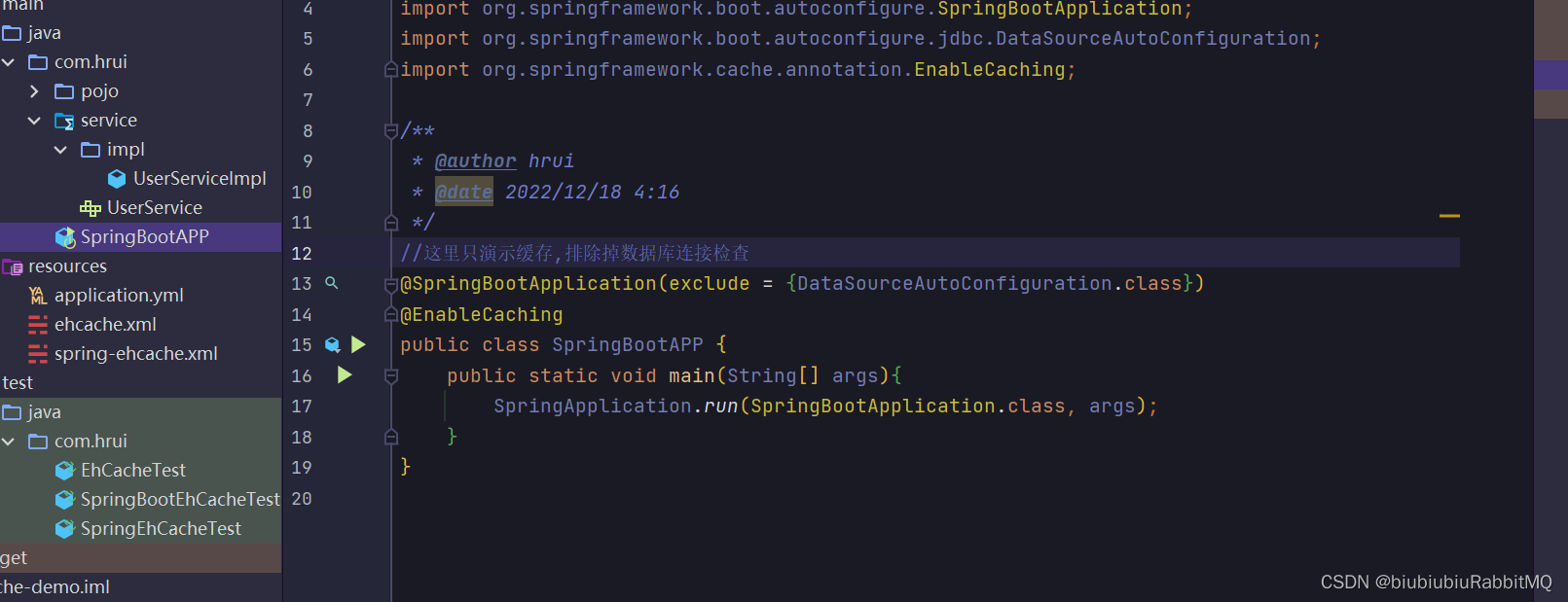
在yml里的配置
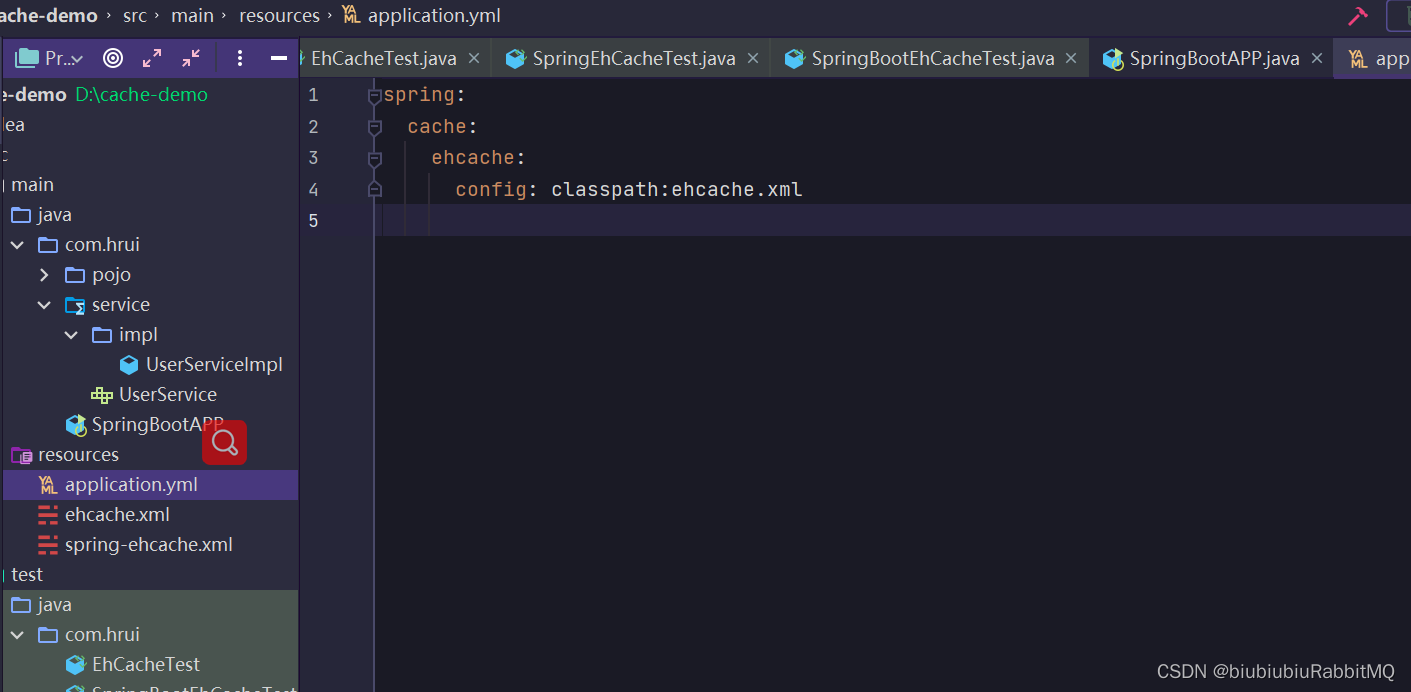
现在用的是SpringBoot,将UserServiceImpl上加上@Service注解
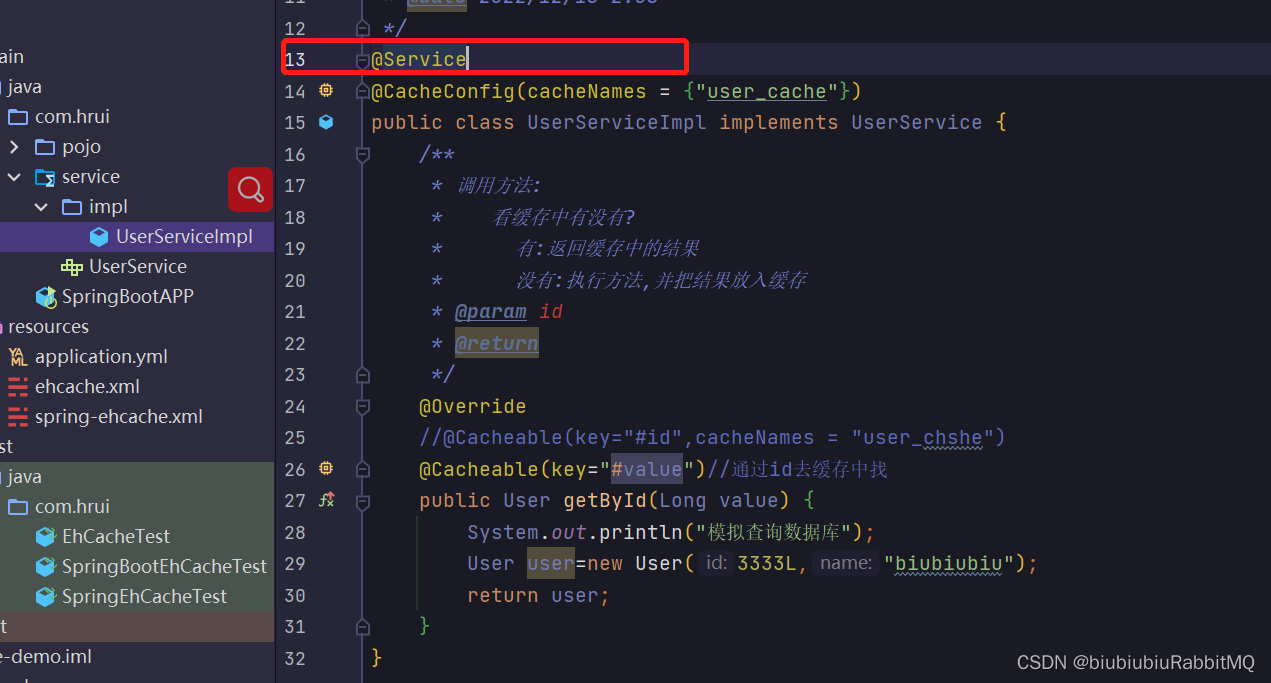
SpringBoot中编程式使用ehcashe和Spring是一样的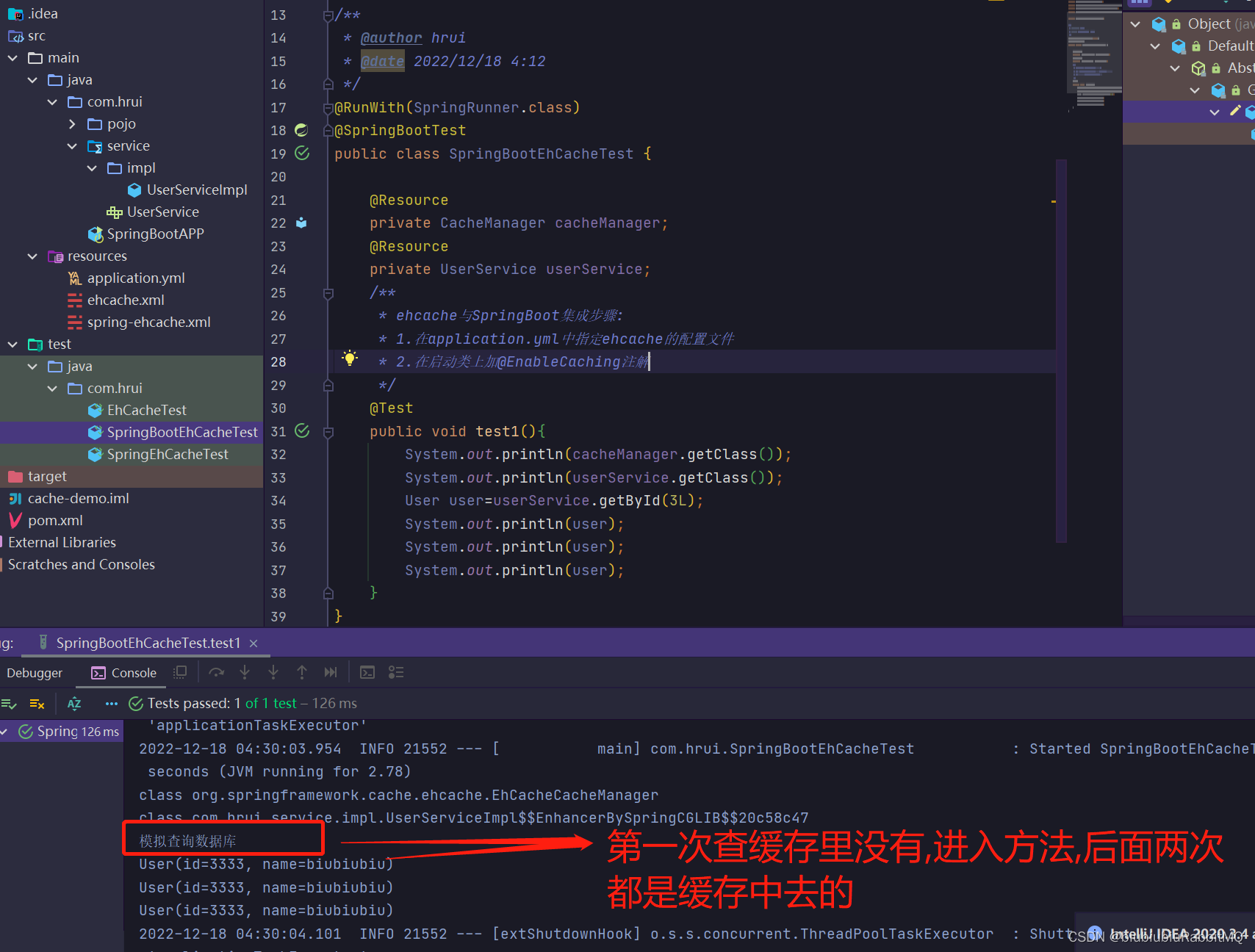
拿到cacheManager目的是为了编程式使用
SpringBoot中简化:注解式使用
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
关于guava的cache
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>29.0-jre</version>
</dependency>
单独使用guava的cache,guava的cache分为两种:
第一种:Cache--实现类是LoadingCache的内部类com.google.common.cache.LocalCache.LocalLoadingCache
特点:缓存中获取不到值得时候,会根据指定得loader进行加载,加载后自动放入缓存
第二种:Cache--实现类com.google.common.cache.LocalCache.LocalManualCache
特点类似ehcache
