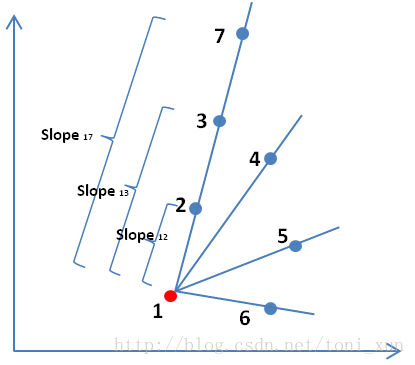
As we know, for three arbitrary points, A, B and C, if the slope of the line<A, B> equals to the slope of line<A, C>, we can confirm that these three points are on a same line. Further, if line<A, B>, line<A, C> ... line<A, X> all have the same slope, point A, B, C ... X are on a same line, too.
(The picture is from Yu's Coding Garden)
So, we can loop through the array of points, and determine the max points on a same line.
However, we should note that we shouldn't use a double variate to represent the slopes. Slope is a double variate values from 0 to infinity, and may contains tiny error that cause unspecified behavior in our program. For example, ">>> 0.6 - 0.65 == -0.05" leads to a "False" in my Python interpreter.
The solution is simple, too. Because the points in the array are all given as pairs of integers, the slope can be represented as a pair of integer(x, y) that slope equals x / y. Then, we reduce x / y to irreducible fraction, and if x or y equals zero, the pair is <0, 1> or <1, 0>.
There is my C++ solution.
/**
* Definition for a point.
* struct Point {
* int x;
* int y;
* Point() : x(0), y(0) {}
* Point(int a, int b) : x(a), y(b) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxPoints(vector<Point> &points) {
int ans = 0;
for (auto iter = points.begin();
iter != points.end();
++iter) {
ans = max(ans, calc(points, *iter));
}
return ans;
}
int calc(vector<Point> &points, const Point& p) {
map<pair<int, int>, int> mp;
int base = 0;
for (auto iter = points.begin();
iter != points.end();
++iter) {
int x = iter -> x - p.x;
int y = iter -> y - p.y;
if (!x && !y) base++;
else if (!x) {
mp[make_pair<int, int>(0, 1)]++;
}
else if (!y) {
mp[make_pair<int, int>(1, 0)]++;
} else {
long long t = x * y;
x = abs(x);
y = abs(y);
int g = gcd(x, y);
x /= g;
y /= g;
x *= t < 0? -1 : 1;
mp[make_pair<int, int>(int(x), int(y))]++;
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (auto iter = mp.begin(); iter != mp.end(); ++iter) {
ans = max(ans, iter->second);
}
return base + ans;
}
int gcd(int x, int y) {
if (x % y == 0) return y;
else return gcd(y, x % y);
}
};However, there are many solutions on the Internet that use a map<double, int> to count the number of points. I have to say they are lucky enough to get an " Accepted".























 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








