在 栈和队列 一文中提到,栈可以处理具有 完全包含 关系的问题。
而树分为两部分:结点 和 边。结点可以理解为集合,边称为关系。树的根结点就叫做全集,子节点叫做子集,子集并起来就得到了全集。
根结点就是待解决的问题,可能是个大问题,可以划分为多个子问题,即是子结点。
树也存在着一种完全包含关系。树和栈是有一定关联的,遍历树的时候就要使用栈,而且使用到的是系统栈,用到系统栈的表现形式就是递归。
1、树的深度、高度和度
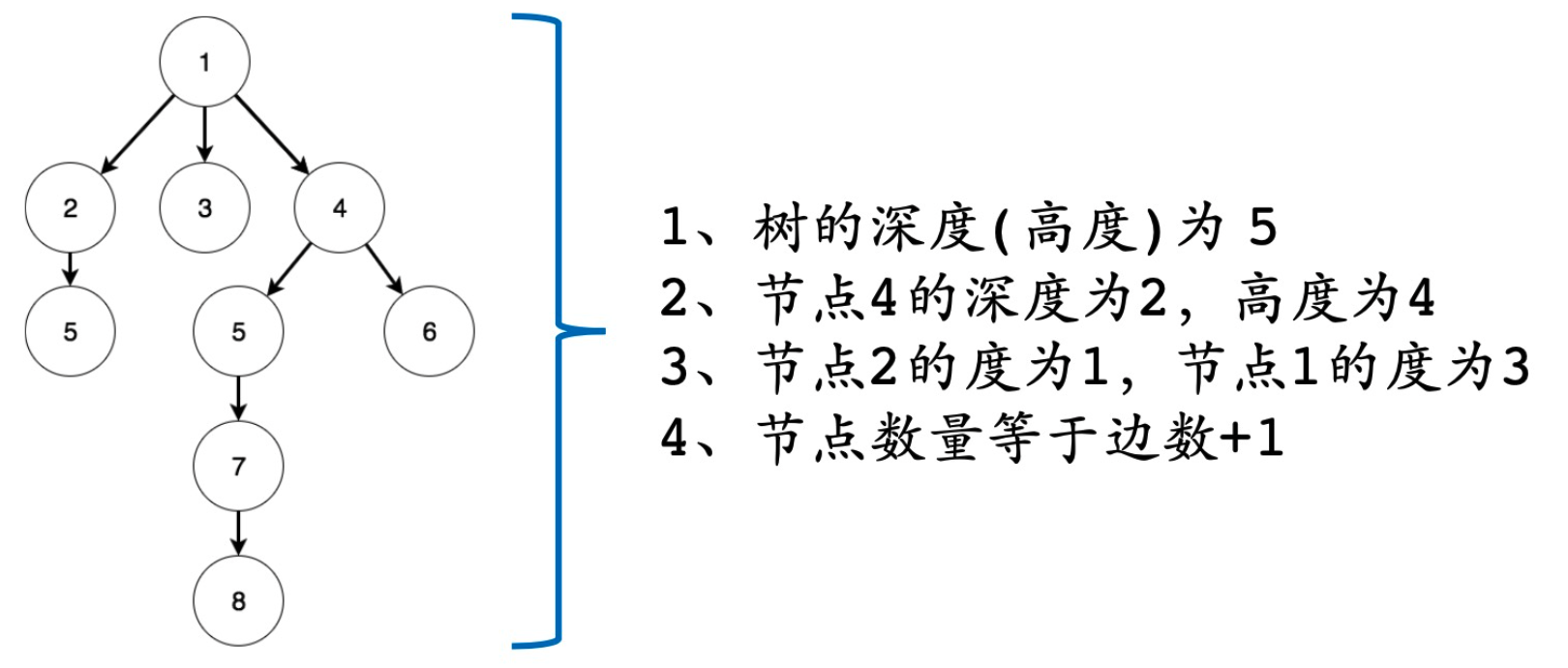
- 树的根结点所在层数为第一层。结点下有几个子结点,度就为几。
- 深度 是从根往下的层数,高度 是从最后一层往上到该结点的层数。
- 结点数量 = 边数 + 1
2、二叉树
计算机底层是用二进制存储的,二进制可以表示任何进制的数。同理,二叉树可以表示任意多的树形结构。
通过 左孩子-右兄弟(十字链表法)的表示法,可以将任意的树形结构转化成二叉树。
如上面的三叉树转化为二叉树如下所示:

N
N
N 叉树是一个非确定性问题,但是可以使用二叉树来实现,即是将一个非确定性问题转换为了一个确定性问题。所以如果要实现
N
N
N 叉树,不需要问
N
N
N 是多少,只需要实现二叉树的结构定义即可,因为任何形式的树形结构都能转化成二叉树形式。
3、二叉树的性质

- 度为 0 的结点称为叶子结点
- “度为 0 的结点比度为 2 的结点多 1 个”结论的推导依据:结点个数 = 边数+ 1
推导过程:
n
1
+
n
0
+
n
2
(
结
点
数
)
=
n
1
+
0
+
2
∗
n
2
+
1
(
边
数
)
n_1 + n_0 + n_2(结点数)= n_1 + 0 + 2 * n_2 + 1 (边数)
n1+n0+n2(结点数)=n1+0+2∗n2+1(边数) =>
n
0
=
n
2
+
1
n_0 = n_2 + 1
n0=n2+1。
其中,
n
1
n_1
n1 表示度为 1 的结点个数,
n
0
n_0
n0 表示度为 0 的结点个数,
n
2
n_2
n2 表示度为 2 的结点个数。
n
0
=
n
2
+
1
n_0 = n_2 + 1
n0=n2+1,即度为 0 的结点比度为 2 的结点多 1 个。
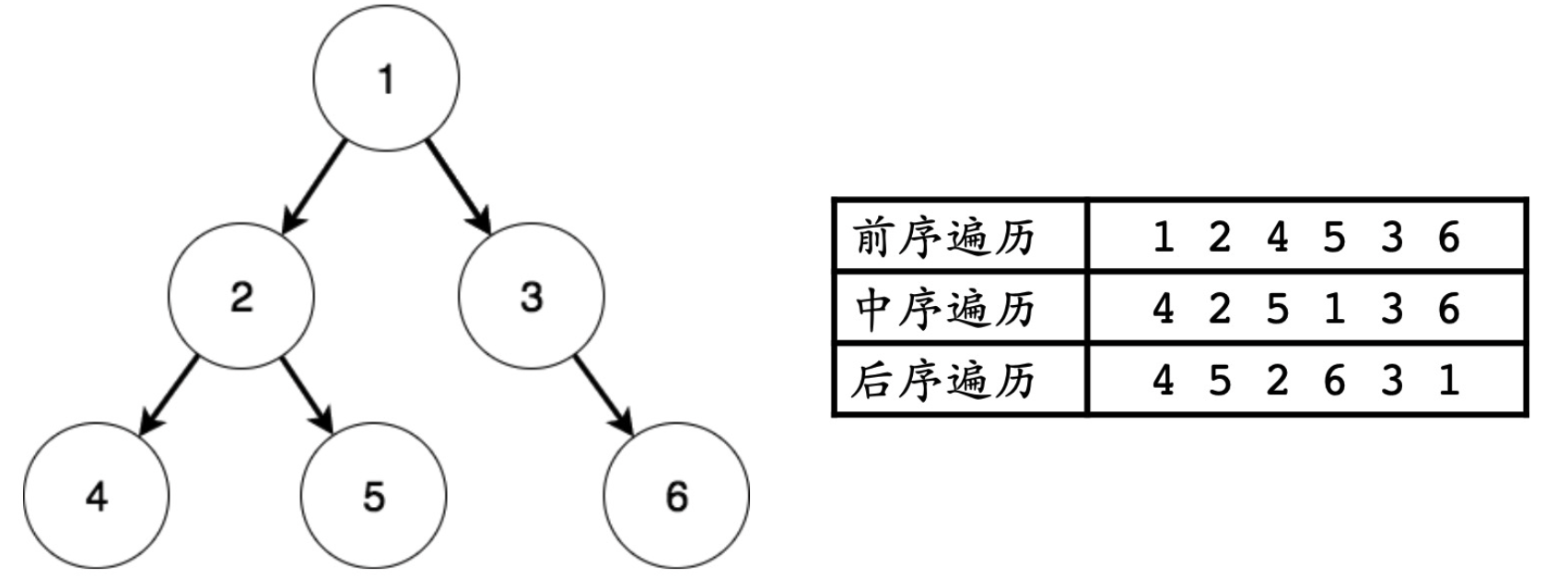
4、二叉树的遍历方式
遍历即访问每个结点。

5、中国版二叉树和国际版二叉树
- 中国版二叉树

- 国际版二叉树

满二叉树:只存在度为 0 和度为 2 的结点。
6、 完全二叉树

因为子结点的编号是连续的,所以可以使用连续空间存储。
可以根据当前结点的编号,计算出它的左右孩子的编号。即完全二叉树可以用数组实现,每个结点可以从记录式变为计算式。
7、广义表


上图的右侧为该树的几种广义表表示方法,通常都是使用前两种,因为更直观。
8、广义表转二叉树的代码实现
【要求】将广义表还原构建为一棵二叉树。
【思路】广义表是用括号嵌套来表示的,而对于括号这样的问题,可以使用栈来解决。根据左括号入栈、右括号出栈。从左到右遍历字符串,遇到非括号字符封装成一个二叉树结点信息,记录该结点的地址,遇到左括号,将当前结点入栈;下一个非括号字符也封装成一个二叉树结点,其父节点就是栈顶元素,需要判断它是左孩子还是右孩子,可以根据逗号,如果没遇到逗号,就是左孩子,取出栈顶元素,将栈顶元素的左孩子的指向该结点。遇到右括号,出栈。
【代码】
// 广义表转二叉树
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
/*
* 【要求】将广义表还原构建为一棵二叉树。
* 【思路】
* 广义表是用括号嵌套来表示的,而对于括号这样的问题,可以使用栈来解决。根据左括号入栈、右括号出栈。
* 从左到右遍历字符串,遇到非括号字符封装成一个二叉树结点信息,记录该结点的地址,遇到左括号,将当前结点入栈;下一个非括号字符也封装成一个二叉树结点,其父节点就是栈顶元素。
* 需要判断它是左孩子还是右孩子,可以根据逗号。如果没遇到逗号,就是左孩子,取出栈顶元素,将栈顶元素的左孩子的指向该结点;遇到右括号,出栈。
*/
typedef struct Node { //二叉树结点
char data;
struct Node *lchild, *rchild;
} Node;
typedef struct Tree {
Node *root; //根结点
int n; //当前节点个数
} Tree;
typedef struct Stack {
Node **data; //开辟一片连续的存储空间,每个位置都是存储的Node *这样的地址
