1 浅析 Linux 初始化 init 系统
第1部分sysvinit: https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/1407_liuming_init1/
第2部分UpStart: https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/1407_liuming_init2/
第3部分Systemd: https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/1407_liuming_init3/
1.1 SysVInit
1.2 UpStart
1.3 Systemd
1.3.1 基本
1 System单元的概念
系统初始化需要做的事情非常多。需要启动后台服务,比如启动 SSHD 服务;需要做配置工作,比如挂载文件系统。这个过程中的每一步都被 systemd 抽象为一个配置单元,即 unit。
单元的常见类型:
service unit : 文件扩展名为.service,用于定义系统类服务
target unit : 文件扩展为.target,用于实现模拟”运行级别”
device unit : 文件扩展为.device,用于定义内核识别的设备。
mount unit : 文件扩展为.mount,定义文件系统挂载点,利用logind服务,为用户的会话进程分配CGroup资源
socket unit : 文件扩展为.socket,用于标识进程间通信的socket文件
snapshot unit : 文件扩展为.snapshot,管理系统快照
swap unit : 文件扩展为.swap,用于标识swap设备
automount unit : 文件扩展为.automount,文件系统自动挂载设备
path unit : 文件扩展为.path,用于定义文件系统中的一个文件或目录
timer unit : 文件扩展为.timer,定时器配置单元,用来定时触发用户定义的操作,这类配置单元取代了atd、crond等传统的定时服务
1.3.2 初始化过程

2. MBR从Grub或LILO引导程序读取相关信息并初始化内核。接下来将由Grub或LILO继续引导系统。如果你在grub配置文件里指定了systemd作为引导管理程序,之后的引导过程将由systemd完成。Systemd使用“target”来处理引导和服务管理过程。这些systemd里的“target”文件被用于分组不同的引导单元以及启动同步进程。
root@compute:~# grep -R systemd /etc/grub.d/*
/etc/grub.d/10_linux:SUPPORTED_INITS="sysvinit:/lib/sysvinit/init systemd:/lib/systemd/systemd upstart:/sbin/upstart"
/etc/grub.d/20_linux_xen:SUPPORTED_INITS="sysvinit:/lib/sysvinit/init systemd:/lib/systemd/systemd upstart:/sbin/upstart"root@compute:~# systemctl get-default
graphical.target查看运行级别:
root@compute:~# runlevel
N 5root@compute:~# find / -name "graphical.target"
/lib/systemd/system/graphical.targetroot@compute:~# cat /lib/systemd/system/graphical.target
# This file is part of systemd.
#
# systemd is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
# under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
[Unit]
Description=Graphical Interface
Documentation=man:systemd.special(7)
Requires=multi-user.target
Wants=display-manager.service
Conflicts=rescue.service rescue.target
After=multi-user.target rescue.service rescue.target display-manager.service
AllowIsolate=yesroot@compute:~# cat /lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target
[Unit]
Description=Multi-User System
Documentation=man:systemd.special(7)
Requires=basic.target
Conflicts=rescue.service rescue.target
