标准连接池的实现
javax.sql.DataSource.
Java.sql.*
DataSource 接口由驱动程序供应商实现。共有三种类型的实现:
1. 基本实现 - 生成标准的 Connection 对象 – 一个DataSource数据源中,只有一个Connection ,这个不是池管理。2. 连接池实现 - 生成自动参与连接池的 Connection 对象。
3. 分布式事务实现 - 生成一个 Connection 对象,该对象可用于分布式事务,大多数情况下总是参与连接池。JTA.jar – SUN。
标准的连接池,要求:
1:实现dataSource接口。2:声明一个集合类用于管理多个连接。
3:必须要拥有一种能力,回收连接。
4:必须要实现一个方法,getConnection以获取一个连接。
6:在一个程序中,要求只拥有一个DataSource实例就可以了。
以下是具体的实现:
/**
* 标准的连接
*/
public class DBPool implements DataSource {
//声明一个池管理对象
private LinkedList<Connection> pool = new LinkedList<Connection>();
//在初始化这个DataSourc的子类时在构造方法设置多个连接
public DBPool(){
try{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql:///db909?characterEncoding=UTf8";
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root","1234");
//将生成的这个连接。放到pool
pool.add(con);
}
}catch(Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(),e);
}
}
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return pool.removeFirst();
}
///其他的方法。不实现
}
2:动态实现连接的回收
/**
* 标准的连接
*/
public class DBPool implements DataSource {
//声明一个池管理对象
private LinkedList<Connection> pool = new LinkedList<Connection>();
//在初始化这个DataSourc的子类时在构造方法设置多个连接
public DBPool(){
try{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql:///db909?characterEncoding=UTf8";
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
final Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root","1234");
Object proxyedConn = //1类加载器
Proxy.newProxyInstance(DBPool.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{Connection.class}, //2被代理的类的父接口
new InvocationHandler() { //3句柄,获取被代理的类的方法
public Object invoke(Object proxyedConnection, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
if(method.getName().equals("close")){
synchronized (pool) {
pool.addLast((Connection) proxyedConnection);
pool.notify();
}
return null;
}
//目标方法的返回值 表示con里面的方法正在被调用
Object returnValue=method.invoke(con, args);
return returnValue; 第一个参数:你要代理的对象
第二个参数:
}
});
pool.add((Connection) proxyedConn);
}
}catch(Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(),e);
}
}
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
synchronized (pool) {
if(pool.size()==0){
try {
pool.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return getConnection();
}
Connection con = pool.removeFirst();
System.err.println("siize:"+pool.size());
return con;
}
}
}
以下通过包装实现对close方法的修改,以回收连接
1:实现Connection接口,拥有一个Connection的成员。
2:修改close方法。
3:其他的方法都调用成员变量的connection。
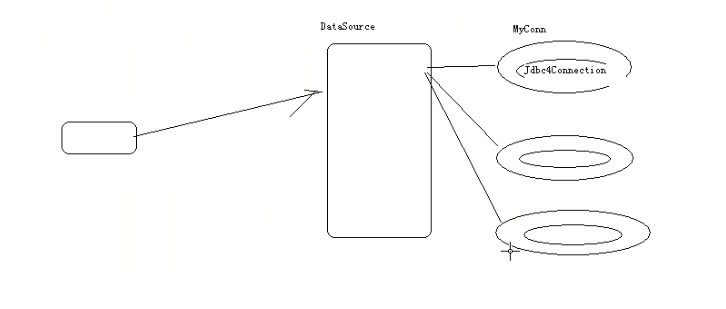
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource {
private LinkedList<Connection> pool = new LinkedList<Connection>();
public MyDataSource() {
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql:///db909?characterEncoding=UTf8";
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
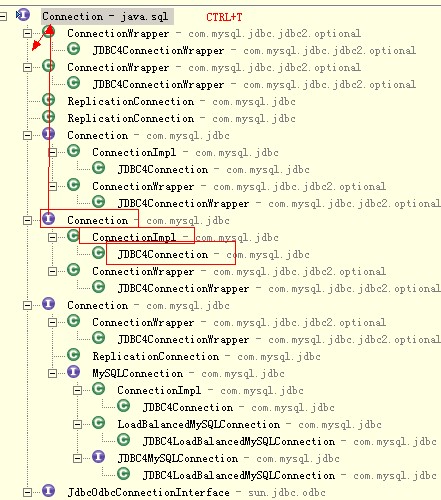
// 创建原生的连接,// com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@8888
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root",
"");
// 声明包装类
MyConn conn = new MyConn(con);
pool.add(conn);// 将包装类添加到池中去
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 此方法来自于datasource,用于返回一个连接
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
synchronized (pool) {
if (pool.size() == 0) {
try {
pool.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return getConnection();
}
Connection con = pool.removeFirst();
System.err.println("siize:" + pool.size());
return con;
}
}
// 以下包装connection
class MyConn implements Connection {
// 声明被包装类的成员
private Connection conn;
// 通过构造接收MySql的connection的对象JDBC4Connection@8888
public MyConn(Connection con) {
this.conn = con;
}
// 关闭连接
public void close() throws SQLException {
synchronized (pool) {
// 有人调用了关闭方法,不能关
System.err.println("有人还连接了。。。。" + this);
pool.add(this);
pool.notify();
}
}
// ****************************************************************
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return conn.unwrap(iface);
}
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return conn.isWrapperFor(iface);
}
public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {
return conn.createStatement();
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql)
throws SQLException {
return conn.prepareStatement(sql);
}
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException {
return conn.prepareCall(sql);
}
public String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException {
return conn.nativeSQL(sql);
}
public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException {
conn.setAutoCommit(autoCommit);
}
public boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException {
return conn.getAutoCommit();
}
public void commit() throws SQLException {
conn.commit();
}
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
conn.rollback();
}
public boolean isClosed() throws SQLException {
return conn.isClosed();
}
public DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException {
return conn.getMetaData();
}
public void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException {
conn.setReadOnly(readOnly);
}
public boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException {
return conn.isReadOnly();
}
public void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException {
conn.setCatalog(catalog);
}
public String getCatalog() throws SQLException {
return conn.getCatalog();
}
public void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException {
conn.setTransactionIsolation(level);
}
public int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException {
return conn.getTransactionIsolation();
}
public SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException {
return conn.getWarnings();
}
public void clearWarnings() throws SQLException {
conn.clearWarnings();
}
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType,
int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return conn.createStatement(resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency);
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql,
int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency)
throws SQLException {
return conn.prepareStatement(sql, resultSetConcurrency);
}
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType,
int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return conn.prepareCall(sql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency);
}
public Map<String, Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException {
return conn.getTypeMap();
}
public void setTypeMap(Map<String, Class<?>> map) throws SQLException {
conn.setTypeMap(map);
}
public void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException {
conn.setHoldability(holdability);
}
public int getHoldability() throws SQLException {
return conn.getHoldability();
}
public Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException {
return conn.setSavepoint();
}
public Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException {
return conn.setSavepoint(name);
}
public void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
conn.rollback(savepoint);
}
public void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
conn.releaseSavepoint(savepoint);
}
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType,
int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability)
throws SQLException {
return conn.createStatement(resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency,
resultSetHoldability);
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql,
int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency,
int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return conn.prepareStatement(sql, resultSetType,
resultSetConcurrency, resultSetHoldability);
}
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType,
int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability)
throws SQLException {
return conn.prepareCall(sql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency,
resultSetHoldability);
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql,
int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException {
return conn.prepareStatement(sql, autoGeneratedKeys);
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql,
int[] columnIndexes) throws SQLException {
return conn.prepareStatement(sql, columnIndexes);
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql,
String[] columnNames) throws SQLException {
return conn.prepareStatement(sql, columnNames);
}
public Clob createClob() throws SQLException {