int top; //栈顶
int capacity; //容量
} Stack;
/*
* 树结点的创建
*/
Node *createNewNode(char val) {
Node *p = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->data = val;
p->lchild = NULL;
p->rchild = NULL;
return p;
}
/*
* 树的初始化
*/
Tree *initTree() {
Tree *tree = (Tree *)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
tree->root = NULL;
tree->n = 0;
return tree;
}
/*
* 栈的初始化
*/
Stack *initStack(int n) {
Stack *s = (Stack *)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
s->data = (Node **)malloc(sizeof(Node *) * n);
s->top = -1;
s->capacity = n;
return s;
}
/*
* 获取栈顶元素
*/
Node *top(Stack *s) {
return s->data[s->top];
}
/*
* 判断栈是否为空
*/
int isEmpty(Stack *s) {
return s->top == -1;
}
/*
* 入栈
*/
int push(Stack *s, Node *val) {
if (s == NULL) return -1;
if (s->top == s->capacity - 1) return -1;
s->data[++(s->top)] = val;
return 0;
}
/*
* 出栈
*/
int pop(Stack *s) {
if (s == NULL) return -1;
if (isEmpty(s)) return -1;
s->top--;
return 0;
}
/*
* 栈的销毁
*/
void destroyStack(Stack *s) {
if (s == NULL) return ;
free(s->data);
free(s);
return ;
}
/*
* 二叉树结点的销毁
*/
void destroyNode(Node *node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
destroyNode(node->lchild);
destroyNode(node->rchild);
free(node);
return ;
}
/*
* 二叉树的销毁
*/
void destroyTree(Tree *tree) {
if (tree == NULL) return ;
destroyNode(tree->root);
free(tree);
return ;
}
/*
* 广义表转二叉树
*/
Node *buildNode(const char *str, int *node_cnt) {
Stack *s = initStack(strlen(str));
Node *temp = NULL;
Node *p = NULL; //p记录根结点,即栈中最后弹出的元素
int flag = 0;
while (str[0]) {
switch (str[0]) {
case '(':
push(s, temp);
flag = 0;
break;
case ')':
p = top(s);
pop(s);
break;
case ',':
flag = 1;
break;
case ' ':
break;
default:
temp = createNewNode(str[0]);
if (!isEmpty(s) && flag == 0) {
top(s)->lchild = temp;
} else if (!isEmpty(s) && flag == 1) {
top(s)->rchild = temp;
}
++(*node_cnt);
break;
}
++str;
}
if (p == NULL) p = temp; //只有一个结点时因为没有括号,就没有了入栈操作,故单独判断这种情况
destroyStack(s);
return p;
}
/*
* 先序遍历
*/
