1,使用SharedPrefrences
用于简单少量的数据,数据的格式简单:都是普通的字符串,标量类型的值等,比如各种配置信息等等
SharedPrefrences与Editor简介:
创建SharedPreferences实例,通过Context.getSharedPreferences(String name,int mode);方法来获取SharedPreferences的实例
mode的值:
*Context.MODE_PRIVATE;该SharedPreferences数据只能被本应用程序调读,写
* Context.MODE_WORLD_READABLE;该SharedPreferences数据能被其他程序读,但是不能写
* Context.MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE;该SharedPreferences数据能被其他程序读,写
SharedPreferences保存的数据主要是类似于配置信息格式的数据,因此他保存的数据主要是简单类型的key-value对
* SharedPreferences接口主要负责读取应用程序的Preferences数据,提供如下常用的方法访问key-value对
* boolean contains(String key);判断是否包含key的数据
* abstract Map<String,?> getAll();获取全部键值对
* boolean getXxx(String key,xxx,defValue);获取指定的key对应的value值,如果key不存在,返回默认defvalue,xxx可以是Boolean,float,int,long,String等各种基本类型的值
SharedPreferences接口本身并没有提供写入数据的能力,而是通过 SharedPreferences的内部接口Editor写入数据,SharedPreferences调用edit()方法即可获得它所对应的Editor对象
Editor提供了如下方法:
* SharedPreferences.Editor clear();清空所有数据
* SharedPreferences.Editor putXxx(String key,xxx value);存入指定key对应的数据,xxx可以是Boolean,float,int,long,String等各种基本类型的值
* SharedPreferences.Editor remove(String key);删除指定key的数据
* Boolean commit();当Editor编辑完成之后,调用该方法提交修改
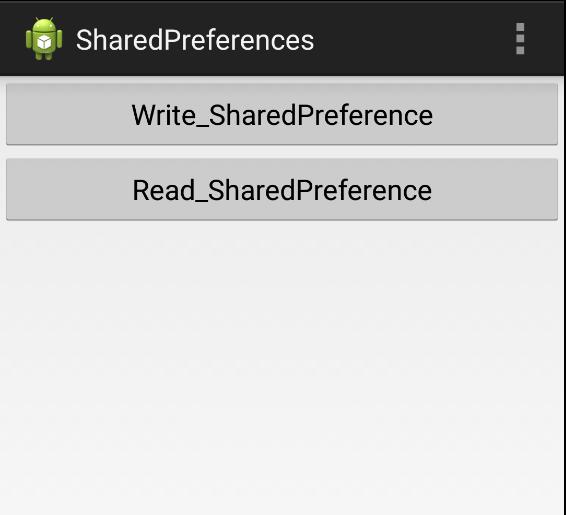
例子:一个按钮写数据,一个按钮读数据
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/root"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Write_SharedPreference" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Read_SharedPreference" />
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity.java
package com.hust.sharedpreferences;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
/*
* 创建SharedPreferences实例,通过Context.getSharedPreferences(String name,int mode);方法来获取SharedPreferences的实例
* mode的值:
* Context.MODE_PRIVATE;该SharedPreferences数据只能被本应用程序调读,写
* Context.MODE_WORLD_READABLE;该SharedPreferences数据能被其他程序读,但是不能写
* Context.MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE;该SharedPreferences数据能被其他程序读,写
*
*
* SharedPreferences保存的数据主要是类似于配置信息格式的数据,因此他保存的数据主要是简单类型的key-value对
*
* SharedPreferences接口主要负责读取应用程序的Preferences数据,提供如下常用的方法访问key-value对
* boolean contains(String key);判断是否包含key的数据
* abstract Map<String,?> getAll();获取全部键值对
* boolean getXxx(String key,xxx,defValue);获取指定的key对应的value值,如果key不存在,返回默认defvalue,xxx可以是Boolean,float,int,long,String等各种基本类型的值
*
