Unlock the Cell Phone
Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65768/65768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 632 Accepted Submission(s): 289
Problem Description
Modern high-tech cell phones use unlock patterns to unlock the system. The pattern is usually a 3*3 dot array. By moving your finger over there dots, you can generate your personal unlock pattern. More specifically, press your finger over any starting dot, then slide all the way to the next dot, touch it, and so on. Jumping is not allowed. For example, starting from dot 1, you can slide to touch dot 2, dot 4 and dot 5, but sliding directly to dot 3, dot 7 or dot 9 are not allowed. Note that sliding from 1 to 6 and 8 is also allowed because they are not considered as jumping over any dot. However, you can jump a dot if it has been touched before. For example, staring with 1-5-9-6, you can slide directly to dot 4.
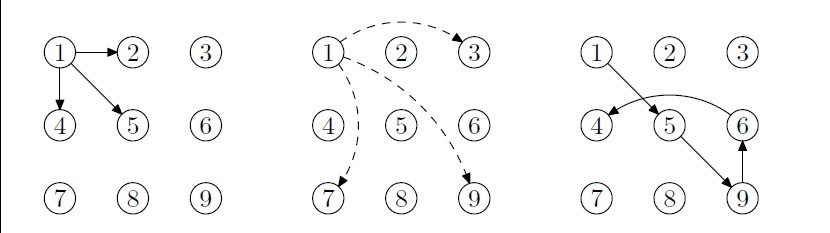
Here is a very particular cell phone. It has a dot array of size n*m. Some of the dots are ordinary ones: you can touch, and slide over them when touched before; some are forbidden ones: you cannot touch or slide over them; some are inactive ones: you cannot touch them, but can slide over them. Each dot can only be touched once. You are required to calculate how many different unlock patterns passing through all the ordinary dots.

Here is a very particular cell phone. It has a dot array of size n*m. Some of the dots are ordinary ones: you can touch, and slide over them when touched before; some are forbidden ones: you cannot touch or slide over them; some are inactive ones: you cannot touch them, but can slide over them. Each dot can only be touched once. You are required to calculate how many different unlock patterns passing through all the ordinary dots.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case begins with a line containing two integers n and m (1 <= n, m <= 5), indicating the row and column number of the lock keypad. The following n lines each contains m integers kij indicating the properties of each key, kij=0 stands for an ordinary key, kih=1 stands for a forbidden key; and kij=2 stands for an inactive key. The number of ordinary keys is greater than zero and no more than 16.
Output
For each test, output an integer indicating the number of different lock patterns.
Sample Input
2 2 0 0 0 0 3 3 0 0 0 0 2 1 0 0 0
Sample Output
24 2140
Source
Recommend
lcy
一,预处理每两个点间有哪些点。
二,把每个能按的点编号,1-16最多。
三,状态DP(i,sta),表示当前在i这个点,sta是二进制表示走过哪些点。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int maxn = 1<<17;
ll dp[20][maxn];
int visited[20][maxn] , vis , n , m;
int mp[6][6] , ID[6][6] , cnt;
struct Node{
int r , c;
Node(int a = 0 , int b = 0){
r = a , c = b;
}
}node[20];
vector<Node> between[6][6][6][6];
bool check(int r1 , int r2 , int c1 ,int c2 ,int r ,int c){
if(r == r1 && c == c1) return false;
if(r == r2 && c == c2) return false;
if(r >= min(r1 , r2) && r <= max(r1 , r2) && c >= min(c1 , c2) && c <= max(c1 , c2)){
if((r2-r)*(c-c1) == (r-r1)*(c2-c)) return true;
return false;
}
return false;
}
void init(){
memset(dp , 0 , sizeof dp);
memset(visited , 0 , sizeof visited);
vis = 0;
for(int r1 = 0; r1 < 6; r1++){
for(int c1 = 0; c1 < 6; c1++){
for(int r2 = 0; r2 < 6; r2++){
for(int c2 = 0; c2 < 6; c2++){
if(r1 == r2 && c1 == c2) continue;
for(int r = 0; r < 6; r++){
for(int c = 0; c < 6; c++){
if(check(r1 , r2 , c1 , c2 , r , c)){
between[r1][c1][r2][c2].push_back(Node(r , c));
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
void initial(){
memset(mp , 0 , sizeof mp);
memset(ID , 0 , sizeof ID);
cnt = 0;
vis++;
}
void readcase(){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
scanf("%d" , &mp[i][j]);
if(mp[i][j] == 0){
ID[i][j] = cnt;
node[cnt++] = Node(i , j);
}
}
}
}
ll DP(int k , int sta){
//cout << "k=" <<k << " sta=" << sta << endl;
if(sta == (1<<cnt)-1) return 1;
if(visited[k][sta] == vis) return dp[k][sta];
visited[k][sta] = vis;
int r1 = node[k].r , c1 = node[k].c;
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < cnt; i++){
if((sta&(1<<i)) <= 0){
int r2 = node[i].r , c2 = node[i].c;
bool flag = true;
for(int j = 0; j < between[r1][c1][r2][c2].size(); j++){
int r = between[r1][c1][r2][c2][j].r , c = between[r1][c1][r2][c2][j].c;
//cout << "r1=" << r1 << " c1=" << c1 << " r2=" << r2 << " c2=" << c2 << " r=" << r << " c=" << c << endl;
if(mp[r][c] == 1) flag = false;
if(mp[r][c] == 0 && (sta&(1<<ID[r][c])) <= 0) flag = false;
if(!flag) break;
}
if(flag) ans += DP(i , (sta+(1<<i)));
}
}
return dp[k][sta] = ans;
}
void computing(){
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < cnt; i++){
ans += DP(i , (1<<i));
//cout << i << ":" << ans << endl;
}
printf("%I64d\n" , ans);
}
int main(){
init();
while(~scanf("%d%d" , &n , &m)){
initial();
readcase();
computing();
}
return 0;
}























 345
345

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








