视频地址 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1sP4y1o7kB
约定
因为不同类型的SQL执行其实是有些不一样的,这里就以最简单的一个类型为例讲解
public interface TestMapper {
String funOne(@Param("userId") String userId,@Param("status") Integer status);
}
<select id="funOne" resultType="java.lang.String">
SELECT user_id
FROM xdx_test_one
WHERE user_id = ${userId}
<if test="status != null and status == 0">
AND 1 = 1
</if>
LIMIT 1
</select>
注:这里是讲解MyBatis执行的逻辑的一个基础版本,虽说如此,但东西已经很多了,可以先理解个大概,然后再逐步去细化理解,比如
- xml具体是如何解析的
- 事务是如何执行的
- 缓存是如何处理的
- 怎么创建自定义插件、插件在何时执行
- …
一、自动注入(基本配置完成)
现在我们几乎都是在 SpringBoot 里面去使用的,我们会引入 mybatis-spring-boot-starter
几乎任何的 starter 都会有一个自从注入的类,我们找到这个类,看看它默认的时候做了些什么
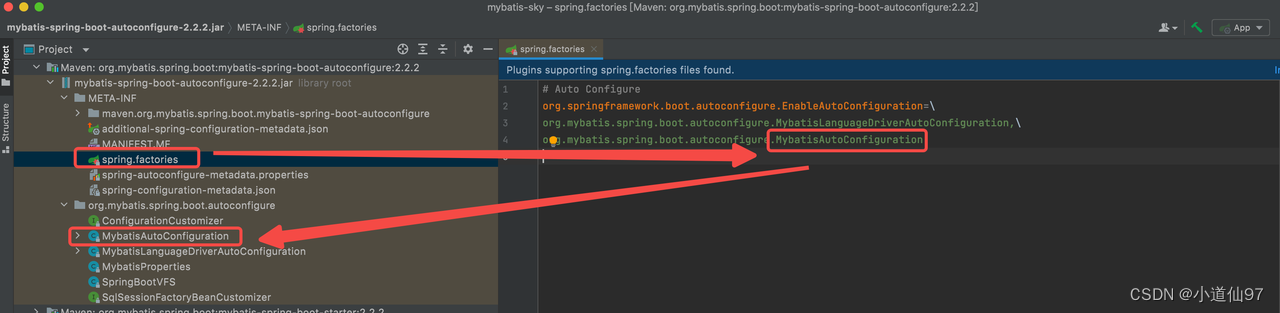
1-1、MybatisAutoConfiguration
删除了里面的逻辑代码,里面会注入2个bean
- SqlSessionFactory
- SqlSessionTemplate
@org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ SqlSessionFactory.class, SqlSessionFactoryBean.class })
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(DataSource.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MybatisProperties.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class, MybatisLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration.class })
public class MybatisAutoConfiguration implements InitializingBean {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
// ...
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
// ...
