昨天去面试,问了很多基础问题,诸如Service两种启动方式的区别、Handler的作用、Activity的四种加载模式等等。这些问题在项目实现中都接触过,但我一直是觉得,知道有这么个东西就好。是,记忆中是有这些知识点,但当要求让我表述的时候,我却支支吾吾说不清楚,总之就是知识不扎实。找工作有时跟找恋人一样,要认真,好好投资发展自己,世上哪有那么多刚好眼瞎的人看上丑不拉几的你。回来后,我反省了下自己面试中的种种表现,还是脚踏实地写写代码学习学习。
一、生命周期
看一下官方给出的两种服务的生命周期图:
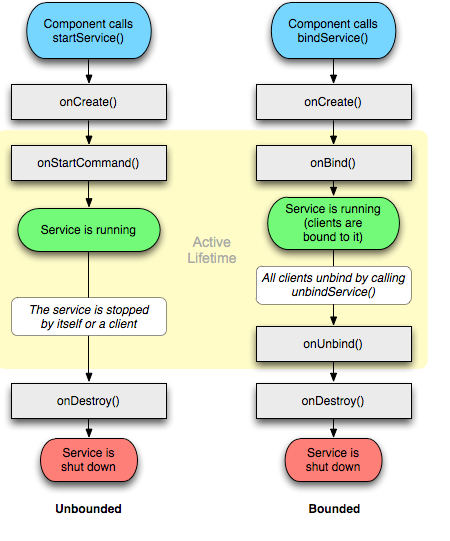
Service有两种启动方式,这两种启动方式对Service的生命周期的影响是不一样的。
1 通过startService方式
onCreate -> onStartCommand -> onStart -> onDestroy
如果是调用者自己直接退出而没有调用stopService的话,Service会一直在后台运行。当service再次重启,则只会依次调用onStartCommand和onStart,不会调用onCreate。无论何时,都会先调用onStartCommand(),在调用onStart()。那onStartCommand和onStart究竟有什么差别呢?我们稍后会讲。
2 通过bindService方式
onCreate -> onBind(只一次,不可多次绑定) -> onUnbind -> onDestroy
这种方式是将服务的调用者和服务绑定在一起,调用者退出了,绑定在一起的服务也就死亡了(如果是按home,则是把它放到后台,没有退出。)。这种绑定的方式可以使得调用方调用服务上的其他的方法。
那有人要问了,如果两种方式中的一些方法交织使用可以吗?可以交织使用,但是有一些原则。我们可以通过下面一个例子来进行实验。
注意:在Service每一次的开启关闭过程中,只有onStart可被多次调用(通过多次startService调用),
其他onCreate,onBind,onUnbind,onDestory在一个生命周期中只能被调用一次。
二、使用例子
1、myservice.xml
<span style="font-size:18px;"><?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="time" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/startservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="startService" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/stopservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="stopService" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/bindservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="bindService" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/unbindservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="unbindService" />
</LinearLayout></span>2、建立一个MyService继承service的类
</pre><pre name="code" class="java"><span style="font-size:18px;">package myservicestest;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyService extends Service{
private static final String TAG="Service";
private MyBinder binder=new MyBinder();
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) {
Log.v(TAG,"start IBinder--");
return binder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.e(TAG, "start onCreate--");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.e(TAG, "start Destroy--");
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.e(TAG, "start onStartCommand--");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
@Deprecated
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
Log.e(TAG, "start onStart--");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
Log.e(TAG, "start onUnbind~~~");
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
public String getSystemTime(){
/*Time t=new Time();
t.setToNow();*/
SimpleDateFormat format=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
return format.format(new Date());
}
public class MyBinder extends Binder{
public MyService getService(){
return MyService.this;
}
}
}</span> 3、ServiceDemoActivity类
<pre name="code" class="java">package myservicestest;
import com.example.enter5.R;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class ServiceDemoActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener{
private MyService mMyService;
private TextView mTextView;
private Context mContext;
private Button startServiceButton;
private Button stopServiceButton;
private Button bindServiceButton;
private Button unbindServiceButton;
private ServiceConnection mServiceConnection =new ServiceConnection(){
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName arg0, IBinder service) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mMyService=((MyService.MyBinder)service).getService();
mTextView.setText("I am frome Service :" + mMyService.getSystemTime());
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
};
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.myservice);
setupViews();
};
public void setupViews(){
mContext=this;
mTextView=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.text);
startServiceButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.startservice);
stopServiceButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.stopservice);
bindServiceButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.bindservice);
unbindServiceButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.unbindservice);
startServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
stopServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
bindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
unbindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
switch(view.getId()){
case R.id.startservice:
Intent i=new Intent();
i.setClass(this, MyService.class);
mContext.startService(i);
break;
case R.id.stopservice:
Intent i1 = new Intent();
i1.setClass(ServiceDemoActivity.this, MyService.class);
mContext.stopService(i1);
break;
case R.id.bindservice:
Intent i2=new Intent();
i2.setClass(ServiceDemoActivity.this, MyService.class);
mContext.bindService(i2, mServiceConnection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE );
break;
case R.id.unbindservice:
mContext.unbindService(mServiceConnection);
break;
}
}
}