* SharedPreferences接口本身并没有提供写入数据的能力,而是通过 SharedPreferences的内部接口Editor写入数据,SharedPreferences调用edit()方法即可互殴它所对应的Editor对象
* Editor提供了如下方法:
* SharedPreferences.Editor clear();清空所有数据
* SharedPreferences.Editor putXxx(String key,xxx value);存入指定key对应的数据,xxx可以是Boolean,float,int,long,String等各种基本类型的值
* SharedPreferences.Editor remove(String key);删除指定key的数据
* Boolean commit();当Editor编辑完成之后,调用该方法提交修改
*
* */
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
//
SharedPreferences preferences;
SharedPreferences.Editor editor;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//实例化SharedPreferences对象,读数据
preferences=getSharedPreferences("test",Context.MODE_WORLD_READABLE);
//实例化Editor对象,写数据
editor=preferences.edit();
Button read=(Button) findViewById(R.id.button2);
Button write=(Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
read.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String time=preferences.getString("time", null);
int rnd=preferences.getInt("rnd", 0);
String result=time==null?"您暂时还未写入数据":"写入时间:"+time+"\n上次生成的数据数是:"+rnd;
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, result, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
write.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日"+"hh:mm:ss");
editor.putString("time", sdf.format(new Date()));
editor.putInt("rnd", (int)(Math.random()*1000));
editor.commit();
}
});
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will
// automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long
// as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml.
int id = item.getItemId();
if (id == R.id.action_settings) {
return true;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
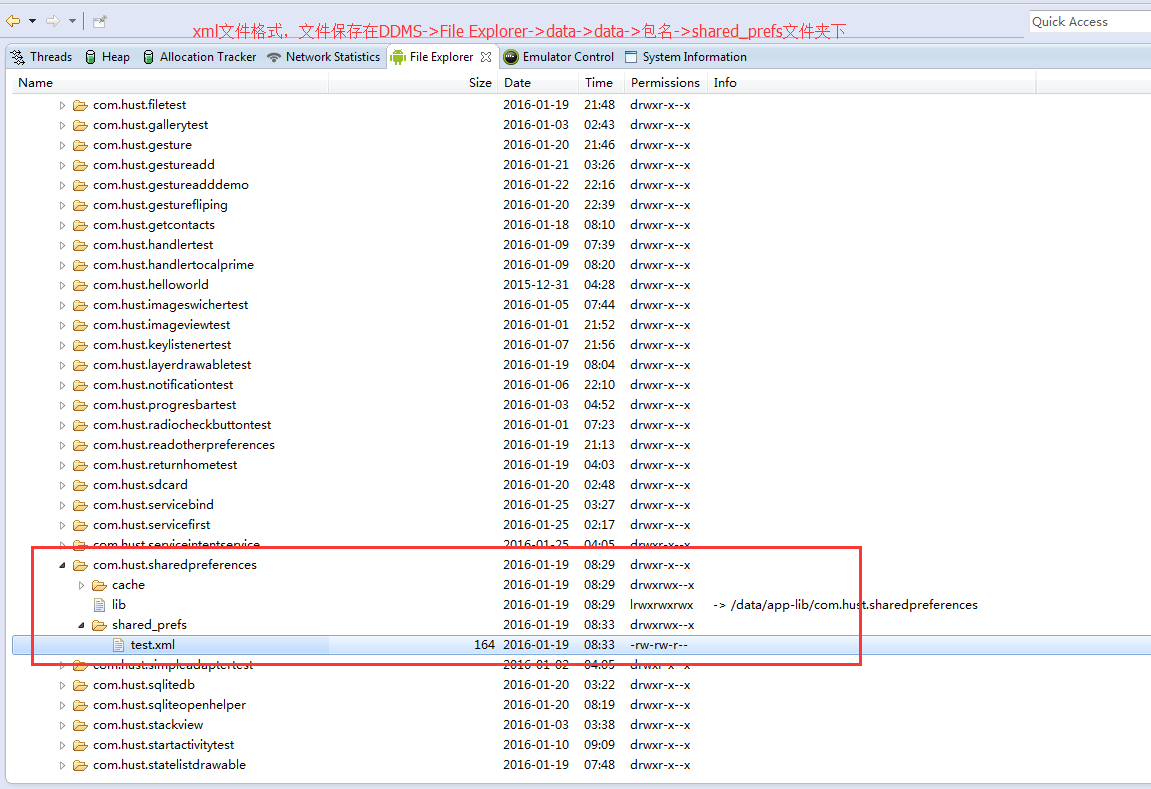
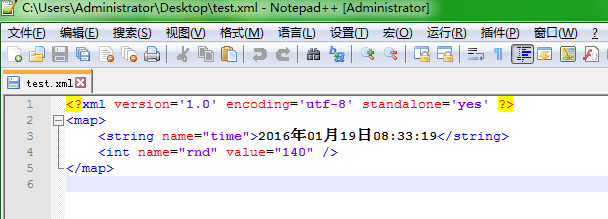
test.xml
二,使用File存储
Context 提供了两种方法来打开本应用程序的数据文件夹里的文件IO流
1,FileInputStream openFileInput(String filename);打开应用程序的数据文件夹下(文件在DDMS>File Explor>data>data>包名>files>filename)的filename文件对应的输入流
2, FileOutputStream openFileOutput(String name,int mode);打开应用程序的数据文件夹下name文件对应的输出流
第二个参数:
* MODE_PRIVATE;该文件只能被当前程序读写,且每次写入前,以前写的内容会清空,不追加
* MODE_APPEND: 追加的方式打开该文件,应用程序可以向该文件中追加内容
* MODE_WORLD_READABLE:该文件的内容可以被其他程序读取
* MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE:该文件的内容可以被其他程序读,写
package com.hust.filetest;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