}
}
1-2、SqlSessionFactory
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
// 创建一个 SqlSessionFactoryBean
SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
// 赋值数据源
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
factory.setVfs(SpringBootVFS.class);
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) {
factory.setConfigLocation(this.resourceLoader.getResource(this.properties.getConfigLocation()));
}
// 申请 Configuration
applyConfiguration(factory);
// 设置 mybatis 外部配置文件
// this.properties 就是我们的mybatis配置文件了
if (this.properties.getConfigurationProperties() != null) {
factory.setConfigurationProperties(this.properties.getConfigurationProperties());
}
// 设置mybatis 插件(其实就是拦截器)
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.interceptors)) {
factory.setPlugins(this.interceptors);
}
// 设置databaseId
if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {
factory.setDatabaseIdProvider(this.databaseIdProvider);
}
// 设置实体包别名
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage())) {
factory.setTypeAliasesPackage(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage());
}
// 设置包别名类型
if (this.properties.getTypeAliasesSuperType() != null) {
factory.setTypeAliasesSuperType(this.properties.getTypeAliasesSuperType());
}
// 设置类型处理器的包
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage())) {
factory.setTypeHandlersPackage(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage());
}
// 设置类型处理器
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) {
factory.setTypeHandlers(this.typeHandlers);
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations())) {
factory.setMapperLocations(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations());
}
Set<String> factoryPropertyNames = Stream
.of(new BeanWrapperImpl(SqlSessionFactoryBean.class).getPropertyDescriptors()).map(PropertyDescriptor::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
Class<? extends LanguageDriver> defaultLanguageDriver = this.properties.getDefaultScriptingLanguageDriver();
if (factoryPropertyNames.contains("scriptingLanguageDrivers") && !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.languageDrivers)) {
// Need to mybatis-spring 2.0.2+
factory.setScriptingLanguageDrivers(this.languageDrivers);
if (defaultLanguageDriver == null && this.languageDrivers.length == 1) {
defaultLanguageDriver = this.languageDrivers[0].getClass();
}
}
if (factoryPropertyNames.contains("defaultScriptingLanguageDriver")) {
// Need to mybatis-spring 2.0.2+
factory.setDefaultScriptingLanguageDriver(defaultLanguageDriver);
}
applySqlSessionFactoryBeanCustomizers(factory);
// 返回当前的 SqlSessionFactory
return factory.getObject();
}
1-3、applyConfiguration
通过配置文件生成 configuration
private void applyConfiguration(SqlSessionFactoryBean factory) {
Configuration configuration = this.properties.getConfiguration();
if (configuration == null && !StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) {
configuration = new Configuration();
}
if (configuration != null && !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.configurationCustomizers)) {
for (ConfigurationCustomizer customizer : this.configurationCustomizers) {
customizer.customize(configuration);
}
}
factory.setConfiguration(configuration);
}
1-4、SqlSessionTemplate
在创建 SqlSessionTemplate 的时候,会判断当前的ExecutorType 类型,可以在配置文件里面配置,但一般我们都是不用配置的,也就是走下面的 else 会有一个默认的执行类型,默认是 SIMPLE
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
ExecutorType executorType = this.properties.getExecutorType();
if (executorType != null) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory, executorType);
} else {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
this(sqlSessionFactory, sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getDefaultExecutorType());
}
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
一路点进去最后的实现方法如下 ( 注意这个的 SqlSessionTemplate 也是基于代理生成的,生成的时候加了一个 拦截器 SqlSessionInterceptor )
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");
notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.executorType = executorType;
this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class }, new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
1-5、MappedStatement
在xml里面的每一个 select、insert、update、delete 都会解析成为一个MappedStatement
我们看来一下,我们上面这个 select 会被解析成什么样的 MappedStatement
![[图片]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/262aaa4efc13481ab6abcbbc72e4fbd9.png)
下面我们来看一下这个 MappedStatement 是何时注入进去的(具体如何注入的就不细说了,涉及到xml的解析还是很复杂的,可以自己去细看)
上面我们不是创建了一个 SqlSessionFactoryBean 它实现了 InitializingBean 接口,并且重写了里面的afterPropertiesSet方法,也就是在bean初始化之后会去执行这个方法
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
final Configuration targetConfiguration;
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
// 配置 configuration
if (this.configuration != null) {
targetConfiguration = this.configuration;
if (targetConfiguration.getVariables() == null) {
targetConfiguration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties);
} else if (this.configurationProperties != null) {
targetConfiguration.getVariables().putAll(this.configurationProperties);
}
} else if (this.configLocation != null) {
xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), null, this.configurationProperties);
