个人博客原文:Thrift Server介绍及代码实现
摘要:本文介绍Thrift几个Server,以及其代码的实现。
Thrift为服务器端提供了多种工作模式,本文中将涉及以下5中工作模式:TSimpleServer、TNonblockingServer、THsHaServer、TThreadPoolServer、TThreadedSelectorServer,这5中工作模式的详细工作原理如下:
TSimpleServer
介绍
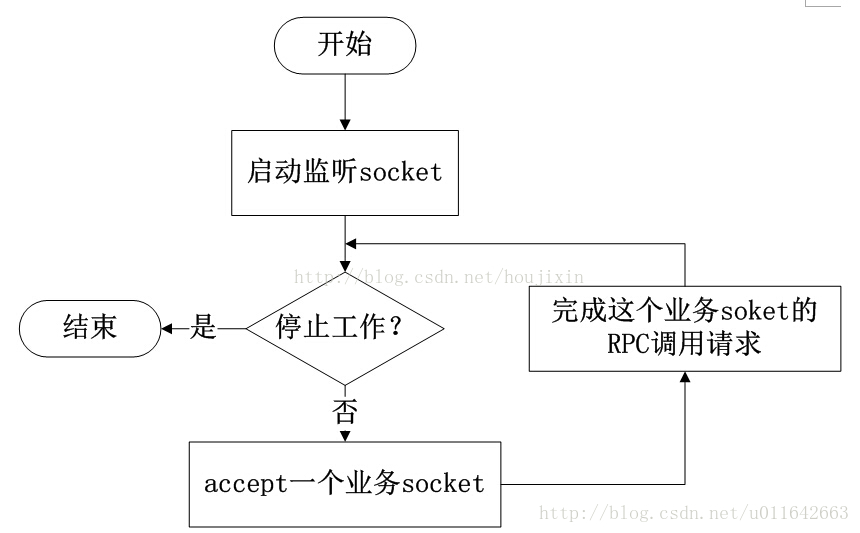
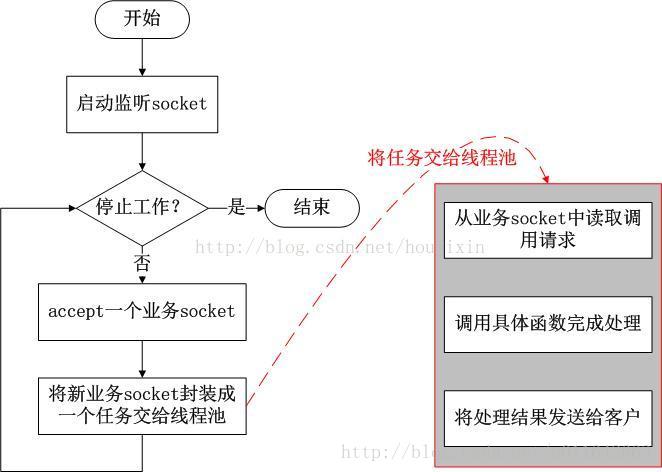
TSimpleServer的工作模式只有一个工作线程,循环监听新请求的到来并完成对请求的处理,它只是在简单的演示时候使用,它的工作方式如下图所示:
TSimpleServer的工作模式采用最简单的阻塞IO,实现方法简洁明了,便于理解,但是一次只能接收和处理一个socket连接,效率比较低,主要用于演示Thrift的工作过程,在实际开发过程中很少用到它。
代码
上篇博客已经有了
Thrift 简单例子
TNonblockingServer
介绍
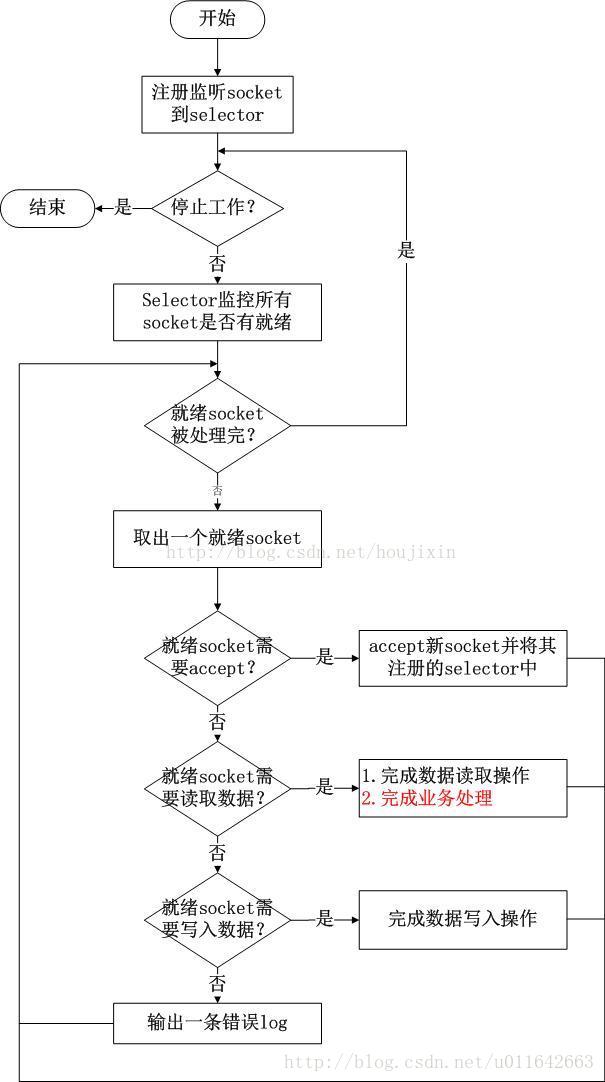
TNonblockingServer工作模式,该模式也是单线程工作,但是该模式采用NIO的方式,所有的socket都被注册到selector中,在一个线程中通过seletor循环监控所有的socket,每次selector结束时,处理所有的处于就绪状态的socket,对于有数据到来的socket进行数据读取操作,对于有数据发送的socket则进行数据发送,对于监听socket则产生一个新业务socket并将其注册到selector中,如下图所示:
上图中读取数据之后的业务处理就是根据读取到的调用请求,调用具体函数完成处理,只有完成函数处理才能进行后续的操作;
TNonblockingServer模式优点:
相比于TSimpleServer效率提升主要体现在IO多路复用上,TNonblockingServer采用非阻塞IO,同时监控多个socket的状态变化;
TNonblockingServer模式缺点:
TNonblockingServer模式在业务处理上还是采用单线程顺序来完成,在业务处理比较复杂、耗时的时候,例如某些接口函数需要读取数据库执行时间较长,此时该模式效率也不高,因为多个调用请求任务依然是顺序一个接一个执行。
代码
Server端:
public class ThriftServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 设置服务器端口
TNonblockingServerSocket serverTransport = new TNonblockingServerSocket(9090);
// 设置二进制协议工厂
Factory protocolFactory = new TBinaryProtocol.Factory();
// 处理器关联业务实现
Processor<TestService.Iface> processor = new TestService.Processor<TestService.Iface>(
new TestServiceImpl());
TNonblockingServer.Args args = new TNonblockingServer.Args(serverTransport)
.processor(processor)
.protocolFactory(protocolFactory);
TServer server = new TNonblockingServer(args);
System.out.println("开启thrift服务器,监听端口:9090");
server.serve();
} catch (TTransportException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Client端:
public class ThriftClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
TProtocolFactory protocolFactory = new TBinaryProtocol.Factory();
TAsyncClientManager clientManager = new TAsyncClientManager();
TNonblockingSocket transport = new TNonblockingSocket("localhost", 9090);
TestService.AsyncClient client = new TestService.AsyncClient(protocolFactory, clientManager, transport);
Test test = new Test();
test.setBool_(true);
test.setI8_((byte) 1);
test.setI16_((short) 2);
test.setI32_(3);
test.setI64_(4L);
test.setDouble_(5.0);
test.setString_("abc");
test.setBinary_("abc".getBytes());
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
