首先IOC 有四步骤 初始化 - 定位 - 载入 - 解析 -注册
首先看一段配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.1.xsd">
<!-- 使用spring管理对象的创建,还有对象的依赖关系 -->
<bean id="userDao4Mysql" class="com.tgb.spring.dao.UserDao4MysqlImpl"/>
<bean id="userDao4Oracle" class="com.tgb.spring.dao.UserDao4OracleImpl"/>
<bean id="userManager" class="com.tgb.spring.manager.UserManagerImpl">
<!-- (1)userManager使用了userDao,Ioc是自动创建相应的UserDao实现,都是由容器管理-->
<!-- (2)在UserManager中提供构造函数,让spring将UserDao实现注入(DI)过来 -->
<!-- (3)让spring管理我们对象的创建和依赖关系,必须将依赖关系配置到spring的核心配置文件中 -->
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao4Oracle"></property>
</bean>
</beans>可以看出容器之中是根据配置文件自动桥接的 并且是注入的方式导入Dao层
public static void main(String[] args){
BeanFactory factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//到IOC容器中获取UserManager
UserManager userManager = (UserManager) factory.getBean("userManager");
//UserManager使用UserDao,在配置文件已经有依赖关系
userManager.addUser("jiuqiyuliang", "123456");
} 最后直接通过容器 或者可以理解成工厂模式调用dao层的方法
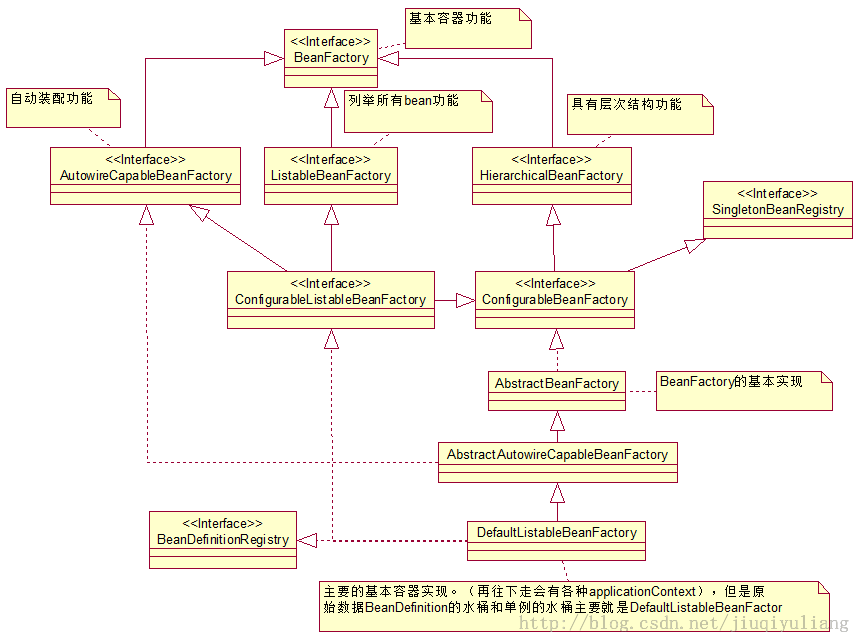
附上这一类接口层的关系图
ListableBeanFactory 接口表示这些 Bean 是可列表的 而 HierarchicalBeanFactory 表示的是这些 Bean 是有继承关系的 所以每一个接口都是有自己的用处的 具体的还是多查API 有很大帮助的
附上一个小栗子
public interface BeanFactory {
/**
* Used to dereference a {@link FactoryBean} instance and distinguish it from
* beans <i>created</i> by the FactoryBean.
* 对FactoryBean的转义定义,因为如果使用bean的名字检索FactoryBean得到的对象是工厂生成的对象,
* 如果需要得到工厂本身,需要转义
*/
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
* 根据bean的名字,获取在IOC容器中得到bean实例
*/
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
* 根据bean的名字和Class类型来得到bean实例,增加了类型安全验证机制。
*/
<T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
/**
* Return the bean instance that uniquely matches the given object type, if any.
* 根据Class类型来得到bean实例,增加了类型安全验证机制。
*/
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
*
*/
Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException;
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
*/
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException;
/**
* Does this bean factory contain a bean definition or externally registered singleton
* instance with the given name?