targetConfiguration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();
} else {
LOGGER.debug(
() -> "Property 'configuration' or 'configLocation' not specified, using default MyBatis Configuration");
targetConfiguration = new Configuration();
Optional.ofNullable(this.configurationProperties).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVariables);
}
// 参数校验
Optional.ofNullable(this.objectFactory).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setObjectFactory);
Optional.ofNullable(this.objectWrapperFactory).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setObjectWrapperFactory);
Optional.ofNullable(this.vfs).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVfsImpl);
// 加载包别名
if (hasLength(this.typeAliasesPackage)) {
scanClasses(this.typeAliasesPackage, this.typeAliasesSuperType).stream()
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isAnonymousClass()).filter(clazz -> !clazz.isInterface())
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isMemberClass()).forEach(targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry()::registerAlias);
}
// 加载类型别名
if (!isEmpty(this.typeAliases)) {
Stream.of(this.typeAliases).forEach(typeAlias -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAlias(typeAlias);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered type alias: '" + typeAlias + "'");
});
}
// 添加插件(拦截器)
if (!isEmpty(this.plugins)) {
Stream.of(this.plugins).forEach(plugin -> {
targetConfiguration.addInterceptor(plugin);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered plugin: '" + plugin + "'");
});
}
// 配置类型处理器包
if (hasLength(this.typeHandlersPackage)) {
scanClasses(this.typeHandlersPackage, TypeHandler.class).stream().filter(clazz -> !clazz.isAnonymousClass())
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isInterface()).filter(clazz -> !Modifier.isAbstract(clazz.getModifiers()))
.forEach(targetConfiguration.getTypeHandlerRegistry()::register);
}
// 配置类型处理器
if (!isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) {
Stream.of(this.typeHandlers).forEach(typeHandler -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(typeHandler);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered type handler: '" + typeHandler + "'");
});
}
// 设置默认枚举处理器
targetConfiguration.setDefaultEnumTypeHandler(defaultEnumTypeHandler);
if (!isEmpty(this.scriptingLanguageDrivers)) {
Stream.of(this.scriptingLanguageDrivers).forEach(languageDriver -> {
targetConfiguration.getLanguageRegistry().register(languageDriver);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered scripting language driver: '" + languageDriver + "'");
});
}
Optional.ofNullable(this.defaultScriptingLanguageDriver)
.ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setDefaultScriptingLanguage);
if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {// fix #64 set databaseId before parse mapper xmls
try {
targetConfiguration.setDatabaseId(this.databaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId(this.dataSource));
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed getting a databaseId", e);
}
}
Optional.ofNullable(this.cache).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::addCache);
if (xmlConfigBuilder != null) {
try {
xmlConfigBuilder.parse();
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed configuration file: '" + this.configLocation + "'");
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse config resource: " + this.configLocation, ex);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
targetConfiguration.setEnvironment(new Environment(this.environment,
this.transactionFactory == null ? new SpringManagedTransactionFactory() : this.transactionFactory,
this.dataSource));
// 判断当前xml不为空
if (this.mapperLocations != null) {
if (this.mapperLocations.length == 0) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was specified but matching resources are not found.");
} else {
// 循环每一个xml资源
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
continue;
}
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
targetConfiguration, mapperLocation.toString(), targetConfiguration.getSqlFragments());
// 处理xml资源,也是在这里进去创建添加 MappedStatement 的
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
}
}
} else {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified.");
}
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(targetConfiguration);
}
parse
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 下一步
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
configurationElement
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.isEmpty()) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
// 下一步
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
buildStatementFromContext
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list) {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
buildStatementFromContext(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
buildStatementFromContext(list, null);
}
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
// 下一步
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
parseStatementNode
public void parseStatementNode() {
// ...
