适配器模式定义:
Adapter是将一个类的接口变换成客户端所期待的另一种接口,从而使得原本因接口不匹配的而无法一起工作的类可以一起工作 。
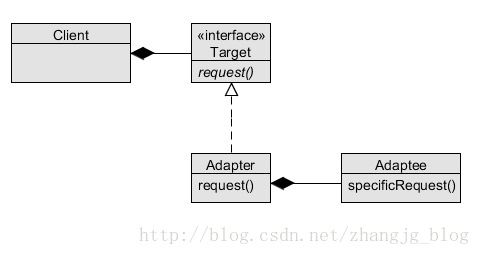
下图为适配器模式通用类图
适配器模式的三个角色:
1.Target目标角色 : 该角色定义把其它类转换为何种接口,也就是我们的期望接口
2 Adaptee角色 : 该角色是已经存在的运行良好的类或者对象,经过适配器角色的包装,它会成为一个崭新的角色,即目标角色
3 Adapter 适配器角色:它通过继承或者是类关联的方法将源角色转换为目标角色
一个最简单的例子:假设你缺苹果对象,想用一些橘子来冒充,显然因为橘子接口不同,没我们不能公然拿来用。可以写一个适配器来实现接口相容,在AppleAadpter中用构造器取得要适配的对象引用,然后利用这个引用对象的方法来实现目标角色接口中的方法
下面是java编程思想的一个例子:
客户使用适配器的过程如下:
1 客户通过目标接口调用适配器的方法对适配器发出请求
2.适配器使用被适配者接口把请求装换成被适配者的一个或者多个调用接口
3.客户接收到调用的结果,并未察觉这一切是适配器在起作用
总结一下:
适配器模式的三个特点:
1.Target目标角色 : 该角色定义把其它类转换为何种接口,也就是我们的期望接口
2 Adaptee角色 : 该角色是已经存在的运行良好的类或者对象,经过适配器角色的包装,它会成为一个崭新的角色,即目标角色
3 Adapter 适配器角色:它通过继承或者是类关联的方法将源角色转换为目标角色
一个最简单的例子:假设你缺苹果对象,想用一些橘子来冒充,显然因为橘子接口不同,没我们不能公然拿来用。可以写一个适配器来实现接口相容,在AppleAadpter中用构造器取得要适配的对象引用,然后利用这个引用对象的方法来实现目标角色接口中的方法
class Apple {
public void getAcolor(String str) {
System.out.println("Apple color is: " + str);
}
}
class Orange {
public void getOColor(String str) {
System.out.println("Orange color is: " + str);
}
}
class AppleAdapter extends Apple {
private Orange orange;
public AppleAdapter(Orange orange){
this.orange = orange;
}
public void getAcolor(String str){
orange.getOColor(str);
}
}
public class TestAdapter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Apple apple1 = new Apple();
Apple apple2 = new Apple();
apple1.getAcolor("green");
Orange orange = new Orange();
AppleAdapter aa = new AppleAdapter(orange);
aa.getAcolor("red");
}
}下面是java编程思想的一个例子:
//使用适配器模式 实现在默认得到前向迭代器的基础上,添加产生反向迭代器的能力
//添加一个能够产生Itrerable对象的方法
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
class ReversibleArrayList<T> extends ArrayList<T>{
public ReversibleArrayList(Collection<T> c) { super(c); }
public Iterable<T> reversed() {
return new Iterable() {
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new Iterator<T>() {
int current = size() -1;
public boolean hasNext() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return current > -1;
}
public T next() { return get(current--);}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
};
}
};
}
}
public class AdapterMethodIdiom {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ReversibleArrayList<String> ral =
new ReversibleArrayList<String>(
Arrays.asList("To be or not to be".split(" ")));
for (String s : ral)
System.out.print(s + " ");
System.out.println();
for(String s : ral.reversed())
System.out.print(s+ " ");
}
客户使用适配器的过程如下:
1 客户通过目标接口调用适配器的方法对适配器发出请求
2.适配器使用被适配者接口把请求装换成被适配者的一个或者多个调用接口
3.客户接收到调用的结果,并未察觉这一切是适配器在起作用
总结一下:
适配器模式的三个特点:
1 适配器对象实现原有接口
2 适配器对象组合一个实现新接口的对象(这个对象也可以不实现一个接口,只是一个单纯的对象)
3 对适配器原有接口方法的调用被委托给新接口的实例的特定方法






















 207
207

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