return conn.createClob();
}
public Blob createBlob() throws SQLException {
return conn.createBlob();
}
public NClob createNClob() throws SQLException {
return conn.createNClob();
}
public SQLXML createSQLXML() throws SQLException {
return conn.createSQLXML();
}
public boolean isValid(int timeout) throws SQLException {
return conn.isValid(timeout);
}
public void setClientInfo(String name, String value)
throws SQLClientInfoException {
conn.setClientInfo(name, value);
}
public void setClientInfo(Properties properties)
throws SQLClientInfoException {
conn.setClientInfo(properties);
}
public String getClientInfo(String name) throws SQLException {
return conn.getClientInfo(name);
}
public Properties getClientInfo() throws SQLException {
return conn.getClientInfo();
}
public Array createArrayOf(String typeName, Object[] elements)
throws SQLException {
return conn.createArrayOf(typeName, elements);
}
public Struct createStruct(String typeName, Object[] attributes)
throws SQLException {
return conn.createStruct(typeName, attributes);
}
public void setSchema(String schema) throws SQLException {
conn.setSchema(schema);
}
public String getSchema() throws SQLException {
return conn.getSchema();
}
public void abort(Executor executor) throws SQLException {
conn.abort(executor);
}
public void setNetworkTimeout(Executor executor, int milliseconds)
throws SQLException {
conn.setNetworkTimeout(executor, milliseconds);
}
public int getNetworkTimeout() throws SQLException {
return conn.getNetworkTimeout();
}
//**********************************
}
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password)
throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}}
用包装处理get方式的乱码
public class BaseServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
String methodName = req.getParameter("cmd");
try{
Method mm = this.getClass().getMethod(methodName,HttpServletRequest.class,HttpServletResponse.class);
//声明包装类
MyRequest mr = new MyRequest(req);
mm.invoke(this,mr,resp);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//包装request
class MyRequest extends HttpServletRequestWrapper{
private HttpServletRequest req;
public MyRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
super(request);
this.req=request;
}
//修改getparameter方法
@Override
public String getParameter(String name) {
String value = req.getParameter(name);
if(req.getMethod().equals("GET")){
System.err.println("转码");
try{
value = new String(value.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"),"UTF-8");
}catch(Exception e){
}
}
return value;
}
@Override
public String[] getParameterValues(String name) {
String[] vals = req.getParameterValues(name);
if(req.getMethod().equals("GET")){
for(int i=0;i<vals.length;i++){
try {
vals[i] = new String(vals[i].getBytes("ISO-8859-1"),req.getCharacterEncoding());
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return vals;
}
@Override
public Map getParameterMap() {
Map<String,String[]> mm = req.getParameterMap();
if(req.getMethod().equals("GET")){
Iterator<String[]> it= mm.values().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String[] ss = it.next();
for(int i=0;i<ss.length;i++){
try {
ss[i] = new String(ss[i].getBytes("ISO-8859-1"),req.getCharacterEncoding());
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
return mm;
}
}
小总结
代理:必须要根据给定的接口,在内存中创建这个接口的子类。$Proxy0。
包装:不需要接口,但声明声明一个类,变成被包装类的子类,同时拥有一个被包装类的成员。
2:代理基本代码:
Object proxyedObj =
Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader,
New class[]{被代理的类的接口数组.class},
New InvocationHandler(){//执行句柄
Public Object invode(Object 代理,Method 方法反射,object[] args){
Reutrn method.invode(被代理类,args);
}
}
3:包装:
如果一个类是某个类的包装类,则:
A extends B{
Privet B b;
}
4:什么情况下,使用包装,什么情况下使用代理
如果官方(SUN)提供了包装类适配器,则应该优先使用包装。如HttpServletRequest,它的包装类就是HtpServletRequestWraper.
如果官方没有提供包装类的适配器,则可以使用动态代理。如Connection。
5:我们已经学习过的类中哪些是包装模式:
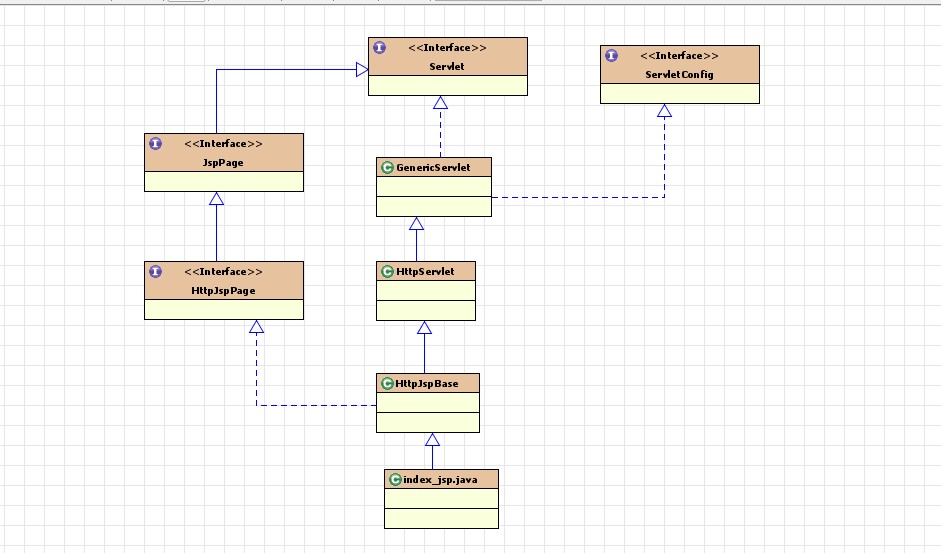
GenericServlet- 包装模式。
public abstract class GenericServlet
implements Servlet, ServletConfig, java.io.Serializable
private transient ServletConfig config;
IO
New BufferedReader(New FileReader(new FileInpjutStreamRreader(new FileInputSteam()));






















 2179
2179

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