// 创建MappedStatement 并加入到 configuration
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
二、mapper代理怎么注册到bean容器
2-1、入口 @MapperScan
我们在使用Mybatis的时候都会加上一个 @MapperScan ,这个注解上面加了一个注解 @Import(MapperScannerRegistrar.class)
2-2、MapperScannerRegistrar
public class MapperScannerRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, ResourceLoaderAware
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 接口里面有一个方法 registerBeanDefinitions,通过这个方法会把bean 注册到 BeanDefinitionRegistry 里面
BeanDefinitionRegistry 其实就是spring的bean容器,默认实现是 DefaultListableBeanFactory,所有的bean都以key-value的形式存入 currentHashMap
我们来看看MapperScannerRegistrar 重写的 registerBeanDefinitions方法
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 获取 MapperScan 注解的参数值
AnnotationAttributes mapperScanAttrs = AnnotationAttributes
.fromMap(importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(MapperScan.class.getName()));
if (mapperScanAttrs != null) {
registerBeanDefinitions(importingClassMetadata, mapperScanAttrs, registry,
generateBaseBeanName(importingClassMetadata, 0));
}
}
void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata annoMeta, AnnotationAttributes annoAttrs,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, String beanName) {
// 构建一个 MapperScannerConfigurer 类型的 BeanDefinition
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(MapperScannerConfigurer.class);
builder.addPropertyValue("processPropertyPlaceHolders", true);
// 设置 MapperScannerConfigurer 类的参数值, addPropertyValue 可以简单理解成class的set方法
Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass = annoAttrs.getClass("annotationClass");
if (!Annotation.class.equals(annotationClass)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("annotationClass", annotationClass);
}
// 下面都是类似的判断并赋值,这里简化一下,只保留赋值过程,方便阅读,后续大家可以去参看源码
builder.addPropertyValue("markerInterface", markerInterface);
builder.addPropertyValue("nameGenerator", BeanUtils.instantiateClass(generatorClass));
builder.addPropertyValue("mapperFactoryBeanClass", mapperFactoryBeanClass);
builder.addPropertyValue("sqlSessionTemplateBeanName", annoAttrs.getString("sqlSessionTemplateRef"));
builder.addPropertyValue("sqlSessionFactoryBeanName", annoAttrs.getString("sqlSessionFactoryRef"));
builder.addPropertyValue("lazyInitialization", lazyInitialization);
builder.addPropertyValue("defaultScope", defaultScope);
builder.addPropertyValue("basePackage", StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(basePackages));
builder.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
// 注册到bean容器里面去
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, builder.getBeanDefinition());
}
2-3、MapperScannerConfigurer
上面我们往 BeanDefinitionRegistry 里面注册了一个MapperScannerConfigurer 现在我们就来看看这个类
public class MapperScannerConfigurer implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware
它实现了一个 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口,里面有一个方法 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 这个方法可以对注册到 BeanDefinitionRegistry 里面的 BeanDefinition 进行进一步的处理
MapperScannerConfigurer 重写的 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法如下
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) {
processPropertyPlaceHolders();
}
// 创建一个 ClassPathMapperScanner 对象并对里面的数据赋值
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig);
scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass);
scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName);
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator);
scanner.setMapperFactoryBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);
if (StringUtils.hasText(lazyInitialization)) {
scanner.setLazyInitialization(Boolean.valueOf(lazyInitialization));
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(defaultScope)) {
scanner.setDefaultScope(defaultScope);
}
// 对scanner 一些数据进行过滤
scanner.registerFilters();
scanner.scan(
StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
}
2-4、ClassPathMapperScanner
public class ClassPathMapperScanner extends ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 通过包路径把下面的 beanDefinition 注册到 BeanDefinitionRegistry 里面
上一步调用了 scanner.scan() 方法,子类没有,调用父类的,代码如下
public int scan(String... basePackages) {
int beanCountAtScanStart = this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount();
doScan(basePackages);
// Register annotation config processors, if necessary.
if (this.includeAnnotationConfig) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
return (this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() - beanCountAtScanStart);
}
子类重写了 doScan 方法,我们来看下子类的方法
@Override
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
// 调用父类的 doScan 方法,把包下的beanDefinition 注入
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> "No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages)
+ "' package. Please check your configuration.");
} else {
// 对 beanDefinition 进行进一步完善
processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
父类的doScan 方法,返回全部的 beanDefinition
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder =
AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
processBeanDefinitions
private void processBeanDefinitions(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions) {
AbstractBeanDefinition definition;
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = getRegistry();
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) {
definition = (AbstractBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition();
// ...
// 设置 bean的类型,这里设置为 MapperFactoryBean 后面会用代理生成 MapperFactoryBean
definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);
// ...