/*
* Context 提供了两种方法来打开本应用程序的数据文件夹里的文件IO流
* 1,FileInputStream openFileInput(String filename);打开应用程序的数据文件夹下(文件在DDMS>File Explor>data>data>包名>files>filename)的filename文件对应的输入流
* 2, FileOutputStream openFileOutput(String name,int mode);打开应用程序的数据文件夹下name文件对应的输出流
*
* 第二个参数:
* MODE_PRIVATE;该文件只能被当前程序读写,且每次写入前,以前写的内容会清空,不追加
* MODE_APPEND: 追加的方式打开该文件,应用程序可以向该文件中追加内容
* MODE_WORLD_READABLE:该文件的内容可以被其他程序读取
* MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE:该文件的内容可以被其他程序读,写
*
* */
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
final String FILE_NAME="filetest";//文件名
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button write=(Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
Button read=(Button) findViewById(R.id.button2);
final EditText edit1=(EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText1);
final EditText edit2=(EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText2);
write.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//写入数据
writedata(edit1.getText().toString());
edit1.setText("");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "写入成功!", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
read.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String ss;
try {
//读数据
ss = readdata();
edit2.setText(ss);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
//读数据
protected String readdata() throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
//打开文件输入流
FileInputStream fis=openFileInput(FILE_NAME);
//缓存
byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];
int hasread=0;
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder("");
//循环读入缓存大小的数据,并存放在缓存数组中
while((hasread=fis.read(buffer))>0){
sb.append(new String(buffer,0,hasread));
}
fis.close();
return sb.toString();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
//写数据
protected void writedata(String content) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
//打开文件输出流,以追加的方式
FileOutputStream fos=openFileOutput(FILE_NAME,MODE_APPEND);
//把输出流包装成PrintStream
PrintStream ps=new PrintStream(fos);
//输出文件内容
ps.print(content);
ps.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will
// automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long
// as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml.
