m
e
m
o
[
s
t
a
r
t
]
[
l
e
n
]
=
∑
k
=
1
K
m
e
m
o
[
n
e
x
t
k
]
[
l
e
n
−
1
]
memo[start][len]=\sum_{k=1}^Kmemo[next_k][len-1]
memo[start][len]=k=1∑Kmemo[nextk][len−1]
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N=110;
vector<int> G[N]; //记录图的邻接表
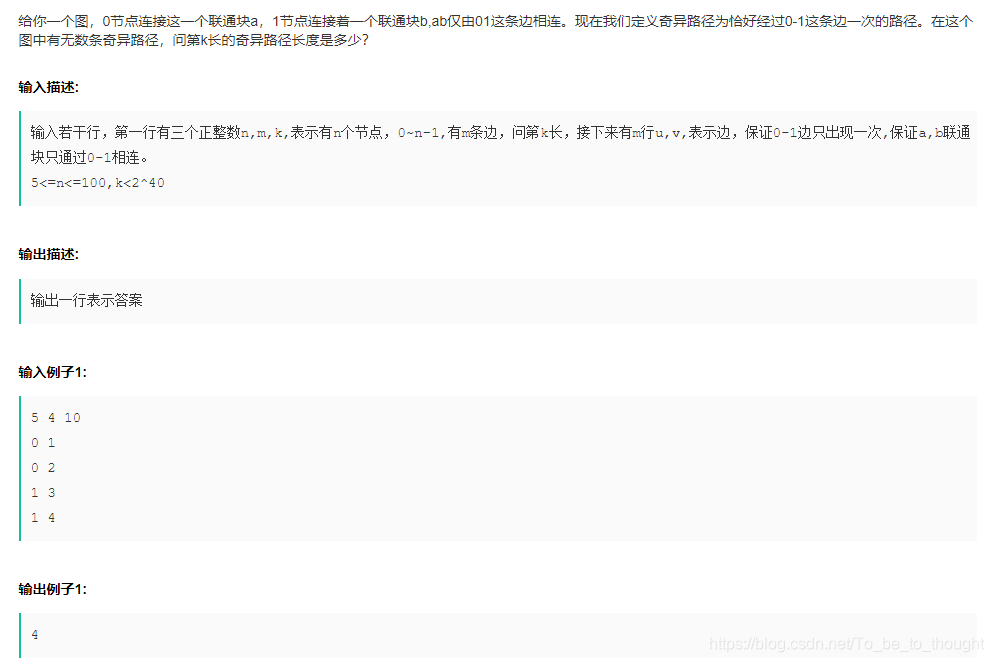
LL memo[N][200]; //memo[stgart][len]表示以start为起点的长度为len的路径数。状态转移方程为
LL getNum(int start,int len){
LL &v=memo[start][len];
if( v!=0)
return v;
if(len==0)
{
v=1;
return 1;
}
LL cur=0;
for(int j:G[start]){
cur+=getNum(j,len-1);
}
v=cur;
return v;
}
int main(){
int n,m;
LL k;
scanf("%d%d%lld\n",&n,&m,&k);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
G[i].clear();
}
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
{
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d\n",&a,&b);
if(a+b==1)
continue;
else{
G[a].push_back(b);
G[b].push_back(a);
}
}
memset(memo,0,sizeof memo);
int ans=0; //长度至少为1
while(k>0){
ans++;
for(int dist=0;dist<=ans-1;dist++){ //从0-ans-1枚举链接0号节点的路径的条数
k-= getNum(0,dist)*getNum(1,ans-1-dist);
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N=6010;
int happy[N];
int heads[N],edges[N],ne[N],idx;
int dp[N][2]; //dp[u][0] 表示所有以u为根的子树选择并且不选择u的方案 dp[u][1]表示所有以u为根的子树选择并且选择u的方案
bool has_father[N];
void add(int start,int end)
{
edges[idx]=end,ne[idx]=heads[start],heads[start]=idx++;
}
void dfs(int node){
dp[node][1]=happy[node]; //
for(int i=heads[node];i!=-1;i=ne[i]){
int j=edges[i];
dfs(j);
dp[node][0]+=max(dp[j][0],dp[j][1]);
dp[node][1]+=dp[j][0];
}
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&happy[i]);
memset(heads,-1,sizeof heads);
for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++){
int son,father;
scanf("%d%d",&son,&father);
add(father,son);
has_father[son]=true;
}
int root=1;
while(has_father[root])
root++;
//cout<<root<<endl;
dfs(root);
cout<<max(dp[root][0], dp[root][1])<<endl;
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N=310;
int grid[N][N];
int dp[N][N];
int dirX[4]={-1,1,0,0},dirY[4]={0,0,-1,1};
int dfs(int x,int y,int R,int C)
{
if(dp[x][y]!=-1)
return dp[x][y];
dp[x][y]=1; //每个块至少为1
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int a=x+dirX[i],b=y+dirY[i];
if(a>=1 && a<=R && b>=1 && b<=C && grid[x][y]>grid[a][b])
dp[x][y]=max(dfs(a,b,R,C)+1,dp[x][y]); //深度优先
}
return dp[x][y];
}
int main(){
int R,C;
scanf("%d%d",&R,&C);
for(int i=1;i<=R;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=C;j++)
scanf("%d",&grid[i][j]);
}
memset(dp,-1,sizeof dp);
int res=1;
for(int i=1;i<=R;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=C;j++){
res=max(res,dfs(i,j,R,C));
}
}
cout<<res<<endl;
return 0;
}
494. Target Sum
算法一:暴力递归
class Solution {
public static int count;
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int S) {
count=0;
recursive(nums,0,0,S);
return count;
}
public static void recursive(int[] nums,int idx,int cur,int target){
if(idx==nums.length)
{
if(cur==target)
count++;
return;
}
recursive(nums,idx+1,cur+nums[idx],target);
recursive(nums,idx+1,cur-nums[idx],target);
}
}
算法二:记忆化搜索
class Solution {
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int S) {
int[][] memo=new int[nums.length][2010];