After=basic.target rescue.service rescue.target
AllowIsolate=yesroot@compute:~# ls /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/
atd.service cron.service lxcfs.service neutron-linuxbridge-agent.service openstack.service rsyslog.service snapd.service
cgmanager.service libvirt-bin.service lxd-containers.service neutron-linuxbridge-cleanup.service open-vm-tools.service snapd.autoimport.service ssh.service
cgproxy.service libvirt-guests.service networking.service nova-compute.service remote-fs.target snapd.refresh.timer ufw.serviceroot@compute:~# cat /lib/systemd/system/basic.target
[Unit]
Description=Basic System
Documentation=man:systemd.special(7)
Requires=sysinit.target
Wants=sockets.target timers.target paths.target slices.target
After=sysinit.target sockets.target paths.target slices.target tmp.mount
Wants=tmp.mountroot@compute:~# cat /lib/systemd/system/sysinit.target
[Unit]
Description=System Initialization
Documentation=man:systemd.special(7)
Conflicts=emergency.service emergency.target
Wants=local-fs.target swap.target
After=local-fs.target swap.target emergency.service emergency.target
root@compute:~# cat /lib/systemd/system/local-fs.target
[Unit]
Description=Local File Systems
Documentation=man:systemd.special(7)
DefaultDependencies=no
Conflicts=shutdown.target
After=local-fs-pre.target
OnFailure=emergency.target
OnFailureJobMode=replace-irreversibly参考资料:
1 http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/03/systemd-tutorial-commands.html
2 http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/03/systemd-tutorial-part-two.html
3 最简明扼要的 Systemd 教程,只需十分钟: https://linux.cn/article-6888-1.html
4 走进Linux之systemd启动过程:https://linux.cn/article-5457-1.html
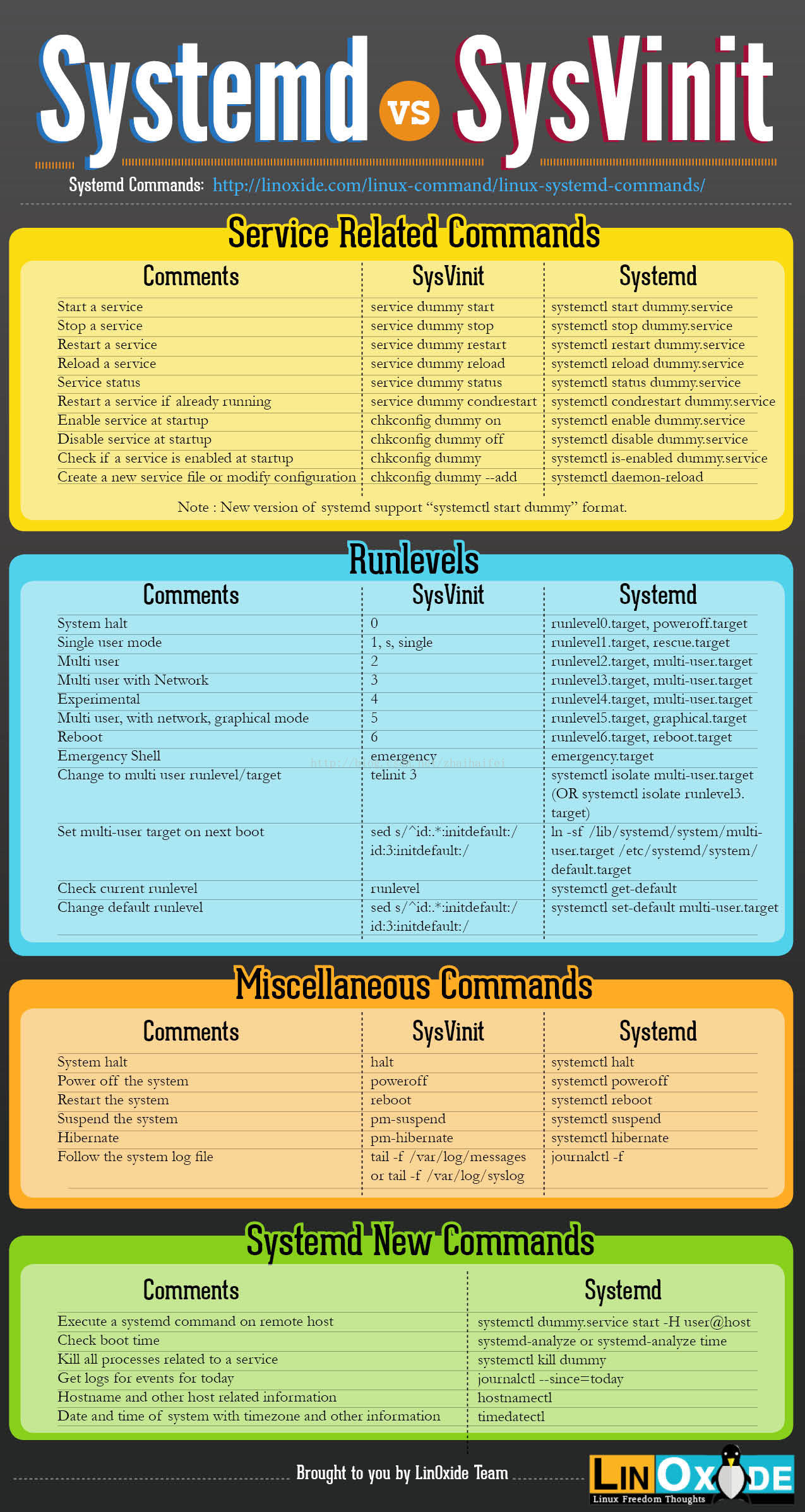
1.4 systemd & sysvinit
主要差别如下:
(2)启动脚本的位置,以前是/etc/init.d目录,符号链接到不同的 RunLevel 目录 (比如/etc/rc3.d、/etc/rc5.d等),现在则存放在/lib/systemd/system和/etc/systemd/system目录。
(3)配置文件的位置,以前init进程的配置文件是/etc/inittab,各种服务的配置文件存放在/etc/sysconfig目录。现在的配置文件主要存放在/lib/systemd目录,在/etc/systemd目录里面的修改可以覆盖原始设置。
2 命令启动Openstck服务
2.1 servcie命令
使用如下形式手动重启、关闭或启动:
service SCRIPT COMMAND [OPTIONS]
The SCRIPT parameter specifies a System V init script, located in /etc/init.d/SCRIPT, or the name of an upstart job in /etc/init.
