一、问题描述
在多线程开发中,由并发引起的问题很不容易发觉,这里分别实现了线程安全和非线程安全的两种计数器。可以明显的看出多线程并发引发的数据丢失问题。
二、问题分析
- 这里非线程安全的计数器的起因是计数器中的
count++;操作是非原子操作。 为解决
count++;非原子操作问题,这里模拟了硬件级解决方案CAS(Compare And Swap,比较并交换),是一种乐观锁方案。CAS有3个操作数,内存位置V,旧的预期值A和新值B。CAS的意思为:我认为V的值应该是A,如果是,那么将其赋值为B,若不是,则不修改,并告诉我应该为多少。它抱着成功的希望进行更新,并且如果另一个线程在上次检查后更新了该变量,它能够发现错误。
CAS模拟代码:
public synchronized int increaseCountWithCas(int exceptValue, int newValue){ int oldValue = count; if(oldValue == exceptValue){ count = newValue; } return oldValue; }- 在模拟多线程并发时,利用两种方式实现线程:
- 扩展Thread类
- 使用runnable
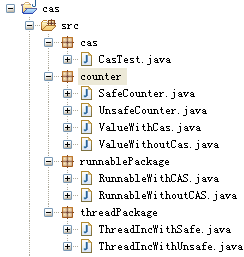
三、代码结构
四、counter代码
非线程安全计数器
package counter; /*** * 非线程线程安全的计数器 * @author zq * */ public class UnsafeCounter { private ValueWithoutCas valueWithoutCas = new ValueWithoutCas(); public int getValue(){ return valueWithoutCas.getCount(); } public int increase(){ valueWithoutCas.increaseCount(); return valueWithoutCas.getCount(); } }其中,ValueWithoutCas代码如下
package counter; /*** * 非线程安全计数器使用的计数类 * @author zq * */ public class ValueWithoutCas { private int count; //不安全的计数值增加 public void increaseCount(){ count++; } public int getCount(){ return count; } }线程安全计数器
package counter; /*** * 基于CAS实现的非阻塞线程安全计数器 * @author zq * */ public class SafeCounter { private ValueWithCas valueWithCas = new ValueWithCas(); public int getValue(){ return valueWithCas.getCount(); } public int increase(){ int v; do{ v = valueWithCas.getCount(); }while(v != valueWithCas.increaseCountWithCas(v, v + 1)); return v + 1; } }其中,valueWithCas 代码如下
package counter; /*** * 线程安全计数器使用的计数类 * @author zq * */ public class ValueWithCas { private int count; //模拟CAS实现计数值增加 public synchronized int increaseCountWithCas(int exceptValue, int newValue){ int oldValue = count; if(oldValue == exceptValue){ count = newValue; } return oldValue; } public synchronized int getCount(){ return count; } }
五、runnable方式模拟线程
操作非线程安全计数器
package runnablePackage; import counter.UnsafeCounter; /*** * 模拟线程:操作非线程安全计数器 * @author zq */ public class RunnableWithoutCAS implements Runnable { private static UnsafeCounter unsafeCounter = new UnsafeCounter(); @Override public void run() { unsafeCounter.increase(); } public static UnsafeCounter getUnsafeCounter(){ return unsafeCounter; } }操作线程安全计数器
package runnablePackage; import counter.SafeCounter; /*** * 模拟线程:操作线程安全计数器 * @author zq */ public class RunnableWithCAS implements Runnable { private static SafeCounter safeCounter = new SafeCounter(); @Override public void run() { safeCounter.increase(); } public static SafeCounter getSafeCounter(){ return safeCounter; } }
六、thread方式模拟线程
操作非线程安全计数器
package threadPackage; import counter.UnsafeCounter; /*** * 模拟线程:操作非线程安全计数器 * @author zq */ public class ThreadIncWithUnsafe extends Thread { UnsafeCounter unsafeCounter; public ThreadIncWithUnsafe(UnsafeCounter unsafeConunter){ super(); this.unsafeCounter = unsafeConunter; } public void run(){ unsafeCounter.increase(); } }操作线程安全计数器
package threadPackage; import counter.SafeCounter; /*** * 模拟线程:操作线程安全计数器 * @author zq */ public class ThreadIncWithSafe extends Thread{ SafeCounter safeCounter; public ThreadIncWithSafe(SafeCounter safeCounter){ super(); this.safeCounter = safeCounter; } public void run(){ safeCounter.increase(); } }
七、测试代码