先来演示第一种:单独使用guava的cache,guava的cache.第一种:Cache--实现类是LoadingCache的内部类com.google.common.cache.LocalCache.LocalLoadingCache
public class GuavaCacheLoadingCacheTest {
/**
* 单独使用guava的cache,guava的cache分为两种:
* 第一种:Cache--实现类是LoadingCache的内部类com.google.common.cache.LocalCache.LocalLoadingCache
* 特点:缓存中获取不到值得时候,会根据指定得loader进行加载,加载后自动放入缓存
*/
@Test
public void test1() throws InterruptedException {
LoadingCache<Long, User> loadingCache= CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
//指定并发级别
.concurrencyLevel(8)
//初始化大小,配合concurrencyLevel做分段锁
.initialCapacity(60)
//最多可以防止多少个元素
.maximumSize(10)
//从写入开始计算,10s过期
.expireAfterWrite(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
//统计命中率
.recordStats()
//缓存中的元素被驱逐出去后会自动回调的到这里
.removalListener(new RemovalListener<Long, User>() {
@Override
public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification<Long, User> removalNotification) {
Long key= removalNotification.getKey();
RemovalCause cause=removalNotification.getCause();
System.out.println("Key:"+key+"被移出缓存,原因:"+cause);
}
})
//缓存中获取不到值得时候,会回调到这里
.build(new CacheLoader<Long, User>() {
//这里的key就是将来LoadingCache.get(key)获取不到而传进来的参数
@Override
public User load(Long key) throws Exception {
//可以在这里进行数据的加载
System.out.println("去存储中加载");
User user=new User(key,"视而不见");
return user;
}
});
for(long i=0;i<20;i++){
//get方法会抛出异常,可以使用getUnchecked()内部try()catch了
//User user=loadingCache.get(i);
User user=loadingCache.getUnchecked(999L);