int id = item.getItemId();
if (id == R.id.action_settings) {
return true;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
SQLite数据是Android集成的一个轻量级的数据库,不想Oracle,MySQL那样的数据库,SQLite只是一个文件,创建或打开一个SQLite数据库时,只是打开一个文件准备读写
SQLiteDatabase类的静态方法来打开一个对应的数据库:
public static SQLiteDatabase openDatabase(String path, CursorFactory factory, int flags),打开path文件所代表的SQLite数据库
public static SQLiteDatabase openOrCreateDatabase(File file, CursorFactory factory)
打开或创建file文件代表的数据库
public static SQLiteDatabase openOrCreateDatabase(String path, CursorFactory factory);打开或创建path文件代表的数据库
调用SQLiteDatabase类的如下方法操作数据库:
1,执行SQL语句
execSQL(String sql)
execSQL(String sql, Object[] bindArgs)。执行带占位符的SQL语句
2,执行带占位符的SQL查询
Cursor rawQuery(String sql, String[] selectionArgs)
3,特定的方法操作SQLite数据库(就是把SQl语句整理成参数)
update(String table, ContentValues values, String whereClause, String[] whereArgs)
insert(String table, String nullColumnHack, ContentValues values)
delete(String table, String whereClause, String[] whereArgs)
Cursor query(String table, String[] columns, String selection,
String[] selectionArgs, String groupBy, String having,
String orderBy)
Cursor query(String table, String[] columns, String selection,
String[] selectionArgs, String groupBy, String having,
String orderBy, String limit)
Cursor对象:
move(int offset);将指针向上或向下指到指定的行数
boolean moveToFirst();指针移动到第一行
boolean moveToLast();
boolean moveToNext();
boolean moveToPosition(int position);
boolean moveToPrevious();
String getColumnName(int columnIndex);由列的索引获得列名
String[] getColumnNames();获得所有列名
String getString(int columnIndex);索引获得值
int getColumnIndex(String columnName);由列名获得索引
使用SQL语句操作Sqlite数据库
package com.hust.sqlitedb;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteException;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
SQLiteDatabase db;
Button btn;
ListView listview;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//创建或打开数据库(需要使用绝对路径)
db=SQLiteDatabase.openOrCreateDatabase(this.getFilesDir().toString()+"/mydb.db3", null);
Log.v("Dir", getFilesDir().toString());//getFilesDir().toString()的值是/data/data/com.hust.sqlitedb/files
listview =(ListView) findViewById(R.id.listView1);
btn=(Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
btn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String title=((EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText1)).getText().toString();
String content=((EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText2)).getText().toString();
try{
inertData(db,title,content);//插入数据表
Cursor cursor=db.rawQuery("select * from info", null);//查询数据表
ShowInList(cursor);//在ListView中显示cursor表
}catch(SQLiteException se){
//数据库对象执行SQL语句,创建表
db.execSQL("create table info(_id integer primary key autoincrement," +
"news_title varchar(20)," +
"news_content varchar(255))");
inertData(db,title,content);
Cursor cursor=db.rawQuery("select * from info", null);
ShowInList(cursor);
}
}
});
}
protected void ShowInList(Cursor cursor) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//SimpleCursorAdapter的用法:1,Context,2,每一行的布局文件,3,数据源cursor。4.字符串数组表示表的列名,像SimpleAdapter表示Map中的key值,5,显示的组件Id
SimpleCursorAdapter ad=new SimpleCursorAdapter(this, R.layout.line, cursor, new String[]{"news_title","news_content"}, new int[]{R.id.textView1,R.id.textView2});
//设置Adapter
listview.setAdapter(ad);
}
protected void inertData(SQLiteDatabase db2, String title, String content) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//独具库对象执行SQL语句,带占位符的语句
db2.execSQL("insert into info values(null,?,?)",new String[]{title,content} );
}
//对出程序是关掉数据库
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
if(db!=null&&db.isOpen()){
db.close();
}
}
1,获取SQLiteDatabase对象,代表与数据库连接
2,调用SQLiteDatabase的方法执行SQL语句
3,操作SQL语句的执行结果,比如用SimpleCusorAdapter封装Cursor
4,关闭SQLiteDatabase,回收资源
SQLiteOpenHelper类:管理数据库的工具类
实际中很少用SQLiteDatabase的静态方法打开数据库,一般是继承SQLiteOpenHelper开发子类,并通过该子类的getReadableDatabase()和getWritableDatabase()方法打开数据库
public SQLiteDatabase getReadableDatabase();以读写的方式打开数据库对应的SQLiteDatabase 对象,就是获取数据库对象
public SQLiteDatabase getWritableDatabase();以写的方式打开数据库对应的SQLiteDatabase 对象,就是获取数据库对象
void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db);当第一次创建数据库时回调该方法
void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion);当数据库版本有更新是回调该方法