}
}
2-5、MapperFactoryBean
public class MapperFactoryBean extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean
FactoryBean 它是一个工程bean,里面有一个 getObject 方法,调用它返回真正的 bean
MapperFactoryBean重写的 getObject 方法
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
// 这里的getSqlSeesion 实际上是 sqlSessionTemplate,在上面的自动注入的时候注入的
public SqlSession getSqlSession() {
return this.sqlSessionTemplate;
}
一路点进去的,最终实现如下,生成了一个代理对象
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
三、mapper代理怎么执行
通过上面的流程,我们知道写的接口最终都会生成 MapperProxy 代理 ,既然是代理真正执行的肯定是 invoke 方法
2-1、MapperProxy的invoke
简化后代码,主要分三步
- 创建 MapperMethod
- 基于MapperMethod 创建 PlainMethodInvoker
- 调用 PlainMethodInvoker 的 invoke 方法
MapperProxy的invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
return MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(methodCache, method, m -> {
if (m.isDefault()) {
// ...
} else {
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}
MapperMethod 的构造方法
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
PlainMethodInvoker 是MapperProxy的 私有静态内部类
interface MapperMethodInvoker {
Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable;
}
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;
public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {
super();
this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
通过上面的代理构建我们知道,现在的sqlSession实际上是 SqlSessionTemplate ,在这个模板里面有一个拦截器,执行之前,我们需要先执行这个拦截在自动注入 SqlSessionTemplate 的时候说了这个拦截器
org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate.SqlSessionInterceptor
// 简化后代码
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType, SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
}
里面有一步是 getSqlSession 这个,这里面会进行事务处理和创建所需的 Executor (这里我们创建的是SimpleExecutor)
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
// ...
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType) {
return openSessionFromDataSource(execType, null, false);
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
2-2、mapperMethod.execute
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
// 定义返回值
Object result;
// 判断当前执行的类型
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
// 根据返回值的类型不同,去执行对应的方法
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// 构建入参
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 下一步去执行,并返回结果
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
2-3、入参构造
public Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) {
return paramNameResolver.getNamedParams(args);
}
// 其实就是以 names 里面的数据为key,args 里面的数据为 values,构造一个 map 返回
private final SortedMap<Integer, String> names;
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {
final int paramCount = names.size();
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
return null;
} else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {
Object value = args[names.firstKey()];
return wrapToMapIfCollection(value, useActualParamName ? names.get(0) : null);
} else {
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<>();
int i = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);
// add generic param names (param1, param2, ...)
final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + (i + 1);
// ensure not to overwrite parameter named with @Param
if (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
}
i++;
}
return param;
}
}
我们来看一下这个 names 是怎么来的
- names 是ParamNameResolver 类里面的一个参数
- ParamNameResolver 是MethodSignature类里面的一个参数
- MethodSignature 是MapperMethod 里面的私有静态内部类
现在我们回到刚刚创建 MapperMethod 的时候,MapperMethod的构造方法在上面
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
public MethodSignature(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
// ....
this.paramNameResolver = new ParamNameResolver(configuration, method);
}
ParamNameResolver 构造方法,获取接口的参数存放在 names 里面
- 如果参数有 @Param 注解,就直接用注解里面的名字
- 如果没有注解,就判断 useActualParamName 配置是否等于 ture (默认就是ture),是的话就用字段的名字
- 如果上述都不满足,就用 0、1、2 …
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {
this.useActualParamName = config.isUseActualParamName();
final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;
// get names from @Param annotations
for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {
if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {
// skip special parameters
continue;
}
String name = null;
for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {
if (annotation instanceof Param) {
hasParamAnnotation = true;
name = ((Param) annotation).value();
break;
}
}
if (name == null) {
// @Param was not specified.
if (useActualParamName) {
name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex);
}
if (name == null) {
// use the parameter index as the name ("0", "1", ...)