System.out.println(user);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}
System.out.println(loadingCache.stats().toString());
}
}上面是单独使用gava cache
接下来是Spring/SpringBoot集成guava cache
Spring/SpringBoot集合第三方框架都有以下特点:
1.Spring:xml或者在@Configuration中加入@Bean注入
2.SpringBoot:starter启动依赖集成或者@Configuration中@Bean注入
Spring集成guava cache
无论是ehcache还是guavacache都离不开 一个应用 一个CacheManager管理多个Cache
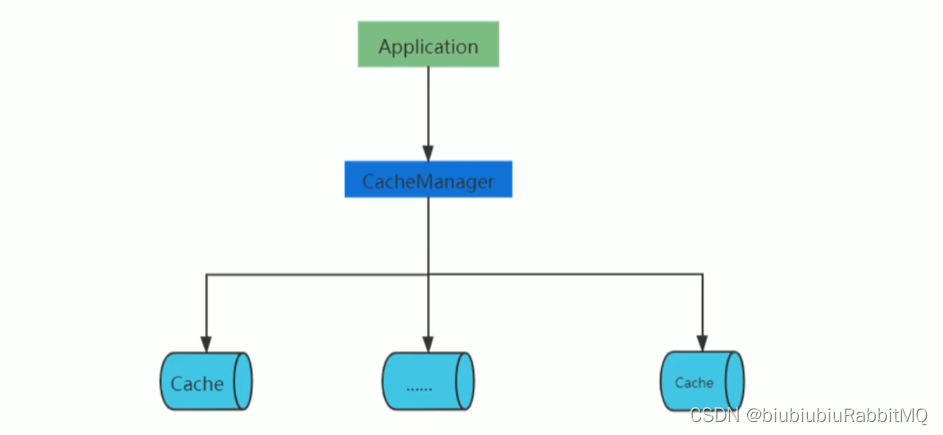
Spring集成guava cache
cacheManager和cache需要自己定义:
/**
* 因为Spring没有guava Cache的实现,这里需要自定义
* @author hrui
* @date 2022/12/19 4:01
*/
public class GuavaCacheCacheManager extends AbstractCacheManager {
/**
* 用来加载当前CacheManager要管理哪些cache
* @return
*/
@Override
protected Collection<? extends Cache> loadCaches() {