void pre_order_node(Node *node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
printf("%c ", node->data);
pre_order_node(node->lchild);
pre_order_node(node->rchild);
return ;
}
/*
* 先序遍历:传入根结点
*/
void pre_order(Tree *tree) {
if (tree == NULL) return ;
printf("pre_order: ");
pre_order_node(tree->root);
printf("\n");
return ;
}
/*
* 中序遍历
*/
void in_order_node(Node *node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
in_order_node(node->lchild);
printf("%c ", node->data);
in_order_node(node->rchild);
return ;
}
void in_order(Tree *tree) {
if (tree == NULL) return ;
printf("in_order: ");
in_order_node(tree->root);
printf("\n");
}
/*
* 后序遍历
*/
void post_order_node(Node *node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
post_order_node(node->lchild);
post_order_node(node->rchild);
printf("%c ", node->data);
return ;
}
void post_order(Tree *tree) {
if (tree == NULL) return ;
printf("post_order: ");
post_order_node(tree->root);
printf("\n");
return ;
}
int main() {
char str[1000] = {0};
int node_cnt = 0;
scanf("%[^\n]s", str);
Tree *tree = initTree(); //二叉树初始化
tree->root = buildNode(str, &node_cnt); //广义表转二叉树结点
tree->n = node_cnt;
pre_order(tree);
in_order(tree);
post_order(tree);
destroyTree(tree);
return 0;
}
测试结果:
A(B(,D),C(E,)) # 输入
pre_order: A B D C E
in_order: B D A E C
post_order: D B E C A
9、二叉搜索树的代码实现
二叉搜索树的特点:左子树结点的值 < 根结点的值 < 右子树结点的值。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
/*
* 二叉搜索树结点定义
*/
typedef struct Node {
int val;
struct Node *lchild;
struct Node *rchild;
} Node;
/*
* 树的结构定义
*/
typedef struct Tree {
Node *root;
int cnt;
} Tree;
/*
* 结点初始化
*/
Node *init_node(int val) {
Node *node = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->val = val;
node->lchild = NULL;
node->rchild = NULL;
return node;
}
/*
* 树的初始化
*/
Tree *init_tree() {
Tree *tree = (Tree *)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
tree->root = NULL;
tree->cnt = 0;
return tree;
}
/*
* 销毁结点
*/
void destroy_node(Node *node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