<span style="font-size:18px;">Service里面的onStartCommand()方法详解
启动service的时候,onCreate方法只有第一次会调用,onStartCommand和onStart每次都被调用。onStartCommand会告诉系统如何重启服务,如判断是否异常终止后重新启动,在何种情况下异常终止
onStartCommand和onStart区别
// This is the old onStart method that will be called on the pre-2.0
// platform. On 2.0 or later we override onStartCommand() so this
// method will not be called.
// 2.0 API level之后,实现onStart等同于重写onStartCommand并返回START_STICKY
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
handleCommand(intent);
}
// 2.0 API level之后,onStart()方法被onStartCommand()取代了
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
handleCommand(intent);
// We want this service to continue running until it is explicitly
// stopped, so return sticky.
return START_STICKY;
}
启动服务时依次执行onCreate,onStartCommand,onStart;如果在系统显示调用stopService和stopSelf之前终止服务,service再次重启,onStartCommand会被调用,重启服务时依次执行onStartCommand,onStart。无论何时,都会先调用onStartCommand(),在调用onStart()。
onStartCommand返回值
onStartComand使用时,返回的是一个(int)整形。
这个整形可以有四个返回值:start_sticky、start_no_sticky、START_REDELIVER_INTENT、START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY。
它们的含义分别是:
1):START_STICKY:如果service进程被kill掉,保留service的状态为开始状态,但不保留递送的intent对象。随后系统会尝试重新创建service,由于服务状态为开始状态,所以创建服务后一定会调用onStartCommand(Intent,int,int)方法。如果在此期间没有任何启动命令被传递到service,那么参数Intent将为null。
2):START_NOT_STICKY:“非粘性的”。使用这个返回值时,如果在执行完onStartCommand后,服务被异常kill掉,系统不会自动重启该服务
3):START_REDELIVER_INTENT:重传Intent。使用这个返回值时,如果在执行完onStartCommand后,服务被异常kill掉,系统会自动重启该服务,并将Intent的值传入。
4):START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY:START_STICKY的兼容版本,但不保证服务被kill后一定能重启。
onStartComand参数flags含义
flags表示启动服务的方式:
Additional data about this start request. Currently either 0, START_FLAG_REDELIVERY, or START_FLAG_RETRY.
START_FLAG_REDELIVERY:如果你实现onStartCommand()来安排异步工作或者在另一个线程中工作, 那么你可能需要使用START_FLAG_REDELIVERY来让系统重新发送一个intent。这样如果你的服务在处理它的时候被Kill掉, Intent不会丢失.
START_FLAG_RETRY:表示服务之前被设为START_STICKY,则会被传入这个标记。 </span>http://blog.csdn.net/huutu/article/details/40357481






















 474
474

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