client.getBool(test, new AsynCallback(latch));
boolean wait;
try {
wait = latch.await(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("latch.await =:" + wait);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
transport.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (TException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}运行结果:
Client端:
Received 0
onComplete
AsynCall result =:true
latch.await =:true
Server端:
开启thrift服务器,监听端口:9090
TestServiceImpl.getBool() + true
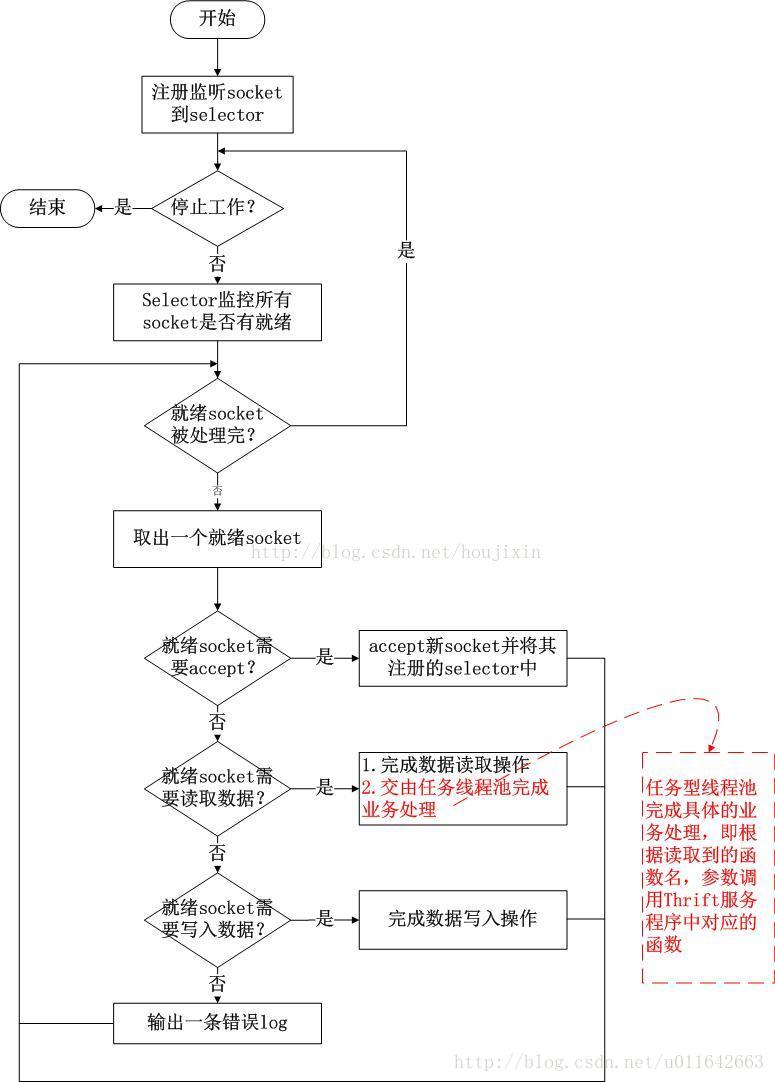
THsHaServer模式(半同步半异步)
介绍
THsHaServer类是TNonblockingServer类的子类,在TNonblockingServer模式中,采用一个线程来完成对所有socket的监听和业务处理,造成了效率的低下,THsHaServer模式的引入则是部分解决了这些问题。THsHaServer模式中,引入一个线程池来专门进行业务处理,如下图所示;
THsHaServer的优点:
与TNonblockingServer模式相比,THsHaServer在完成数据读取之后,将业务处理过程交由一个线程池来完成,主线程直接返回进行下一次循环操作,效率大大提升;
THsHaServer的缺点:
由上图可以看出,主线程需要完成对所有socket的监听以及数据读写的工作,当并发请求数较大时,且发送数据量较多时,监听socket上新连接请求不能被及时接受。
代码
Server端:
public class ThriftServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
TNonblockingServerSocket serverTransport = new TNonblockingServerSocket(9090);
TTransportFactory transportFactory = new TFramedTransport.Factory();
Factory protocolFactory = new TBinaryProtocol.Factory();
Processor<TestService.Iface> processor = new TestService.Processor<TestService.Iface>(
new TestServiceImpl());
Args args = new Args(serverTransport)
.processor(processor)
.transportFactory(transportFactory)
.protocolFactory(protocolFactory);
TServer server = new THsHaServer(args);
System.out.println("开启thrift服务器,监听端口:9090");
server.serve();
} catch (TTransportException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Client 端
public class ThriftClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
TProtocolFactory protocolFactory = new TBinaryProtocol.Factory();
TAsyncClientManager clientManager = new TAsyncClientManager();
TNonblockingSocket transport = new TNonblockingSocket("localhost", 9090);
TestService.AsyncClient client = new TestService.AsyncClient(protocolFactory, clientManager, transport);
Test test = new Test();
test.setBool_(true);
test.setI8_((byte) 1);
test.setI16_((short) 2);
test.setI32_(3);
test.setI64_(4L);
test.setDouble_(5.0);
test.setString_("abc");
test.setBinary_("abc".getBytes());
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
client.getBool(test, new AsynCallback(latch));
boolean wait;
try {
wait = latch.await(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("latch.await =:" + wait);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
