RPM(Redhat Package Manager)是用于Redhat、CentOS、Fedora等Linux 分发版(distribution)的常见的软件包管理器。rpm工具可以用来制作源码安装包和二进制安装包。本文档提供一个示例来说明如何制作一个rpm二进制包。
1. 准备
安装打包需要的程序:yum install rpm-build rpmdevtools
2. 安装一个简单的hello.sh脚本
-
首先我们需要准备需要打包的程序
hello.sh#!/bin/bash echo "Hello World!" -
编写SPEC文档
hello.spec注意:我们的spec文档的名字要和安装程序的名称相同
Name: hello Version: 2.1 Release: 1 Summary: The "Hello World" script Summary(zh_CN): GNU "Hello World" 程序 License: GPLv3+ URL: https://github.com/xxx/hello.git Packager: xxx Software %description The "Hello World" program, done with all bells and whistles of a proper FOSS project, including configuration, build, internationalization, help files, etc. %description -l zh_CN "Hello World" 程序, 包含 FOSS 项目所需的所有部分, 包括配置, 构建, 国际化, 帮助文件等. %install mkdir -p %{buildroot}/usr/local/bin install -m 755 -t %{buildroot}/usr/local/bin /root/dw/rpmTest/hello.sh %files /usr/local/bin/hello.shspec文档说明:
-
表头包含安装包的基本信息,表头项说明如下(* 标识必须包含此项)
- Name *:软件包的名称
- Version *:软件版本号
- Release *:同一版本软件的发布版本号
- Summary *:软件的简短介绍
- License *:软件的授权模式
- Summary(zh_CN):中文版本的简短介绍
- Requires(pre | post | preun | postun):/bin/sh
各个过程需要使用哪种shell脚本
-
内容包含以下项目
- %description
软件的完整介绍,与Summary字段不通,完成内容介绍可以写多行。 - %prep(没有使用)
解压源码的过程。 - %build (没有使用)
编译源码的过程。 - %install
安装脚本。将需要安装的文件拷贝到%{buildroot}目录。%{buildroot}目录相当于安装系统的根目录。 - %files
需要打包的文件列表,注意这里的文件路径是以${buildroot}制定的安装后的根目录。可以使用通配符,如/etc/keepalived/*。注意:使用通配符时,如果安装目录有文件与安装包中冲突,安装失败。 - %changelog(没有使用)
软件的变化记录。 - scriptlets 安装卸载时执行脚本(没有使用)
- 在软体包安装之前 (
%pre) 或之后 (%post) 执行 - 在软体包卸载之前 (
%preun) 或之后 (%postun) 执行 - 在事务开始 (
%pretrans) 或结束 (%posttrans) 时执行
- 在软体包安装之前 (
- %description
-
3. 使用rpm-build命令制作rpm二进制包
执行rpm-build -bb hello.spec生成二进制rpm包,默认情况下会在当前用户生成目录~/rpmbuild
tree rpmbuild/
rpmbuild/
├── BUILD
├── BUILDROOT
├── RPMS
│ └── x86_64
│ └── hello-2.1-1.ky10.x86_64.rpm
├── SOURCES
├── SPECS
└── SRPMS
**建议定义_topdir宏,将安装包生成到制定目录。**下面的命令生成rpm包到当前目录:
rpmbuild -bb hello.spec --define "_topdir $PWD/rpmbuild"
4. 自定义rpm包名称
默认安装包名称定义在/usr/lib/rpm/macros文件中:
%_rpmfilename %{_build_name_fmt}
%_build_name_fmt %%{ARCH}/%%{NAME}-%%{VERSION}-%%{RELEASE}.%%{ARCH}.rpm
在hello.spec的第一行修改%_rpmfilename宏进行自定义包名称安装
%define _rpmfilename hello.rpm
再次执行打包命令,查看rpmbuild/RPMS目录生成自定义rpm包。
tree rpmbuild/
rpmbuild/
├── BUILD
├── BUILDROOT
├── RPMS
│ └── hello.rpm
├── SOURCES
├── SPECS
└── SRPMS
5. 将rpm包中的程序添加systemd`自启动服务
生成systemd自启动服务需要编写hello.service文件,本文并不做hello.service文件格式的具体说明,只是说明打包流程。通过修改hello.spec文件就可以将hello.service添加到systemd自启动服务中:
%install阶段生成/etc/systemd/system/hello.service%post阶段在安装后启动hello.service服务%preun阶段在卸载前停止并禁用hello.service服务
hello.service文件如下:
[Unit]
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/hello.sh
Restart=always
RestartSec=5
StandardOutput=syslog
StandardError=syslog
SyslogIdentifier=%n
修改后的hello.spec文件如下
%define _rpmfilename hello.rpm
Name: hello
Version: 2.1
Release: 1
Summary: The "Hello World" script
Summary(zh_CN): GNU "Hello World" 程序
License: GPLv3+
URL: https://github.com/xxx/hello.git
Packager: XXX Software
%description
The "Hello World" program, done with all bells and whistles of a proper FOSS
project, including configuration, build, internationalization, help files, etc.
%description -l zh_CN
"Hello World" 程序, 包含 FOSS 项目所需的所有部分, 包括配置, 构建, 国际化, 帮助文件等.
