You are given the following points with integer coordinates on the plane:M0, A0, A1, ..., An - 1, wheren is odd number. Now we define the following infinite sequence of pointsMi:Mi is symmetric toMi - 1 according (for every natural numberi). Here point B is symmetric toA according M, ifM is the center of the line segment AB. Given index j find the pointMj.
(for every natural numberi). Here point B is symmetric toA according M, ifM is the center of the line segment AB. Given index j find the pointMj.
On the first line you will be given an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105), which will be odd, andj (1 ≤ j ≤ 1018), wherej is the index of the desired point. The next line contains two space separated integers, the coordinates ofM0. After thatn lines follow, where the i-th line contain the space separated integer coordinates of the pointAi - 1. The absolute values of all input coordinates will not be greater then1000.
On a single line output the coordinates of Mj, space separated.
3 4
0 0
1 1
2 3
-5 3
14 0
3 1
5 5
1000 1000
-1000 1000
3 100
1995 1995
小伙伴为了明天的轻工校赛而找的比赛题目,一共三题,难度好像都不小啊。。。
这个题题意比较难理解,就是给出n,j;之后再给出m[0]的坐标,a[0]-a[n-1]的坐标
让你输出m[j]的坐标,其中m[i]和m[i-1]关于a[(i-1)%n]对称
因为j最大为10的18次方,所以想到找规律。。。
我就把两个样例的m[1]-m[6]都列出来,结果发现m[6]和m[1]重合了!!!
就是说m[i%(2*n)]==m[i]
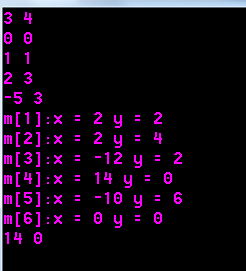
代码如下:
#include <map> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cstdlib> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #define esp 1e-9 #define MAXN 200010 #define ll long long #define INF 0x7FFFFFFF #define BUG system("pause") #define SW(a,b) a^=b;b^=a;a^=b; using namespace std; struct Point{ int x, y; }m[MAXN], a[MAXN]; int main(void){ int n; ll j; while(cin >> n >> j) { cin >> m[0].x >> m[0].y; for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){ cin >> a[i].x >> a[i].y; } for(int i=0; i<2*n; ++i){ m[i+1].x = 2*a[i%n].x-m[i].x; m[i+1].y = 2*a[i%n].y-m[i].y; cout << "m[" << i+1 << "]:x = " << m[i+1].x << " y = " << m[i+1].y << endl; } cout << m[j%(2*n)].x << " " << m[j%(2*n)].y << endl; } return 0; }








 针对一个平面几何问题,通过寻找序列点Mj的规律来解决输入坐标后的大规模索引查询问题。该问题中,一系列点Mi根据特定规则对称变换生成,目标是找出任意指定索引j对应的点Mj坐标。
针对一个平面几何问题,通过寻找序列点Mj的规律来解决输入坐标后的大规模索引查询问题。该问题中,一系列点Mi根据特定规则对称变换生成,目标是找出任意指定索引j对应的点Mj坐标。
















 4026
4026

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