transport.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (TException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}异步处理类:
class AsynCallback implements AsyncMethodCallback<Boolean>{
private CountDownLatch latch;
public AsynCallback(CountDownLatch latch) {
this.latch = latch;
}
public void onComplete(Boolean response) {
System.out.println("onComplete");
try {
// Thread.sleep(1000L * 1);
System.out.println("AsynCall result =:" + response);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
}
public void onError(Exception exception) {
System.out.println("onError :" + exception.getMessage());
latch.countDown();
}
} 运行结果:
Client端:
Received 0
onComplete
AsynCall result =:true
latch.await =:true
Server端:
开启thrift服务器,监听端口:9090
TestServiceImpl.getBool() + true
TThreadPoolServer
介绍
TThreadPoolServer模式采用阻塞socket方式工作,,主线程负责阻塞式监听“监听socket”中是否有新socket到来,业务处理交由一个线程池来处理,如下图所示:
TThreadPoolServer模式优点:
线程池模式中,数据读取和业务处理都交由线程池完成,主线程只负责监听新连接,因此在并发量较大时新连接也能够被及时接受。线程池模式比较适合服务器端能预知最多有多少个客户端并发的情况,这时每个请求都能被业务线程池及时处理,性能也非常高。
TThreadPoolServer模式缺点:
线程池模式的处理能力受限于线程池的工作能力,当并发请求数大于线程池中的线程数时,新请求也只能排队等待。
代码
Server端:
public ThriftServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
TServerSocket serverTransport = new TServerSocket(9090);
Factory protocolFactory = new TBinaryProtocol.Factory();
Processor<TestService.Iface> processor = new TestService.Processor<TestService.Iface>(new TestServiceImpl());
TThreadPoolServer.Args args = new TThreadPoolServer.Args(serverTransport)
.protocolFactory(protocolFactory)
.processor(processor)
.minWorkerThreads(1000).maxWorkerThreads(1000);
TServer server = new TThreadPoolServer(args);
System.out.println("开启thrift服务器,监听端口:9090");
server.serve();
} catch (TTransportException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Client端:
public ThriftClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 设置调用的服务地址-端口
TTransport transport = new TSocket("localhost", 9090);
// 使用二进制协议
TProtocol protocol = new TBinaryProtocol(transport);
// 使用的接口
TestService.Client client = new TestService.Client(protocol);
// 打开socket
transport.open();
Test test = new Test();
test.setBool_(true);
test.setI8_((byte) 1);
test.setI16_((short) 2);
test.setI32_(3);
test.setI64_(4L);
test.setDouble_(5.0);
test.setString_("abc");
test.setBinary_("abc".getBytes());
System.out.println("Client getBool()" + client.getBool(test));
System.out.println("Client getI8()" + client.getI8(test));