%install
mkdir -p %{buildroot}/usr/local/bin
install -m 755 -t %{buildroot}/usr/local/bin /root/dw/rpmTest/hello.sh
# install the systemd unit file to buildroot.
mkdir -p %{buildroot}/etc/systemd/system
install -t %{buildroot}/etc/systemd/system /root/dw/rpmTest/hello.service
%files
/usr/local/bin/hello.sh
/etc/systemd/system/hello.service
%post
systemctl enable hello.service
systemctl start hello.service
%preun
systemctl stop hello.service
systemctl disable hello.service
安装生成的rpm包,并查看hello.service服务
rpm -ivh rpmbuild/RPMS/hello.rpm
systemctl status hello
● hello.service
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/hello.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: activating (auto-restart) since Tue 2021-10-12 15:16:37 CST; 80ms ago
Process: 288322 ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/hello.sh (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 288322 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
卸载hello包,执行了停止和移除服务命令
rpm -e hello
Removed /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/hello.service.
遇到的问题
1. 执行rpmbuild脚本报错:rpmbuild contains an invalid rpath error 0002
报错信息如下:
+ /usr/lib/rpm/check-rpaths
*******************************************************************************
*
* WARNING: 'check-rpaths' detected a broken RPATH and will cause 'rpmbuild'
* to fail. To ignore these errors, you can set the '$QA_RPATHS'
* environment variable which is a bitmask allowing the values
* below. The current value of QA_RPATHS is 0x0000.
*
* 0x0001 ... standard RPATHs (e.g. /usr/lib); such RPATHs are a minor
* issue but are introducing redundant searchpaths without
* providing a benefit. They can also cause errors in multilib
* environments.
* 0x0002 ... invalid RPATHs; these are RPATHs which are neither absolute
* nor relative filenames and can therefore be a SECURITY risk
* 0x0004 ... insecure RPATHs; these are relative RPATHs which are a
* SECURITY risk
* 0x0008 ... the special '$ORIGIN' RPATHs are appearing after other
* RPATHs; this is just a minor issue but usually unwanted
* 0x0010 ... the RPATH is empty; there is no reason for such RPATHs
* and they cause unneeded work while loading libraries
* 0x0020 ... an RPATH references '..' of an absolute path; this will break
* the functionality when the path before '..' is a symlink
*
*
* Examples:
* - to ignore standard and empty RPATHs, execute 'rpmbuild' like
* $ QA_RPATHS=$(( 0x0001|0x0010 )) rpmbuild my-package.src.rpm
* - to check existing files, set $RPM_BUILD_ROOT and execute check-rpaths like
* $ RPM_BUILD_ROOT=<top-dir> /usr/lib/rpm/check-rpaths
*
*******************************************************************************
rpmbuild在打包时会检查可执行文件的rpath动态链接在本机上是否可用,但是可执行文件在本机上可能没有安装。
一种解决方法时跳过rpath检测,报错信息中也给出了提示:
- 跳过所有
rpath检测:QA_SKIP_RPATHS=1 rpmbuild -bb hello.spec - 跳过不安全和空的
rpath链接:QA_RPATHS=$(( 0x0002|0x0010 )) rpmbuild my-package.src.rpm
2. 打包前后可执行文件的md5值不同
解决方法主要参考这篇文章:编程中的冰山理论——从 RPM 改变文件大小说起
使用rpm2cpio xxxxxx.rpm |cpio -idv命令解压打包文件,发现打包文件占用磁盘空间变小。google了一下,找到了大哥给出的原因:
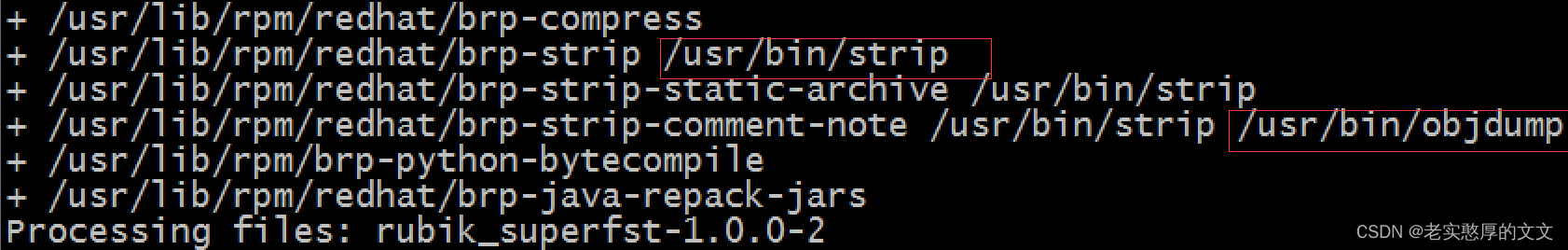
从上图可以看到,打包时调用了strip和objdump命令。strip命令通过除去绑定程序和符号调试程序使用的信息,降低扩展公共对象文件格式(XCOFF)的对象文件的大小。rpm打包不需要携带调试信息,所以rpm打包进行了strip操作。
解决方法:
在spec文件中加入宏命令:%define __strip /bin/true






















 6797
6797











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