// gcode issue #71
name = String.valueOf(map.size());
}
}
map.put(paramIndex, name);
}
names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map);
}
2-4、sqlSession.selectOne
通过上面的代理构建我们知道,现在的sqlSession实际上是 SqlSessionTemplate
SqlSessionTemplate 的 selectOne 方法
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.sqlSessionProxy.selectOne(statement, parameter);
}
当前代理只有一个默认实现类 DefaultSqlSession
DefaultSqlSession 的 selectOne 方法
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
2-5、MappedStatement
通过上面的 selectList 方法我们一路点,最后来到这个方法,也是 DefaultSqlSession 里面的,下面就是通过 configuration 获取MappedStatement,然后调用 MappedStatement 的query方法
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
configuration.getMappedStatement
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements
public MappedStatement getMappedStatement(String id) {
return this.getMappedStatement(id, true);
}
public MappedStatement getMappedStatement(String id, boolean validateIncompleteStatements) {
if (validateIncompleteStatements) {
buildAllStatements();
}
return mappedStatements.get(id);
}
configuration 里面的 MappedStatement 是在项目启动的时候构建 SqlSessionFactoryBean 的时候初始化的,上面也讲到了
org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean#getObject
@Override
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
// 这个方法会初始化mappedStatements
afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}
2-6、executor.query
通过上面的内容,我们知道当前的这个 excutor 其实是 SimpleExecutor 我们看一下这个 Excutor 的继承关系
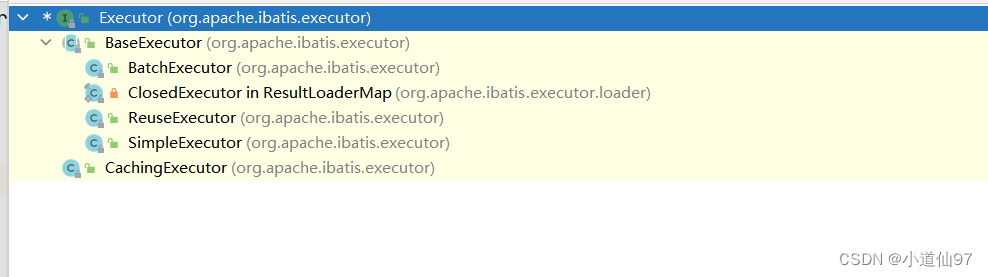
SimpleExcutor 里面没有 query方法,所以执行父类 BaseExcutor 的query方法
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
2-7、ms.getBoundSql(parameter)
这一步就是对动态SQL进行拼接,解析xml里面的那些个动态标签
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// ...
return boundSql;
}
sqlSource 有四个实现类,我们这个sql属于动态sql,所以就是 DynamicSqlSource
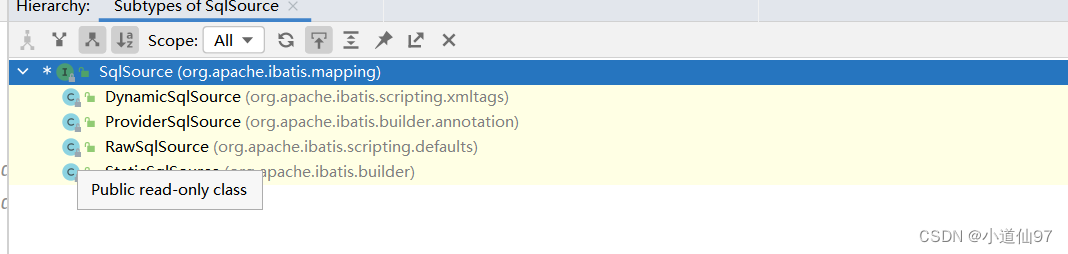
public class DynamicSqlSource implements SqlSource {
private final Configuration configuration;
private final SqlNode rootSqlNode;
public DynamicSqlSource(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.rootSqlNode = rootSqlNode;
}
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
context.getBindings().forEach(boundSql::setAdditionalParameter);
return boundSql;
}
}
这里我们暂时只先关注动态SQL解析的过程,sqlNode 属于解析xml的产物,其实它的实现类就对应动态sql标签的解析了
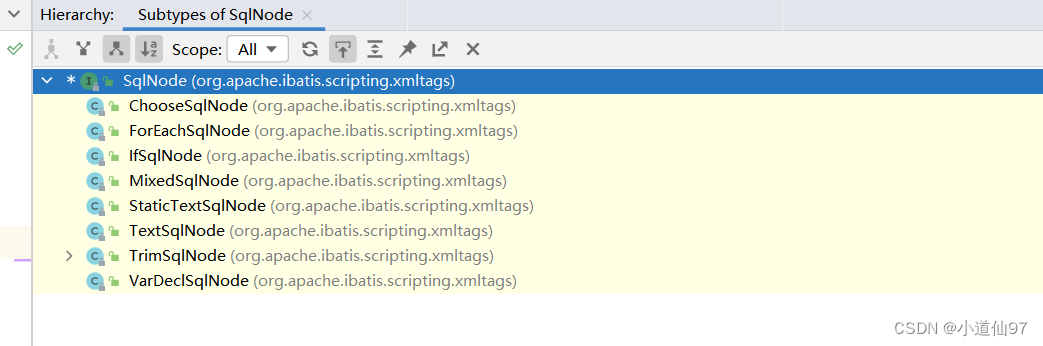
我们这里是当然就是混合类型了,所以看 MixedSqlNode