/*
获取所有的cache
*/
com.google.common.cache.Cache<Object,Object> userCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(100)
.build();
GuavaCache guavaUserCache = new GuavaCache("user_cache", userCache);
// new GuavaCache("book_cache",bookCache);
Collection<Cache> caches = new LinkedHashSet<>();
caches.add(guavaUserCache);
return caches;
}
}/**
* 仿造ehcache
* 自定义cache的场景:
* 1. GuavaCache
* 2. 多级缓存
*/
public class GuavaCache implements Cache {
private String cacheName;
/**
* 使用组合模式持有真正的cache对象
*/
private com.google.common.cache.Cache<Object,Object> internalCache;
public GuavaCache(String cacheName, com.google.common.cache.Cache<Object,Object> internalCache) {
this.cacheName = cacheName;
this.internalCache = internalCache;
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return cacheName;
}
@Override
public Object getNativeCache() {
return internalCache;
}
@Override
public ValueWrapper get(Object key) {
Object object = internalCache.getIfPresent(key);
if (object != null) {
// 返回ValueWrapper的默认实现
return new SimpleValueWrapper(object);
}
return null;
}
//以下是一些类型转换
@Override
public <T> T get(Object key, Class<T> type) {
throw new RuntimeException("这里不实现了,参考get实现");
}
@Override
public <T> T get(Object key, Callable<T> valueLoader) {
throw new RuntimeException("这里不实现了,参考get实现");
}
@Override
public void put(Object key, Object value) {
internalCache.put(key,value);
}
/**
* 逐出单个
* @param key
*/
@Override