* 提供对bean的检索,看看是否在IOC容器有这个名字的bean
*/
boolean containsBean(String name);
/**
* Is this bean a shared singleton? That is, will {@link #getBean} always
* return the same instance?
* 根据bean名字得到bean实例,并同时判断这个bean是不是单例
*/
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Is this bean a prototype? That is, will {@link #getBean} always return
* independent instances?
*/
boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Check whether the bean with the given name matches the specified type.
* More specifically, check whether a {@link #getBean} call for the given name
* would return an object that is assignable to the specified target type.
*
*/
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, Class<?> targetType) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Determine the type of the bean with the given name. More specifically,
* determine the type of object that {@link #getBean} would return for the given name.
* 得到bean实例的Class类型
*/
Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Return the aliases for the given bean name, if any.
* All of those aliases point to the same bean when used in a {@link #getBean} call.
* 得到bean的别名,如果根据别名检索,那么其原名也会被检索出来
*/
String[] getAliases(String name);具体来看一两个方法吧
loadBeanDefinitions();//加载bean的定义,同样是通过用被指定的编码方式来读取流xml资源文件。同样返回定义的bean的数量
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
}
try {
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {//如果指定了编码方式,就用指定的编码为流的编码 inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}//这类调用该方式真正的做到了加载bean定义
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {//关闭流
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
}doLoadBeanDefinitions();该方法真正完成加载bean定义的工作
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {//取得xml文件的文档验证方式,比如dtd,xsd。
int validationMode = getValidationModeForResource(resource);//加载器加载xml文件。
Document doc = this.documentLoader.loadDocument(
inputSource, this.entityResolver, this.errorHandler, validationMode, this.namespaceAware);//调用下面介绍的方法注册bean到工厂
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}registerBeanDefinitions();这里完成注册bean到工厂的工作。
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
if (this.parserClass != null) {//拿到解析器负责从xml解析定义的bean,并负责将它们注册到工厂
XmlBeanDefinitionParser parser =
(XmlBeanDefinitionParser) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this.parserClass);
return parser.registerBeanDefinitions(this, doc, resource);
}//若解析器为null,就创建一个documentReader ,把解析bean定义并注册bean到工厂的工作交给它完成
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}其实仔细看一下的话 这个和之前那个源码解析的差不多 大概就是这么个顺序
附录几个读取资源的方法
//一: XmlBeanFactory 引用资源
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("appcontext.xml");
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
//二: ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 编译路径
ApplicationContext factory=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:appcontext.xml");
// src目录下的
ApplicationContext factory=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("appcontext.xml");
ApplicationContext factory=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] {"bean1.xml","bean2.xml"});
// src/conf 目录下的
ApplicationContext factory=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("conf/appcontext.xml");
ApplicationContext factory=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("file:G:/Test/src/appcontext.xml");
//三: 用文件系统的路径
ApplicationContext factory=new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("src/appcontext.xml");
//使用了 classpath: 前缀,作为标志, 这样,FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 也能够读入classpath下的相对路径
ApplicationContext factory=new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:appcontext.xml");
ApplicationContext factory=new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("file:G:/Test/src/appcontext.xml");
ApplicationContext factory=new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("G:/Test/src/appcontext.xml");
//四: XmlWebApplicationContext是专为Web工程定制的。
ServletContext servletContext = request.getSession().getServletContext();
ApplicationContext ctx = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext );
//五: 使用BeanFactory
BeanDefinitionRegistry reg = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(reg);
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(new ClassPathResource("bean1.xml"));
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(new ClassPathResource("bean2.xml"));
BeanFactory bf=(BeanFactory)reg;
//六:Web 应用启动时加载多个配置文件
//通过ContextLoaderListener 也可加载多个配置文件,在web.xml文件中利用
//<context-pararn>元素来指定多个配置文件位置,其配置如下:
<context-param>
<!-- Context Configuration locations for Spring XML files -->
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
./WEB-INF/**/Appserver-resources.xml,
classpath:config/aer/aerContext.xml,
classpath:org/codehaus/xfire/spring/xfire.xml,
./WEB-INF/**/*.spring.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
//这个方法加载配置文件的前提是已经知道配置文件在哪里,虽然可以利用“*”通配符,但灵活度有限。






















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








