转载:http://weizhulin.blog.51cto.com/1556324/311457
大家好我们今天的教程是在Android 教程中自定义View 的学习,对于初学着来说,他们习惯了Android 传统的页面布局方式,如下代码:
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
</LinearLayout>
当然上面的布局方式可以帮助我们完成简单应用的开发了,但是如果你想写一个复杂的应用,这样就有点牵强了,大家不信可以下源码都研究看看,高手写的布局方式,如上面的布局高手通常是这样写的:
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<A>
<B></B>
</A>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<A>
<B></B>
</A>
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
其中A extends LinerLayout, B extends TextView.
其中A extends LinerLayout, B extends TextView.
其中A extends LinerLayout, B extends TextView.
其中A extends LinerLayout, B extends TextView.
为了帮助大家更容易理解,我写了一个简单的Demo ,具体步骤如下:
首先新建一个Android 工程 命名为ViewDemo .
然后自定义一个View 类,命名为MyView(extends View) .代码如下:
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
package com.android.tutor;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.graphics.Paint.Style;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class MyView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
private Context mContext;
private static final String mString = "Welcome to Mr Wei's blog";
public MyView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyView(Context context,AttributeSet attr)
{
super(context,attr);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDraw(canvas);
mPaint = new Paint();
//设置画笔颜色
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
//设置填充
mPaint.setStyle(Style.FILL);
//画一个矩形,前俩个是矩形左上角坐标,后面俩个是右下角坐标
canvas.drawRect(new Rect(10, 10, 100, 100), mPaint);
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
//绘制文字
canvas.drawText(mString, 10, 110, mPaint);
}
}
package com.android.tutor;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.graphics.Paint.Style;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class MyView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
private Context mContext;
private static final String mString = "Welcome to Mr Wei's blog";
public MyView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyView(Context context,AttributeSet attr)
{
super(context,attr);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDraw(canvas);
mPaint = new Paint();
//设置画笔颜色
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
//设置填充
mPaint.setStyle(Style.FILL);
//画一个矩形,前俩个是矩形左上角坐标,后面俩个是右下角坐标
canvas.drawRect(new Rect(10, 10, 100, 100), mPaint);
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
//绘制文字
canvas.drawText(mString, 10, 110, mPaint);
}
}- 然后将我们自定义的View 加入到main.xml 布局文件中,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<com.android.tutor.MyView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<com.android.tutor.MyView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
/>
</LinearLayout>
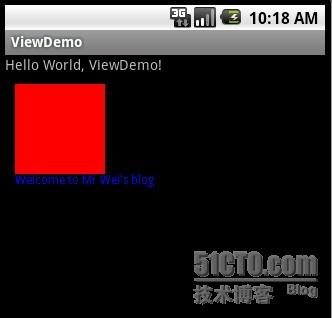
最后执行之,效果如下图:





















 625
625

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