destroy_node(node->lchild);
destroy_node(node->rchild);
free(node);
return ;
}
/*
* 销毁树
*/
void destroy_tree(Tree *tree) {
if (tree == NULL) return ;
destroy_node(tree->root);
free(tree);
return ;
}
/*
* 结点的插入
*/
Node *insert_node(Node *root, int val, int *flag) {
if (root == NULL) {
*flag = 1;
return init_node(val);
}
if (root->val == val) return root; //待插入的值与根节点值相等,不做任何插入操作
if (val < root->val) //待插入的值比根节点值小,则要插在左子树上
root->lchild = insert_node(root->lchild, val, flag);
else //待插入的值比根节点值大,则要插在右子树上
root->rchild = insert_node(root->rchild, val, flag);
return root;
}
/*
* 插入操作
*/
void insert(Tree *tree, int val) {
int flag = 0;
tree->root = insert_node(tree->root, val, &flag);
tree->cnt += flag; //如果flag = 1,表示插入成功,更新节点数
return ;
}
/*
* 先序遍历
*/
void pre_order_node(Node *node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
printf("%d ", node->val);
pre_order_node(node->lchild);
pre_order_node(node->rchild);
return ;
}
void pre_order(Tree *tree) {
if (tree == NULL) return ;
printf("pre_order: ");
pre_order_node(tree->root);
printf("\n");
return;
}
/*
* 中序遍历
*/
void in_order_node(Node *node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
in_order_node(node->lchild);
printf("%d ", node->val);
in_order_node(node->rchild);
return ;
}
void in_order(Tree *tree) {
if (tree == NULL) return ;
printf("in_order: ");
in_order_node(tree->root);
printf("\n");
return;
}
/*
* 后序遍历
*/
void post_order_node(Node *node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
post_order_node(node->lchild);
post_order_node(node->rchild);
printf("%d ", node->val);
return ;
}
void post_order(Tree *tree) {
if (tree == NULL) return ;
printf("post_order: ");
post_order_node(tree->root);
printf("\n");
return;
}
/*
* 节点值的打印
*/
void output_node(Node *node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
printf("%d", node->val);
if (node->lchild == NULL && node->rchild == NULL) return ;
printf("(");
output_node(node->lchild);
printf(",");
output_node(node->rchild);
printf(")");
return ;