System.out.println("Client getI16()" + client.getI16(test));
System.out.println("Client getI32()" + client.getI32(test));
System.out.println("Client getI64()" + client.getI64(test));
System.out.println("Client getDouble()" + client.getDouble(test));
System.out.println("Client getString()" + client.getString(test));
System.out.println("Client getBinary()" + client.getBinary(test));
transport.close();
} catch (TTransportException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (TException te) {
te.printStackTrace();
}
}
}运行结果:
Client端:
Received 1
Client getBool()true
Received 2
Client getI8()1
Received 3
Client getI16()2
Received 4
Client getI32()3
Received 5
Client getI64()4
Received 6
Client getDouble()5.0
Received 7
Client getString()abc
Received 8
Client getBinary()java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=0 lim=3 cap=3]
Server端:
开启thrift服务器,监听端口:9090
TestServiceImpl.getBool() + true
TestServiceImpl.getI8() + 1
TestServiceImpl.getI16() + 2
TestServiceImpl.getI32() + 3
TestServiceImpl.getI64() + 4
TestServiceImpl.getDouble() + 5.0
TestServiceImpl.getString() + abc
TestServiceImpl.getBinary() + java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=0 lim=3 cap=3]
TThreadedSelectorServer
介绍
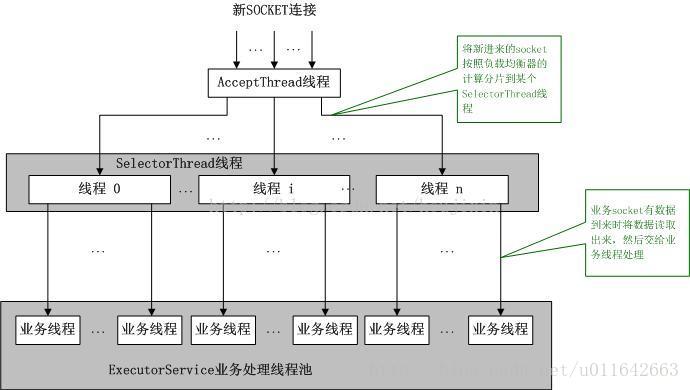
TThreadedSelectorServer模式是目前Thrift提供的最高级的模式,它内部有如果几个部分构成:
1. 一个AcceptThread线程对象,专门用于处理监听socket上的新连接;
2. 若干个SelectorThread对象专门用于处理业务socket的网络I/O操作,所有网络数据的读写均是有这些线程来完成;
3. 一个负载均衡器SelectorThreadLoadBalancer对象,主要用于AcceptThread线程接收到一个新socket连接请求时,决定将这个新连接请求分配给哪个SelectorThread线程。
4. 一个ExecutorService类型的工作线程池,在SelectorThread线程中,监听到有业务socket中有调用请求过来,则将请求读取之后,交个ExecutorService线程池中的线程完成此次调用的具体执行;
如上图所示,TThreadedSelectorServer模式中有一个专门的线程AcceptThread用于处理新连接请求,因此能够及时响应大量并发连接请求;另外它将网络I/O操作分散到多个SelectorThread线程中来完成,因此能够快速对网络I/O进行读写操作,能够很好地应对网络I/O较多的情况;TThreadedSelectorServer对于大部分应用场景性能都不会差,因此,如果实在不知道选择哪种工作模式,使用TThreadedSelectorServer就可以。
代码
Server端:
public class ThriftServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 设置服务器端口
TNonblockingServerSocket serverTransport = new TNonblockingServerSocket(9090);
// 设置二进制协议工厂
Factory protocolFactory = new TBinaryProtocol.Factory();
// 处理器关联业务实现
Processor<TestService.Iface> processor = new TestService.Processor<TestService.Iface>(new TestServiceImpl());
TThreadedSelectorServer.Args args = new TThreadedSelectorServer.Args(serverTransport);
args.processor(processor);
args.protocolFactory(protocolFactory);