以runnable和thread方式分别模拟10000个线程操作线程安全计数器和非线程安全计数器(计数器初始值为0)。正常情况下,10000个线程操作完成后,计数器值应该为10000。
这里使用
Thread.currentThread().join(10)方法实现main线程等待它启动的所有子进程完成后输出计数器结果。package cas; import counter.SafeCounter; import counter.UnsafeCounter; import runnablePackage.RunnableWithCAS; import runnablePackage.RunnableWithoutCAS; import threadPackage.ThreadIncWithSafe; import threadPackage.ThreadIncWithUnsafe; public class CasTest { public static void main(String[] args) { doWithThread(); System.out.println(); doWithRunnable(); } public static void doWithThread(){ //操作非线程安全计数器 UnsafeCounter unsafeCounter = new UnsafeCounter(); for(int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++){ Thread t = new ThreadIncWithUnsafe(unsafeCounter); t.start(); } waitSubThreadComplete(); System.out.println("doWithThread, unsafe result: " + unsafeCounter.getValue()); //操作线程安全计数器 SafeCounter safeCounter = new SafeCounter(); for(int j = 1; j <= 10000; j++){ Thread T = new ThreadIncWithSafe(safeCounter); T.start(); } waitSubThreadComplete(); System.out.println("doWithThread, safe result: " + safeCounter.getValue()); } public static void doWithRunnable(){ //操作非线程安全计数器 for(int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++){ Thread t = new Thread(new RunnableWithoutCAS()); t.start(); } waitSubThreadComplete();//使main线程等待它启动的所有子进程完成后,打印计数器结果 System.out.println("doWithRunnable,unsafe result: " + RunnableWithoutCAS.getUnsafeCounter().getValue()); //操作线程安全计数器 for(int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++){ Thread t = new Thread(new RunnableWithCAS()); t.start(); } waitSubThreadComplete(); System.out.println("doWithRunnable,safe result: " + RunnableWithCAS.getSafeCounter().getValue()); } /*** * 使main线程等待它启动的所有子进程完成 */ public static void waitSubThreadComplete(){ try { Thread.currentThread().join(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }在上述测试代码中,doWithRunnable函数也可以使用CountDownLatch保证main线程等待它启动的所有子进程完成后再输出计数器的值。代码如下:
/** * 使用CountDownLatch保证所有子进程完成后再输出结果 * */ public static void doWithRunnable(){ //操作非线程安全计数器 final CountDownLatch unsafeEndGate = new CountDownLatch(10000); for(int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++){ Thread t = new Thread(){ public void run(){ try{ try{ new RunnableWithoutCAS().run(); }finally{ unsafeEndGate.countDown(); } }catch(Exception e){ } } }; t.start(); } // waitSubThreadComplete();//使main线程等待它启动的所有子进程完成后,打印计数器结果 try { unsafeEndGate.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("doWithRunnable,unsafe result: " + RunnableWithoutCAS.getUnsafeCounter().getValue()); //操作线程安全计数器 final CountDownLatch safeEndGate = new CountDownLatch(10000); for(int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++){ Thread t = new Thread(){ public void run(){ try{ try{ new RunnableWithCAS().run(); }finally{ safeEndGate.countDown(); } }catch(Exception e){ } } }; t.start(); } // waitSubThreadComplete(); try { safeEndGate.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("doWithRunnable,safe result: " + RunnableWithCAS.getSafeCounter().getValue()); }
八、运行结果
doWithThread, unsafe result: 9998
doWithThread, safe result: 10000
doWithRunnable,unsafe result: 9997
doWithRunnable,safe result: 10000


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