}
/*
* 二叉树转广义表
*/
void output(Tree *tree) {
if (tree == NULL) return ;
printf("tree(%d) : ", tree->cnt);
output_node(tree->root);
printf("\n");
return ;
}
int main() {
srand(time(0));
Tree *tree = init_tree();
#define max_op 10
for (int i = 0; i < max_op; i++) {
int val = rand() % 100;
insert(tree, val);
output(tree);
}
pre_order(tree);
in_order(tree);
post_order(tree);
#undef max_op
destroy_tree(tree);
return 0;
}
测试结果:
tree(2) : 7(,62)
tree(3) : 7(,62(48,))
tree(4) : 7(,62(48(19,),))
tree(5) : 7(,62(48(19,),68))
tree(6) : 7(,62(48(19,),68(,90)))
tree(7) : 7(6,62(48(19,),68(,90)))
tree(8) : 7(6,62(48(19(17,),),68(,90)))
tree(9) : 7(6,62(48(19(17,),),68(,90(71,))))
tree(10) : 7(6,62(48(19(17,),53),68(,90(71,))))
pre_order: 7 6 62 48 19 17 53 68 90 71
in_order: 6 7 17 19 48 53 62 68 71 90
post_order: 6 17 19 53 48 71 90 68 62 7
10、相关题目
Leetcode 100.相同的树
【思路】判断两棵树是否相同,就是判断两棵树的各个结点的数据域是否相同,于是需要遍历比较两棵树的相同位置的结点,当然需要使用到递归,递归结束的边界条件就是当前比较的两个结点存在的各种情况。
【代码】
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q){
if (p == NULL && q == NULL) return true;
if (p == NULL || q == NULL) return false;
if (p->val != q->val) return false;
return isSameTree(p->left, q->left) && isSameTree(p->right, q->right);
}
Leetcode 101.对称二叉树
【思路】和Leetcode 100 是相同的思路,不过是对称地进行比较。
【代码】
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isSame(struct TreeNode *left_node, struct TreeNode *right_node) {
if (left_node == NULL && right_node == NULL) return true;
if (left_node == NULL || right_node == NULL || left_node->val != right_node->val) return false;
return isSame(left_node->left, right_node->right) && isSame(left_node->right, right_node->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root){
return isSame(root->left, root->right);
}
Leetcode 102.二叉树的层序遍历
【思路】BFS,但是和一般的BFS的区别在于,每次并不只是只出队一个元素,而是出队同一层的所有元素。
【代码】
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
/**
* Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize.
* The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array.
* Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
//1.判断一层结束:同一层元素处理完毕之后进行下一次迭代,迭代次数就是层数
//2.每层的节点个数:当前队列中的元素个数
//returnSize记录结果中二维数组的行数,returnColumnSizes记录每行的个数
#define max 1024
int** levelOrder(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
if (root == NULL) {
*returnSize = 0;
return NULL;
}
//队列存放树节点
struct TreeNode *queue[max]; //静态数组
int head = 0, tail = 0;
int **ans = malloc(sizeof(int *) * max);
*returnColumnSizes = malloc(sizeof(int) * max);
int level = 0, count = 0; //level为层数
queue[tail++] = root; //根节点入队
count++;
while (head != tail) {
count = tail - head; //当前队列中的元素个数
(*returnColumnSizes)[level] = count; //记录当前层的元素个数
//存储当前层的元素
ans[level] = malloc(sizeof(int) * count);
//相比于普通的队列出队,这里是将同一层的元素全部出队
for (int i = 1; i <= count; i++) { //出队同一层的元素
struct TreeNode *p = queue[head++];
ans[level][i - 1] = p->val;
if (p->left) queue[tail++] = p->left; //入队刚刚出队元素的左孩子子结点
if (p->right) queue[tail++] = p->right;
}
level++;
}
*returnSize = level; //记录总的层数
return ans;
}
Leetcode 104. 二叉树的最大深度
【思路】递归遍历二叉树节点,同时记录深度。
【代码】
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int ans = 0;
void func(TreeNode *p, int depth) {
if (p == nullptr) return ;
ans = max(ans, depth);
func(p->left, depth + 1);
func(p->right, depth + 1);
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
func(root, 1);
return ans;
}
};
Leetcode 107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
【思路】思路同Leetcode102题,只是最后将结果进行反转。
【代码】
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
/**
* Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize.
* The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array.
* Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
#define max 1024
int** levelOrderBottom(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
if (root == NULL) {
*returnSize = 0;
return NULL;
}
struct TreeNode **queue = (struct TreeNode **)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode *) * max);
int head = 0, tail = 0, count = 0, level = 0;
*returnColumnSizes = malloc(sizeof(int) * max);//一维数组
int **ans = (int **)malloc(sizeof(int *) * max);
queue[tail++] = root;
count++;
while (head != tail) {
count = tail - head; //每层节点个数
(*returnColumnSizes)[level] = count; //记录level层的节点个数
ans[level] = malloc(sizeof(int) * count);//开辟空间存储每一层的每个节点
for (int i = 1; i <= count; i++) {
struct TreeNode *p = queue[head++];
ans[level][i - 1] = p->val;
if (p->left) queue[tail++] = p->left;
if (p->right) queue[tail++] = p->right;
}
level++;
}
*returnSize = level;
for (int i = 0, j = level- 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
//交换层
int *temp1 = ans[i];
ans[i] = ans[j];
ans[j] = temp1;
//交换每一层的节点个数
int *temp2 = (*returnColumnSizes)[i];
(*returnColumnSizes)[i] = (*returnColumnSizes)[j];
(*returnColumnSizes)[j] = temp2;
}
return ans;
}
Leetcode 110.平衡二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
int height(struct TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
return fmax(height(root->left), height(root->right)) + 1;
}
bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){
if (root == NULL) return true;
return fabs(height(root->left) - height(root->right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right);
}
Leetcode 111.二叉树的最小深度
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
//深搜 DFS
int minDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
if (root == NULL) return 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) return 1;
int ans = INT_MAX;
if (root->left != NULL) ans = fmin(ans, minDepth(root->left));
if (root->right != NULL) ans = fmin(ans, minDepth(root->right));
return ans + 1;
}
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
//广搜:此处使用了数组实现队列,可以使用链表实现更节省空间
struct QueueNode {
int head, tail;
struct TreeNode **data;
int capacity;
};
struct QueueNode *init(int n) {
struct QueueNode *node = (struct QueueNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct QueueNode));
node->head = 0;
node->tail = 0;
node->data = (struct TreeNode **)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode *) * n);
node->capacity = n;
return node;
}
int minDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
if (root == NULL) return 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) return 1;
struct QueueNode *que = init(100000);
que->data[(que->tail)++] = root;
int depth = 1;
while (que->head != que->tail) {
int size = (que->tail - que->head); //计算队列中的元素
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { //处理每层的节点
struct TreeNode *temp = que->data[que->head++];