TServer server = new TThreadedSelectorServer(args);
System.out.println("开启thrift服务器,监听端口:9090");
server.serve();
} catch (TTransportException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Client端:
public class ThriftClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
TProtocolFactory protocolFactory = new TBinaryProtocol.Factory();
TAsyncClientManager clientManager = new TAsyncClientManager();
TNonblockingSocket transport = new TNonblockingSocket("localhost", 9090);
TestService.AsyncClient client = new TestService.AsyncClient(protocolFactory, clientManager, transport);
Test test = new Test();
test.setBool_(true);
test.setI8_((byte) 1);
test.setI16_((short) 2);
test.setI32_(3);
test.setI64_(4L);
test.setDouble_(5.0);
test.setString_("abc");
test.setBinary_("abc".getBytes());
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
client.getBool(test, new AsynCallback(latch));
boolean wait;
try {
wait = latch.await(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("latch.await =:" + wait);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
transport.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (TException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}异步处理类:
class AsynCallback implements AsyncMethodCallback<Boolean>{
private CountDownLatch latch;
public AsynCallback(CountDownLatch latch) {
this.latch = latch;
}
public void onComplete(Boolean response) {
System.out.println("onComplete");
try {
// Thread.sleep(1000L * 1);
System.out.println("AsynCall result =:" + response);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
}
public void onError(Exception exception) {
System.out.println("onError :" + exception.getMessage());
latch.countDown();
}
} 运行结果:
Client端:
Received 0
onComplete
AsynCall result =:true
latch.await =:true
Server端:
开启thrift服务器,监听端口:9090
TestServiceImpl.getBool() + true
上面代码接口的编写:
testService.thrift
struct Test {
1: required bool bool_; //required 必须填充也必须序列化
2: optional i8 i8_; //optional 不填充则不序列化
3: i16 i16_;
4: i32 i32_;
5: i64 i64_;
6: double double_;
7: string string_;
8: binary binary_;
}
service TestService {
void getVoid(1:Test test);
bool getBool(1:Test test);
i8 getI8(1:Test test);
i16 getI16(1:Test test);
i32 getI32(1:Test test);
i64 getI64(1:Test test);
double getDouble(1:Test test);
string getString(1:Test test);
binary getBinary(1:Test test);
}






















 1599
1599











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