public void evict(Object key) {
// 举个例子:这里如果是多级缓存的话,就需要完成本地缓存和分布式缓存的同步逻辑
// 方法比如通过mq
internalCache.invalidate(key);
}
@Override
public void clear() {
internalCache.invalidateAll();
}
}
Spring的配置文件
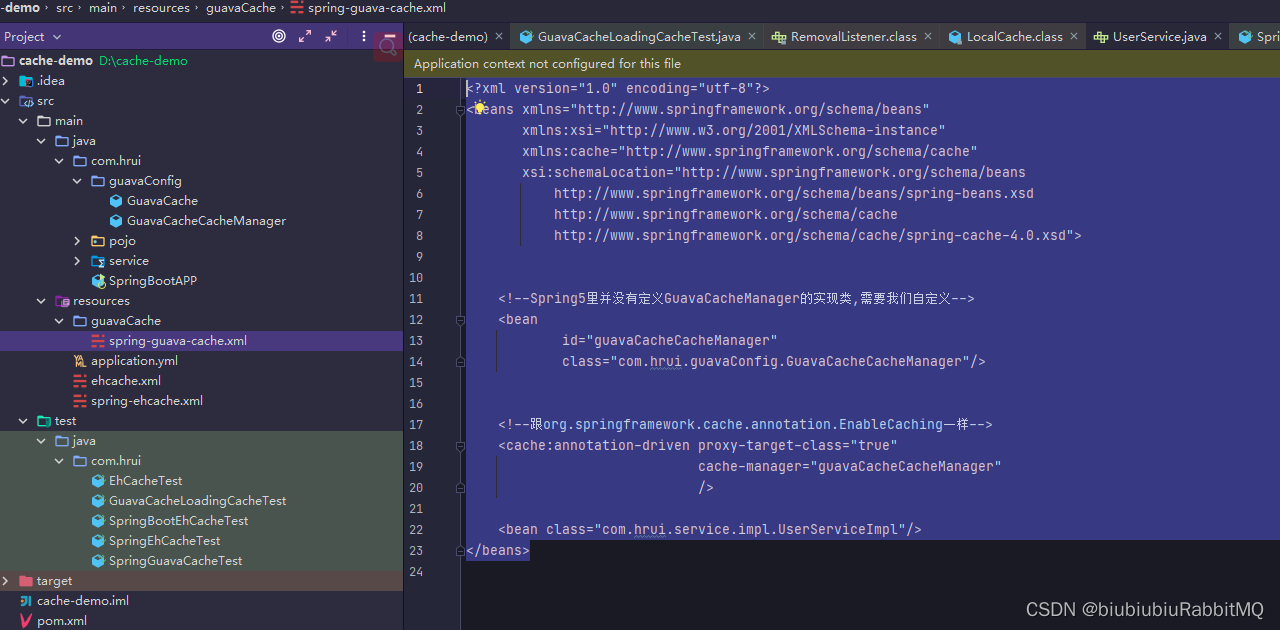
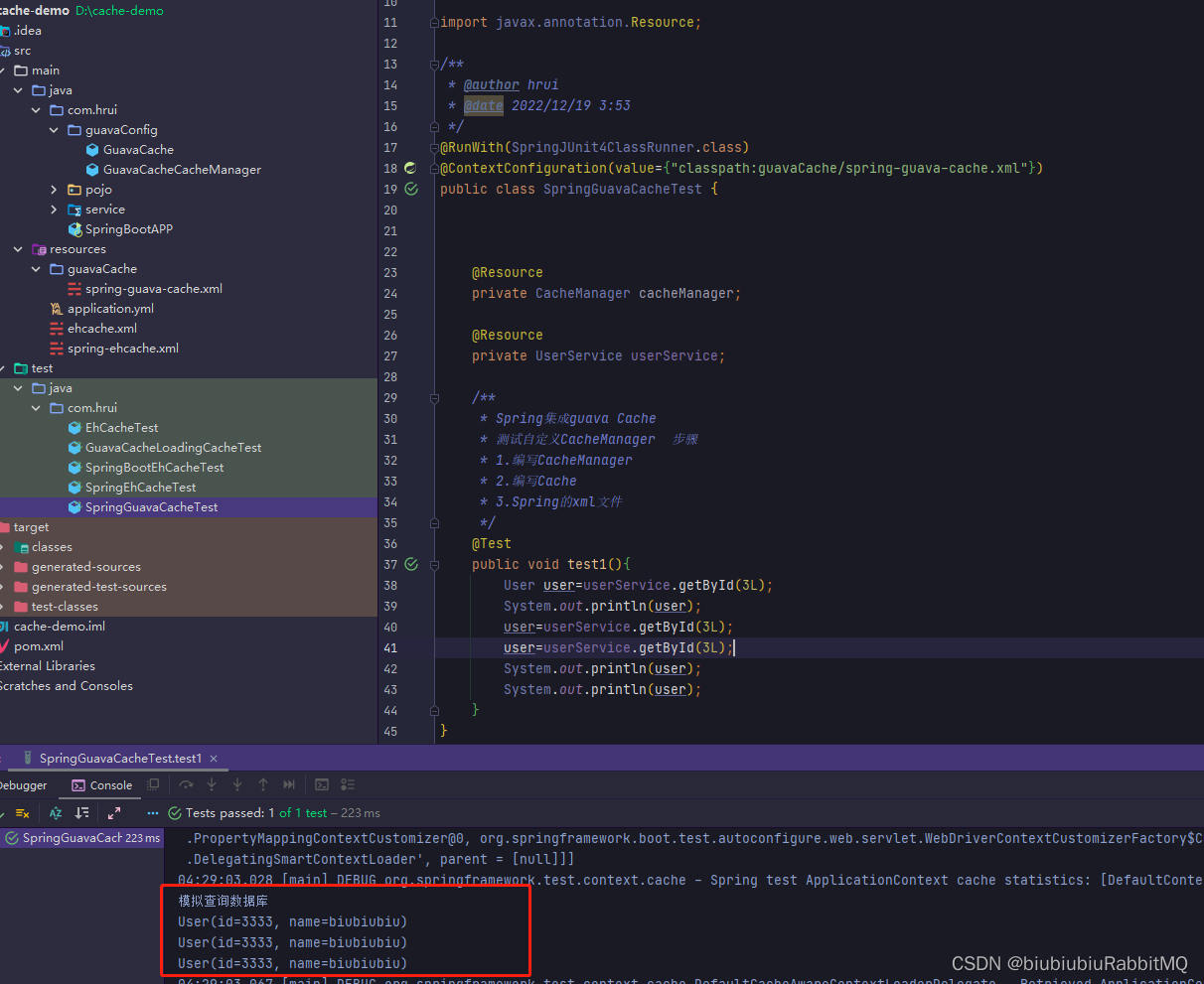
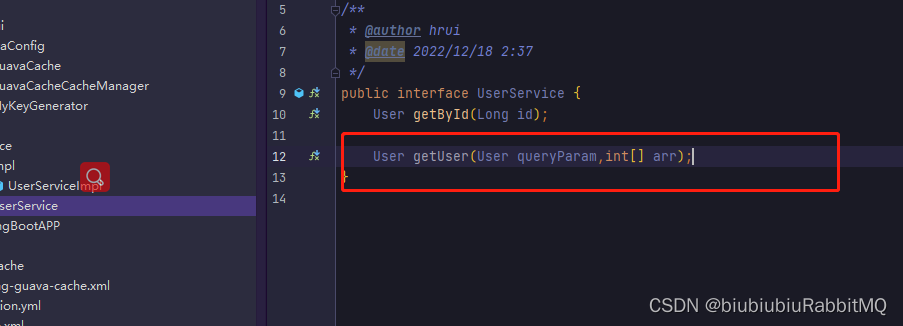
如果现在有这种情况,都是参数比较复杂
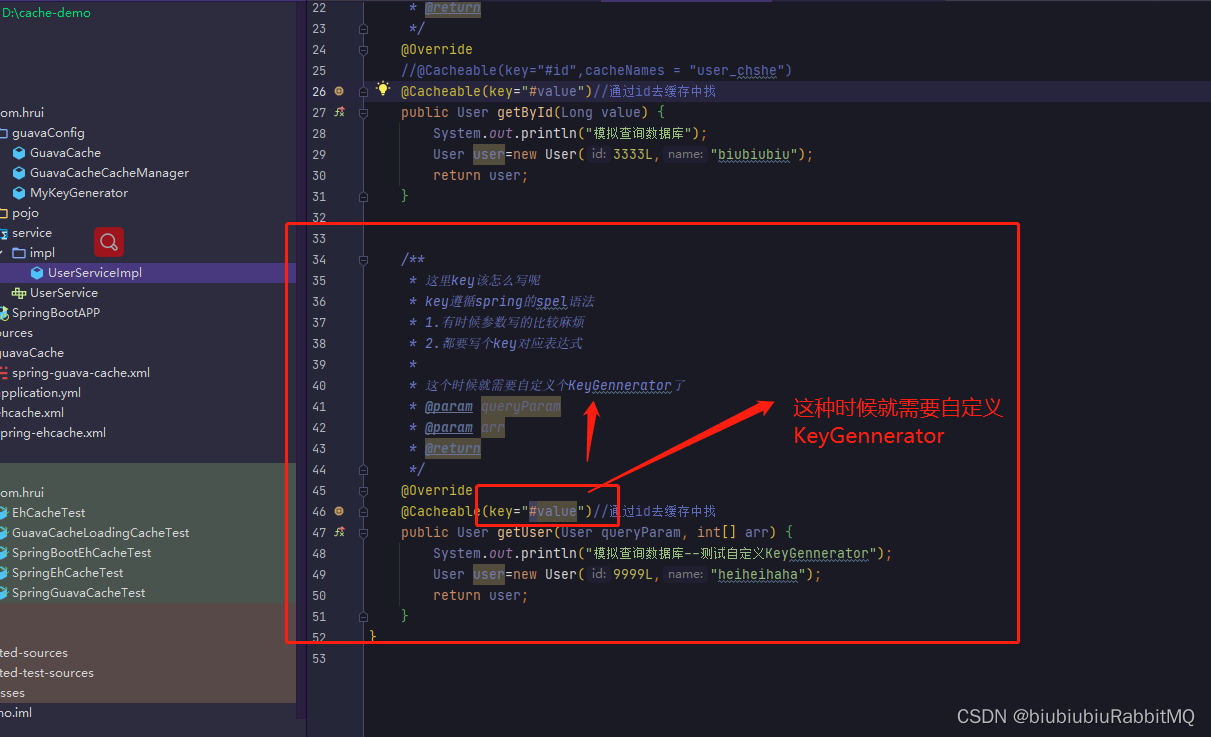
/**
* 缓存的key,spel书写:
* 1.有时候参数写的比较麻烦
* 2.都要写key对应的表达式,可能忘记了
* 3.我写了的话就以写的为准,不写就使用配置的KeyGenerator
*/
public class MyKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {
@Override
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
StringBuilder finalKey = new StringBuilder();
// 方法全限定名
finalKey.append(target.getClass().getName()).append(".")
