介绍:
AIDL是用于进程之间的通信。
比如应用程序A拥有一套复杂的计算方法,我新的应用程序B也想使用这个计算方法。这时候就能使用AIDL。说白了就是从应用程序B里拿出参数,扔到应用程序A里面,让A来计算,最后返回计算结果给应用程序B。
用法:
使用AIDL要创建 .aidl文件.
应用程序A相当于服务端,提供方法。
应用程序B相当于客户端,提供参数并得到结果。
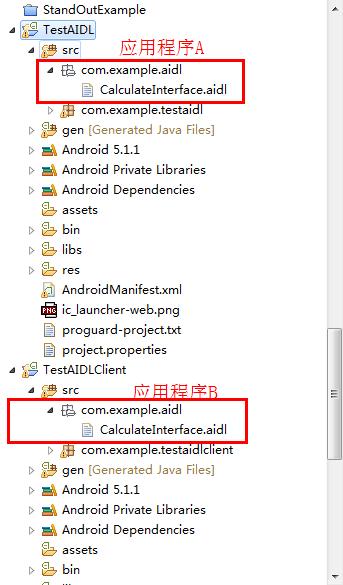
应用程序A和应用程序B的 .aidl文件所在的包名和自身名字必须相同!
在构建好 .aidl文件后IDE会自动在gen目录下生成对应的java文件,我们不需要改动!
CalculateInterface.aidl
package com.example.aidl;
interface CalculateInterface {
double doCalculate(double a, double b);
}CalculateInterface.aidl (xxx.aidl)这个文件在应用程序A和应用程序B都要创建,并且它们的包名以及自身名字必须相等!
应用程序A(相当于服务端)
CalculateService
package com.example.testaidl;
import com.example.aidl.CalculateInterface;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
public class CalculateService extends Service {
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new CalculateInterface.Stub() {
@Override
public double doCalculate(double a, double b)
throws RemoteException {
// 实际上在这里可以调用应用程序A中非常多的类,做非常复杂的算法!
// 这里地方就是aidl的意义所在!
return a + b;
}
};
}
}
应用程序B(相当于客户端)
MainActivity
package com.example.testaidlclient;
import com.example.aidl.CalculateInterface;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private CalculateInterface mService;
private ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
mService = null;
}
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
mService = CalculateInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
mHandler.obtainMessage().sendToTarget();
}
};
private Handler mHandler = new Handler(){
public void handleMessage(android.os.Message msg) {
try {
double c = mService.doCalculate(1.0, 2.0);
Log.v("TAG", "c = " + c);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
};
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// bind
Intent intent = new Intent("com.action.aidl");
bindService(intent, mServiceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
// 这里有一个深坑!!!
// 在bindService后,mService不是立刻被赋值的!
// mService赋值实际是在一个回调函数!
// 所在如下的写法会程序奔溃!因为在bindService后,mService还是等于null!!
// 这个教训要切记啊!!!
// try {
// double c = mService.doCalculate(1.0, 2.0);
// Log.v("TAG", "c = " + c);
// } catch (RemoteException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
//
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
unbindService(mServiceConnection);
}
}
为应用程序A(相当于服务端)配置ANDROIDMANIFEST
<service
android:name="com.example.testaidl.CalculateService" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.action.aidl"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
</intent-filter>
</service>小结:因为service的bind这块没怎么使用过,不了解bindservice的过程。导致学习aidl过程好费了大量的时间~TvT
转载于:
http://www.cnblogs.com/BeyondAnyTime/p/3204119.html
2016/5/23日更新
权限认证功能
应用程序A修改onBind()方法
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// 权限验证
int check = checkCallingOrSelfPermission("com.example.testaidlclient.permission.CHECK");
if (check == PackageManager.PERMISSION_DENIED) {
return null;
}
return new CalculateInterface.Stub() {
@Override
public double doCalculate(double a, double b)
throws RemoteException {
// 实际上在这里可以调用应用程序A中非常多的类,做非常复杂的算法!
// 这里地方就是aidl的意义所在!
return a + b;
}
};
}应用程序B AndroidManifest.xml声明自定义权限
<uses-permission android:name="com.example.testaidlclient.permission.CHECK"/>应用程序A AndroidManifest.xml 声明自定义权限
注意: 应用程序B和应用程序A声明权限的方式不同!
<permission
android:name="com.example.testaidlclient.permission.CHECK"
android:protectionLevel="normal"/>这样代表应用程序A有权限访问应用程序B






















 1338
1338

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