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++)
Arrays.fill(memo[i],-1);
return recursive(nums,0,0,S,memo);
}
public static int recursive(int[] nums,int idx,int curSum,int target,int[][] memo){
if(idx==nums.length){
if(curSum==target)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
if(memo[idx][curSum+1000]!=-1)
return memo[idx][curSum+1000];
int add=recursive(nums,idx+1,curSum+nums[idx],target,memo);
int subtract=recursive(nums,idx+1,curSum-nums[idx],target,memo);
memo[idx][curSum+1000]=add+subtract;
return memo[idx][curSum+1000];
}
}
游游和小伙伴结伴而行,途径一处园林,游游与小伙伴决定进去游览。该园林可以看作一张个点(每个点代表一个景点)条边的无向图(无重边,无自环)。旅途中,两人的初始愉悦度皆为0 ,第 i个景点需要耗费分钟的时间,会让游游和小伙伴的愉悦度分别增加, 。每条边代表一条路径,第 i 条边连接编号为, 的两个景点,从走到或者从走到耗费的时间都是分钟。游游和小伙伴预计在该园林停留 分钟。检票进入园林后,游游和小伙伴会等概率的随机选择一个景点开始游览,每游览完一个景点后,游游和小伙伴会等概率的随机选择一个可以从当前景点直达的且来得及玩的景点作为下一个目的地。如果游览完一个景点后周围没有可以直达的且来得及游览的景点,游游和小伙伴就会提前结束游玩。 请分别计算出游游和小伙伴在游览结束后愉悦度的期望。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main3 {
static class Expectation {
double e1, e2;
public Expectation() {
this.e1 = 0;
this.e2 = 0;
}
public Expectation(double e1, double e2) {
this.e1 = e1;
this.e2 = e2;
}
public boolean unvisited() {
return this.e1 == 0 && this.e1 == 0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = cin.nextInt();
int m = cin.nextInt();
int k = cin.nextInt();
int[] times = new int[n + 1];
int[] h1 = new int[n + 1];
int[] h2 = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
times[i] = cin.nextInt();
h1[i] = cin.nextInt();
h2[i] = cin.nextInt();
}
int[][] adj = new int[n + 1][n + 1];
int start, end;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
start = cin.nextInt();
end = cin.nextInt();
int t = cin.nextInt();
adj[start][end] = t;
adj[end][start] = t;
}
travel(adj, h1, h2, times, k, n);
}
public static void travel(int[][] adj, int[] h1, int[] h2, int[] times, int leftTime, int n) {
Expectation[][] dp = new Expectation[n + 1][leftTime + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= leftTime; j++)
dp[i][j] = new Expectation();
}
Expectation ans = new Expectation();
Expectation tmp;
for (int start = 1; start <= n; start++) {
//枚举合法起点
if (leftTime < times[start])
continue;
tmp = recursive(start, leftTime - times[start], dp, adj, h1, h2, times, n);
ans.e1 += tmp.e1 / n;
ans.e2 += tmp.e2 / n;
}
String result = String.format("%.5f ", ans.e1) + String.format("%.5f", ans.e2);
System.out.print(result);
}
public static Expectation recursive(int start, int leftTime, Expectation[][] dp, int[][] adj, int[] h1, int[] h2, int[] times, int n) {
if (!dp[start][leftTime].unvisited())
return dp[start][leftTime];
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (adj[start][i] > 0 && leftTime >= adj[start][i] + times[i])
cnt++;
}
Expectation ans = new Expectation(h1[start], h2[start]);
Expectation res;
for (int to = 1; to <= n; to++) {
if (adj[start][to] > 0 && leftTime >= adj[start][to] + times[to]) {
res = recursive(to, leftTime - adj[start][to] - times[to], dp, adj, h1, h2, times, n);
ans.e1 += res.e1 / cnt;
ans.e2 += res.e2 / cnt;
}
}
dp[start][leftTime] = ans;
return ans;
}
}





















 885
885











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