.append(method.getName()).append(".");
if (params.length == 0) {
return finalKey.append(0).toString();
}
for (Object param : params) {
if (param == null) {
finalKey.append("null");
}else if (ClassUtils.isPrimitiveArray(param.getClass())) {
// 一个参数为 int[] 等八种基本类型组成数组,不包含保证类
int length = Array.getLength(param);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
finalKey.append(Array.get(param,i)).append(",");
}
} else if (ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(param.getClass())
|| param instanceof String) {
// isPrimitiveOrWrapper: true:8中基本类型+void+8种基本类型的包装类型
finalKey.append(param);
} else {
String paramStr = JSON.toJSONString(param);
// 对字符串生成hash
long murmurHash = Hashing.murmur3_128()
.hashString(paramStr, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)
.asLong();
finalKey.append(murmurHash);
}
// 分隔多个参数
finalKey.append("-");
}
System.out.println("最终的key:"+finalKey.toString());
return finalKey.toString();
}
}
规则就是:我写了的话就以写的为准,不写就使用配置的KeyGennerator
测试
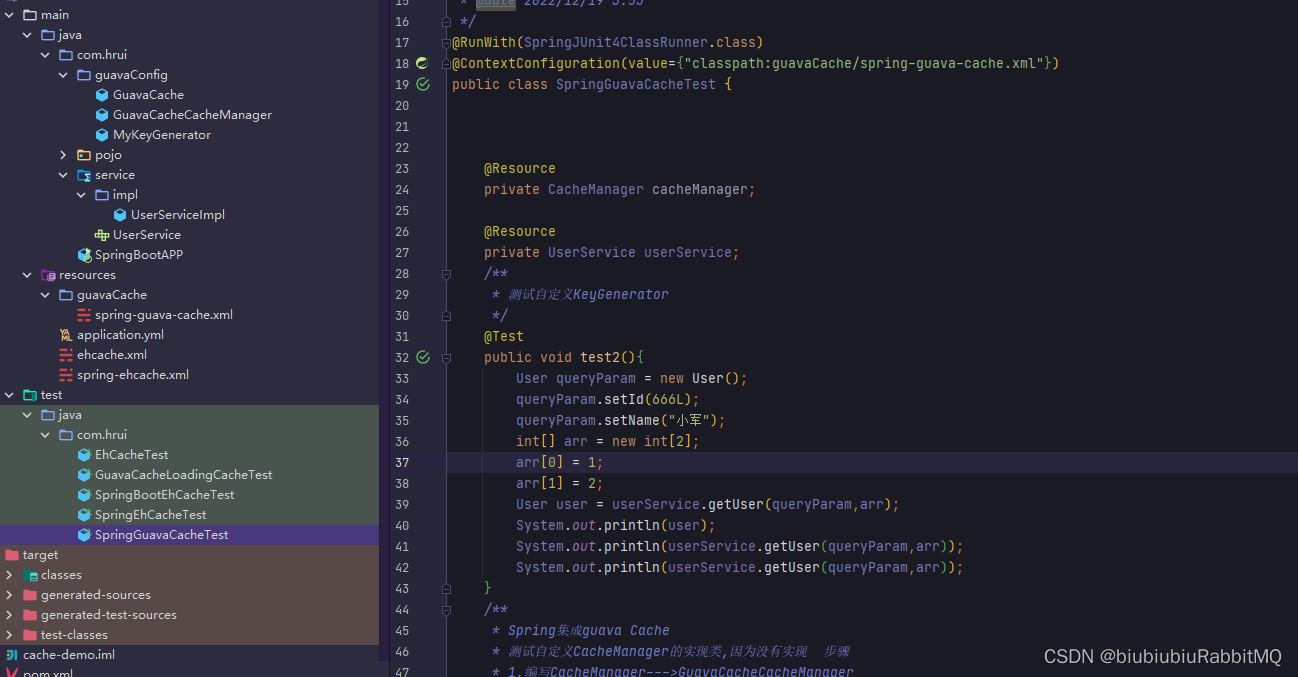
淘汰机制:LRU:最近最少算法 FIFO:先进先出 LFU算法的思想是:如果一个数据在最近一段时间很少被访问到,那么可以认为在将来它被访问的可能性也很小。因此,当空间满时,最小频率访问的数据最先被淘汰。






















 1435
1435

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