这个混合类型也很简单,就是依次循环去执行每一种标签
public class MixedSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final List<SqlNode> contents;
public MixedSqlNode(List<SqlNode> contents) {
this.contents = contents;
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
contents.forEach(node -> node.apply(context));
return true;
}
}
我们来打断点看看我们的 if 解析过程
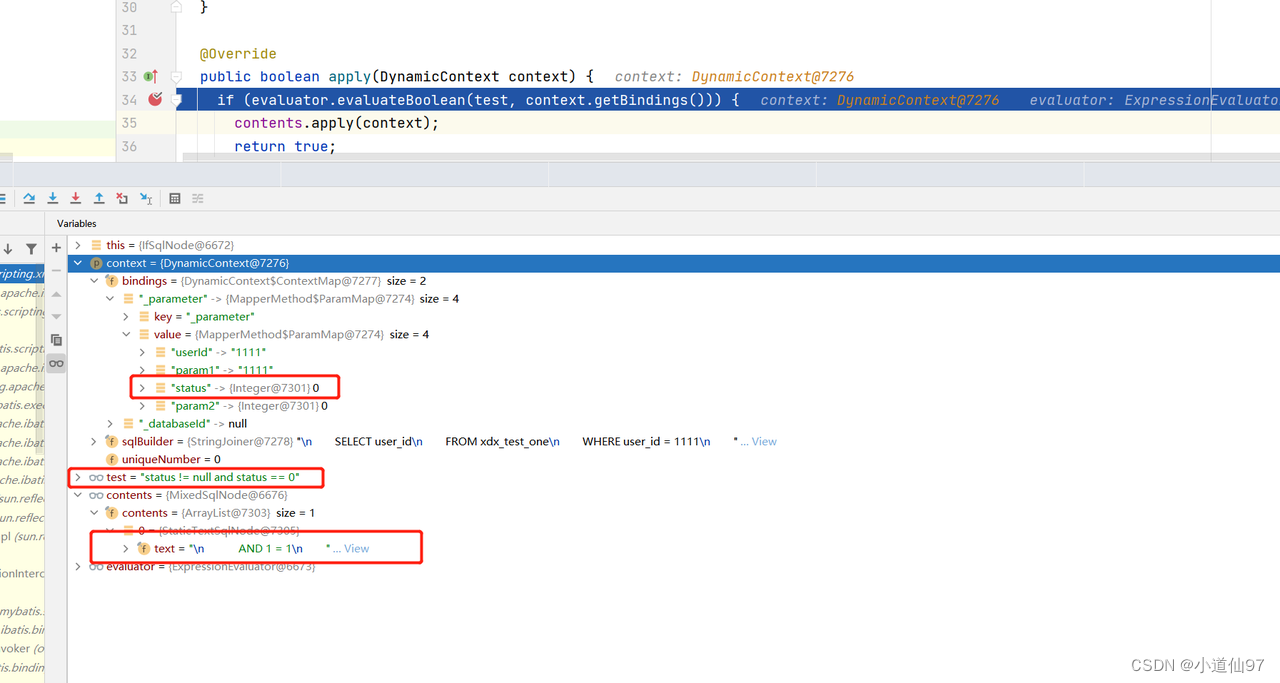
2-8、TextSqlNode
![[图片]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/492a422e2d5a49d49ef4eaac59c3aab4.png)
我们这个SQL被解析了成了三个sqlNode,下面我们来主要看看 TextSqlNode, 我们有一道面试题 # 和 $ 的区别 $就是在这里解析的,我们来看看为何它不能防止sql注入
apply
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
GenericTokenParser parser = createParser(new BindingTokenParser(context, injectionFilter));
context.appendSql(parser.parse(text));
return true;
}
private GenericTokenParser createParser(TokenHandler handler) {
return new GenericTokenParser("${", "}", handler);
}
GenericTokenParser
这个类可以理解成一个正则处理器,根据提供的 openToken、closeToken、handler 进行处理,如果匹配上了前后Token 就调用 handler处理
通过代码我们可以看到当使用 ${} 的时候,是基于字符串拼接的,所以不能防止sql注入
public class GenericTokenParser {
private final String openToken;
private final String closeToken;
private final TokenHandler handler;
public GenericTokenParser(String openToken, String closeToken, TokenHandler handler) {
this.openToken = openToken;
this.closeToken = closeToken;
this.handler = handler;
}
public String parse(String text) {
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// search open token
int start = text.indexOf(openToken);
do {
// ...
// 如果匹配到 就调用 handler 获取返回值 append 进去
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
// ...
} while (start > -1);
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
}
}
org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.TextSqlNode.BindingTokenParser#handleToken
其实就是根据参数名(content 就是参数名)获取到对应的参数数据,校验后返回
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
Object parameter = context.getBindings().get("_parameter");
if (parameter == null) {
context.getBindings().put("value", null);
} else if (SimpleTypeRegistry.isSimpleType(parameter.getClass())) {
context.getBindings().put("value", parameter);
}
Object value = OgnlCache.getValue(content, context.getBindings());
String srtValue = value == null ? "" : String.valueOf(value); // issue #274 return "" instead of "null"
checkInjection(srtValue);
return srtValue;
}
