=============查看数据库==========================
使用SHOW语句找出服务器上当前存在什么数据库:
- mysql> SHOW DATABASES;
- +----------+
- | Database |
- +----------+
- | mysql |
- | test |
- | tmp |
- +----------+
mysql是必需的,因为它描述用户访问权限,test数据库经常作为用户试身手的工作区。
请注意如果没有SHOW DATABASES权限,则不能看见所有数据库
这儿有多个数据库,在操作数据库之前需要先选择一个,使用use命令
mysql> USE testDatabase changed注意,USE,类似QUIT,不需要一个分号。
=============创建数据库、表=========================
create命令用于创建数据库
- mysql> create database tmp;
- Query OK, 1 row affected (0.03 sec)
- mysql> use tmp //使用此数据库
- Database changed
在用户每一次登录时需要重新用use命令选择哪个数据库,如果不想那么麻烦,可以登录时指定
#mysql -uroot -p密码 数据库名
#
创建了数据库后可以创建表了
先查看下当前表,用show tables;
- mysql> show tables;
- Empty set (0.00 sec) //当前为空表
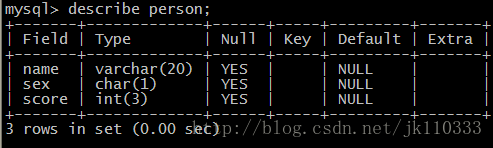
- mysql> create table person (name VARCHAR(20) ,sex char(1),score int(3)); //表名person,包含name类型为varchar长度为20,sex为1位char,score为3为整型
查看表的信息和数据类型,用describe 表名
========================填充表内容=============================
创建表后,需要填入内容。通过LOAD DATA和INSERT语句可以完成该任务。
因为你是从一个空表开始的,填充它的一个简易方法是创建一个文本文件,每个人各一行,然后用一个语句将文件的内容装载到表中。
你可以创建一个文本文件“person.txt”,每行包含一个记录,用定位符(tab)把值分开,并且以CREATE TABLE语句中列出的列次序给出。对于丢失的值(例如未知的性别,或仍然活着的动物的死亡日期),你可以使用NULL值。为了在你的文本文件中表示这些内容,使用\N(反斜线,字母N)。例如,Whistler鸟的记录应为(这里值之间的空白是一个定位符):
装载
用insert语句添加一个或者多个
- mysql> insert into person values('xin','m','90');
- Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
修改表的内容有两个方法:
1、清空表内容,重新从文件中装载
修改文件内容后,再从新使用load data命令装载
- mysql> delete from person;
- Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
- mysql> load data local infile '/root/person.txt' into table person;
- Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
- Records: 3 Deleted: 0 Skipped: 0 Warnings: 0
2、使用update命令
- mysql> update person set sex="m" where name="hexizhuo";
- Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
- Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
- mysql> select * from person;
- +--------------+------+-------+
- | name | sex | score |
- +--------------+------+-------+
- | chen <span style="white-space:pre"> </span> | m | 100 |
- | yang | m | 60 |
- | hex | m | 80 |
- | xin | m | 90 |
- +--------------+------+-------+
- 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- mysql>
========================查询表内容==============================
使用select命令
SELECT语句用来从数据表中检索信息。语句的一般格式是: mysql> SELECT what_to_select FROM which_table WHERE conditions_to_satisfy; what_to_select指出你想要看到的内容,可以是列的一个表,或*表示“所有的列”。
which_table指出你想要从其检索数据的表。
WHERE子句是可选项,如果选择该项,
conditions_to_satisfy指定行必须满足的检索条件。
- mysql> select * from person; //检索所有的信息
- +--------------+------+-------+
- | name | sex | score |
- +--------------+------+-------+
- | chen | m | 100 |
- | yang | m | 60 |
- | hex | NULL | 80 |
- | xin | m | 90 |
- +--------------+------+-------+
- 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- mysql>
- mysql> select * from person where name="chenjiankang";
- +--------------+------+-------+
- | name | sex | score |
- +--------------+------+-------+
- | chen | m | 100 |
- +--------------+------+-------+
- 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
- mysql> //下面使用逻辑运算符and,还有一个是or
- mysql> select * from person where sex="m" and score>80;
- +--------------+------+-------+
- | name | sex | score |
- +--------------+------+-------+
- | chen | m | 100 |
- | xin | m | 90 |
- +--------------+------+-------+
- 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- mysql> select name ,sex from person; //选择某几列,也可以在后面加上where来筛选数据
- +--------------+------+
- | name | sex |
- +--------------+------+
- | chen | m |
- | yang | m |
- | hex | m |
- | xin | m |
- +--------------+------+
- 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- mysql> select name ,sex from person where sex="f";
- Empty set (0.00 sec)
- <pre style="margin: 0cm 0cm 0.0001pt; font-size: 14px; "><strong>去重功能</strong></pre>
- 如果你的数据中有两个数据相同,比如有两个name=qq,如下
- mysql> select name from person;
- +----------+
- | name |
- +----------+
- | siasjack |
- | qq |
- | hehe |
- | xin |
- | qq |
- +----------+
- 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
不想让他在这出现多次,只想出现一次,可以加上distinct选项
- mysql> select distinct name from person;
- +----------+
- | name |
- +----------+
- | siasjack |
- | qq |
- | hehe |
- | xin |
- +----------+
- 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
排序打印功能使用order选项即可,如果想按照score的倒叙打印,需要再加上desc参数
- mysql> select name,score from person order by score;
- +----------+-------+
- | name | score |
- +----------+-------+
- | qq | 60 |
- | hehe | 80 |
- | qq | 88 |
- | xin | 90 |
- | siasjack | 100 |
- +----------+-------+
- 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
模式匹配MySQL提供标准的SQL模式匹配,以及一种基于象Unix实用程序如vi、grep和sed的扩展正则表达式模式匹配的格式。
SQL模式匹配允许你使用“_”匹配任何单个字符,而“%”匹配任意数目字符(包括零字符)。
在 MySQL中,SQL的模式默认是忽略大小写的。下面给出一些例子。注意使用SQL模式时,不能使用=或!=;而应使用LIKE或NOT LIKE比较操作符。
- mysql> select *from person where name like '%sias%'; //名字中以sias开头,或者包含sias的
- +----------+------+-------+
- | name | sex | score |
- +----------+------+-------+
- | siasjack | m | 100 |
- +----------+------+-------+
- 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
- mysql> select *from person where name like '____'; //名字中正好四个字符
- +------+------+-------+
- | name | sex | score |
- +------+------+-------+
- | hehe | f | 80 |
- +------+------+-------+
- 1 row in set (0.00 sec)


























 628
628

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








