知识点:
1.自定义ViewGroup
1.onMeasure:测量子View的宽和高,设置自己的宽和高
2.onLayout:设置子View的位置
onMeasure:根据子View的布局文件,为子View设置测量模式和测量值
测量=测量模式+测量值
测量模式:3种
1、EXACTLY: 100dp, match_parent
2、AT_MOST: warp_content
3、UNSPECIFIED: 子控件想多大就多大,很少见
子View.getLayoutParams()–>LinearLayout.LayoutParams(实际上市父布局)
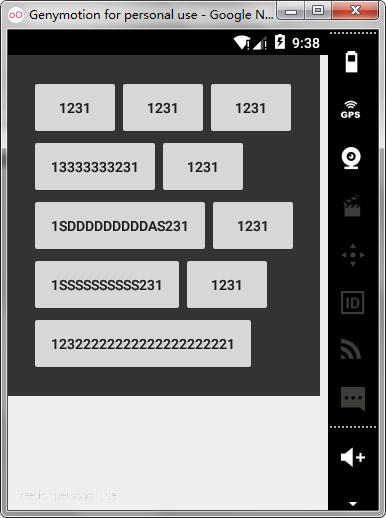
效果
xml
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
>
<com.example.day0227.FlowLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="23dp"
android:background="#333">
<!--可以不带padding -->
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="1231"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="1231"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="1231"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="13333333231"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="1231"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="1sdddddddddas231"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="1231"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="1ssssssssss231"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="1231"></Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="12322222222222222222221"
/>
</com.example.day0227.FlowLayout>
</RelativeLayout>FlowLayout
package com.example.day0227;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup{
// 使用自定义属性
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//warp_content
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
//记录每一行的宽和高
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
//得到内部元素的个数
int cCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
//测量子View的宽和高
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//得到LayoutParams
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//子View占据的宽度
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
//子View占据的高度
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
//换行
if (lineWidth + childWidth > widthSize - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight()) {
//对比得到最大的宽度
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth);
lineWidth = childWidth;
//重置lineWidth
lineWidth = childWidth;
//记录行高
height += lineHeight;
lineHeight = childHeight;
} else {
//未换行
//叠加行宽
lineWidth += childWidth;
//得到当前行的最大宽度
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
}
//到达最后一个空间
if (i == cCount - 1) {
width = Math.max(lineWidth, width);
height += lineHeight;
}
//wrap_content
// if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
// setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
// } else {
// setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
// }
setMeasuredDimension((widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? widthSize : width + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight(),
(heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? heightSize : height + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom());
}
//如果没有注释掉下面父类方法,会导致warp_content也是全屏显示!!!
// super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
/**
* 存储所有的View
*/
private List<List<View>> mAllViews = new ArrayList<List<View>>();
/**
* 存储每行的高度
*/
private List<Integer> mLineHeights = new ArrayList<Integer>();
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
mAllViews.clear();
mLineHeights.clear();
//当前ViewGroup的宽度
int width = getWidth();
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
List<View> lineViews = new ArrayList<View>();
int cCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) getLayoutParams();
int childWith = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
//如果需要换行
if (childWith+lineWidth+lp.leftMargin+lp.rightMargin > width - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight()) {
//记录LineHeight
mLineHeights.add(lineHeight);
//记录当前行的Views
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
//重置我们的行宽和行高
lineWidth = 0;
lineHeight = childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
//重置我们的View集合
lineViews = new ArrayList<View>();
}
lineWidth += childWith + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);;
lineViews.add(child);
}
//for end
//处理最后一行
mLineHeights.add(lineHeight);
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
//设置子View的位置
int left = getPaddingLeft();
int top = getPaddingTop();
//行数
int lineNum = mAllViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lineNum; i++) {
// 当前行的所有View
lineViews = mAllViews.get(i);
lineHeight = mLineHeights.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j++) {
View child = lineViews.get(j);
//判断child的状态
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
continue;
}
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int lc = left + lp.leftMargin;
int tc = top +lp.topMargin;
int rc = lc + child.getMeasuredWidth();
int bc = tc + child.getMeasuredHeight();
//为子View进行布局
child.layout(lc, tc, rc, bc);
left += child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin +lp.rightMargin;
}
left = getPaddingLeft();
top += lineHeight;
}
}
/**
* 与当前Group对应的LayoutParams
*/
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
}
注意:
1.如果使用代码添加Button,若不创建MarginParams pl =…,每个Buton默认width=“match..”,即占据一行(视频结尾提到,达不到上图效果)
2.Button默认带有margin,若用TextView则需在为TextView添加margin属性(为了实现上图效果)






















 2527
2527

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