2-9、query
分析完动态SQL解析,我们继续回到刚刚的query,复制一下
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 这个 CacheKey 里面存了一个集合,把各种参数复制存入,尽可能地形成一个唯一地缓存key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
// ...
// 从缓存中获取数据
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 执行查询逻辑
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
// ...
return list;
}
queryFromDatabase
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
// 先把缓存占位
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 执行具体的方法
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
// 删除缓存占位
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 缓存新结果
localCache.putObject(key, list);
// 如果是 CALLABLE 类型,增加一个缓存
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
2-10、doQuery
上面我们知道 当前的excutor 是 simpleExcutor 所以我们直接去里面看看
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 获取配置
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 获取处理器
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 设置参数
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行查询
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
2-11、newStatementHandler
- 根据不同的类型,创建对应的处理器
- 把处理器加入到 拦截插件里面去
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}
2-12、prepareStatement
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 获取连接
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 设置事务超时时间
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 设置查询参数
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
StatementHandler 的实现类
![[图片]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/dd99be5d0250435ba92e766f5819d572.png)
我们这个当然是 PreparedStatementHandler
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
// ...
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
// ...
}
}
}
@Override
public void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
// ...
setNonNullParameter(ps, i, parameter, jdbcType);
// ...
}
![[图片]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a679237f804e4333a6b0d51acbc7ed1c.png)
我们以 Integer 类型的参数为例,看看实现类
底层是调用 PreparedStatement 的 setXxx 方法
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, Integer parameter, JdbcType jdbcType)
throws SQLException {
ps.setInt(i, parameter);
}
2-13、 handler.query
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}























 8372
8372











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