if (temp->left != NULL) {
que->data[(que->tail)++] = temp->left;
}
if (temp->right != NULL) {
que->data[(que->tail)++] = temp->right;
}
if (temp->left == NULL && temp->right == NULL) {
return depth;
}
}
depth++;
}
return false;
}
Leetcode 112. 路径总和
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
if (root == NULL) return false;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && root->val == targetSum) return true;
return hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->val);
}
Leetcode 226. 翻转二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root){
if (root == NULL) return NULL;
struct TreeNode *left = root->left;
root->left = root->right;
root->right = left;
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
return root;
}
Leetcode 235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
【思路】一次遍历。利用二叉搜索树的性质,分为三种情况:
- 如果当前节点大于
p和q的值,则p和q的最近公共祖先在当前节点的左子树; - 如果当前节点小于
p和q的值,则p和q的最近公共祖先在当前节点的右子树; - 如果上述情况都不满足,则当前节点就是"分岔节点",此时要么
p和q在当前节点的不同子树中,要么其中一个节点就是当前节点。
【代码】
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) {
struct TreeNode *ancestor = root;
while (true) {
if (ancestor->val > p->val && ancestor->val > q->val) {
ancestor = ancestor->left;
} else if (ancestor->val < p->val && ancestor->val < q->val) {
ancestor = ancestor->right;
} else {
break;
}
}
return ancestor;
}
Leetcode 257.二叉树的所有路径
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
//深搜
void construct_paths(TreeNode *root, string path, vector<string> &paths) {
if (root != nullptr) {
path += to_string(root->val);
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) { //当前节点是叶子节点
paths.push_back(path); //路径加入到答案中
} else {
path += "->"; //当前节点不是叶子节点,继续递归遍历
construct_paths(root->left, path, paths);
construct_paths(root->right, path, paths);
}
}
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string> ans;
construct_paths(root, "", ans);
return ans;
}
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
//广搜
typedef struct {
TreeNode *node;
string val;
} Node;
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string> ans;
queue<Node> que;
que.push({root, to_string(root->val)});
while (!que.empty()) {
TreeNode *node = que.front().node;
string path = que.front().val;
que.pop();
if (node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr) {
ans.push_back(path);
} else {
if (node->left != nullptr) {
que.push({node->left, path + "->" + to_string(node->left->val)});
}
if (node->right != nullptr) {
que.push({node->right, path + "->" + to_string(node->right->val)});
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Leetcode 297.二叉树的序列化与反序列化
【思路】深搜,先序遍历得到先序序列,反序列化就根据先序序列得到一棵树。
【代码】官方题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Codec {
public:
//深搜,先序遍历得到序列
void rserialize(TreeNode *root, string &str) {
if (root == nullptr) {
str += "None,";
} else {
str += to_string(root->val) + ",";
rserialize(root->left, str);
rserialize(root->right, str);
}
}
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
string ret;
rserialize(root, ret);
return ret;
}
//根据"None"解析先序遍历的序列得到一棵树
TreeNode *rdeserialize(list<string> &dataArray) {
if (dataArray.front() == "None") {
dataArray.erase(dataArray.begin());
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(stoi(dataArray.front()));
dataArray.erase(dataArray.begin());
root->left = rdeserialize(dataArray);
root->right = rdeserialize(dataArray);
return root;
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
list<string> dataArray;
string str;
for (auto &ch: data) {
if (ch == ',') {
dataArray.push_back(str);
str.clear();
} else {
str.push_back(ch);
}
}
if (!str.empty()) {
dataArray.push_back(str);
str.clear();
}
return rdeserialize(dataArray);
}
};
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec ser, deser;
// TreeNode* ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root));
【复杂度分析】
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。序列化和反序列化函数中,每个节点只访问一次,因此时间复杂度是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),其中 n n n 为节点数,即树的大小。
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。序列化和反序列化函数中,递归会用到栈空间,递归的深度即为空间复杂度,故渐进空间复杂度为 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。








 本文介绍了树的基本概念,包括树的深度、高度和度,重点讲解了二叉树的性质,如度为0的结点比度为2的结点多1个,并展示了二叉树的遍历方式。此外,讨论了如何从广义表构建二叉树,以及二叉搜索树的插入、遍历和相关LeetCode题目,如相同树、对称二叉树、层序遍历等。
本文介绍了树的基本概念,包括树的深度、高度和度,重点讲解了二叉树的性质,如度为0的结点比度为2的结点多1个,并展示了二叉树的遍历方式。此外,讨论了如何从广义表构建二叉树,以及二叉搜索树的插入、遍历和相关LeetCode题目,如相同树、对称二叉树、层序遍历等。
















 2225
2225

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