DBHelper.java
package com.hust.sqliteopenhelper;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
public class DBHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {//继承SQLiteOpenHelper
//建表的SQl语句
String SQL="create table dict(id integer primary key autoincrement," +
"news_word varchar(20)," +
"news_detail varchar(100))";
public DBHelper(Context context, String name, CursorFactory factory,
int version) {//name是数据库文件名
super(context, name, factory, version);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
//如果数据库不存在时就自动生成一个数据库,并调用onCreate方法,可以添加一些对数据库的初始操作,比如建表。添加初始记录数据
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
db.execSQL(SQL);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("--onUpdate Called--"+oldVersion+"-->"+newVersion);
}
}
package com.hust.sqliteopenhelper;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
DBHelper dbhelper;
Button write;
Button search;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
write=(Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
search=(Button) findViewById(R.id.button2);
dbhelper=new DBHelper(this, "Dict.db3", null, 1);//第二个参数是数据库名
write.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
EditText editword=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText1);
EditText editdetail=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText2);
String word=editword.getText().toString();
String detail=editdetail.getText().toString();
SQLiteDatabase db=dbhelper.getReadableDatabase(); //获得可读写的数据库,如果没有自动创建一个数据库
db.execSQL("insert into dict values(null,?,?)",new String[]{word,detail});//数据库执行插入sql语句
editword.setText("");
editdetail.setText("");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "添加到数据库成功!", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
search.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
SQLiteDatabase db=dbhelper.getReadableDatabase();
String key=((EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText3)).getText().toString();
//数据库对象执行占位符查询sql语句
Cursor cursor=db.rawQuery("select * from dict where news_word like ?",new String[]{"%"+key+"%"});
//创建显式Intent对象
Intent intent=new Intent(MainActivity.this,ResultActivity.class);
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putSerializable("data", Cursor_To_List(cursor));//把Cursor转换成ArrayList对象
intent.putExtras(bundle);//Intent携带Bundle对象
//开启intent对应的Activity
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
protected ArrayList<Map<String,String>> Cursor_To_List(Cursor cursor) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ArrayList<Map<String,String>> list=new ArrayList<Map<String,String>>();
while(cursor.moveToNext()){//游标移到下一行
//获取每个记录的字段值
String word=cursor.getString(1);
String detail=cursor.getString(2);
//放进一个Map中
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<String,String>();
map.put("word", word);
map.put("detail", detail);
list.add(map);//map放进list中
}
return list;
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/tableRow1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Word :"
android:textSize="25dp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10" >
</EditText>
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/tableRow2"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Detail:"
android:textSize="25dp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10" >
</EditText>
</TableRow>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Add_To_Dict" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10" >
</EditText>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Seach_From_Dict" />
</TableLayout>

ResultActivity.java
package com.hust.sqliteopenhelper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
public class ResultActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_result);
//获得ListView组件
ListView listview=(ListView) findViewById(R.id.listView1);
//获得Intent对象
Intent intent=getIntent();
ArrayList<Map<String,String>> list=(ArrayList<Map<String, String>>) intent.getSerializableExtra("data");
//simpleadapter对象
SimpleAdapter sa=new SimpleAdapter(this,list,R.layout.line,new String[]{"word","detail"},new int[]{R.id.text1,R.id.text2});
//设置adapter
listview.setAdapter(sa);
}























 875
875

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