The existence of an upstart job of the same name as a script in /etc/init.d will cause the upstart job to take precedence over the init.d script.
The supported values of COMMAND depend on the invoked script. service passes COMMAND and OPTIONS to the init script unmodified.
For upstart jobs, start, stop, status, are passed through to their upstart equivalents.
Restart will call the upstart 'stop' for the job, followed immediately by the 'start', and will exit with the return code of the start command.
All scripts should support at least the start and stop commands. # service nova-api restart
/etc/init
The directory containing upstart jobs.
/etc/init.d
The directory containing System V init scripts.
/etc/rc?.d/
The directories containing the links used by init and managed by update-rc.d.
/etc/init.d/skeleton
Model for use by writers of init.d scripts.
/var/lib/sysv-rc/legacy-bootsequence
Flag indicating the machine is using legacy mode for boot script ordering.2.2 systemctl
stop NAME... Stop (deactivate) one or more units
reload NAME... Reload one or more units
restart NAME... Start or restart one or more units
root@compute:~# ps -ef | grep nova
nova 3489 1 0 May19 ? 00:03:01 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/nova-compute --config-file=/etc/nova/nova.conf --config-file=/etc/nova/nova-compute.conf --log-file=/var/log/nova/nova-compute.log
root@compute:~# systemctl stop nova-compute
root@compute:~# ps -ef | grep nova
root 9624 1821 0 09:19 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nova
root@compute:~# systemctl start nova-compute
root@compute:~# ps -ef | grep nova
nova 9644 1 99 09:19 ? 00:00:02 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/nova-compute --config-file=/etc/nova/nova.conf --config-file=/etc/nova/nova-compute.conf --log-file=/var/log/nova/nova-compute.log3 开机自启动
3.1 sysvinit
root@controller:~# ls /etc/init.d/nova-api
/etc/init.d/nova-api
root@controller:~# cat /etc/init.d/nova-api
#!/bin/sh
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: nova-api
# Required-Start: $network $local_fs $remote_fs $syslog
# Required-Stop: $remote_fs
# Should-Start: postgresql mysql keystone rabbitmq-server ntp
# Should-Stop: postgresql mysql keystone rabbitmq-server ntp
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: Nova API server
# Description: Frontend Nova API server
### END INIT INFO
# Author: Julien Danjou <acid@debian.org>
# PATH should only include /usr/* if it runs after the mountnfs.sh script
PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin
DESC="OpenStack Compute API"
PROJECT_NAME=nova
NAME=${PROJECT_NAME}-api
#!/bin/sh
# The content after this line comes from openstack-pkg-tools
# and has been automatically added to a .init.in script, which
# contains only the descriptive part for the daemon. Everything
# else is standardized as a single unique script.
# Author: Thomas Goirand <zigo@debian.org>
# PATH should only include /usr/* if it runs after the mountnfs.sh script
PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin
if [ -z "${DAEMON}" ] ; then
DAEMON=/usr/bin/${NAME}
fi
PIDFILE=/var/run/${PROJECT_NAME}/${NAME}.pid
if [ -z "${SCRIPTNAME}" ] ; then
SCRIPTNAME=/etc/init.d/${NAME}
fi
if [ -z "${SYSTEM_USER}" ] ; then
SYSTEM_USER=${PROJECT_NAME}
fi
if [ -z "${SYSTEM_USER}" ] ; then
SYSTEM_GROUP=${PROJECT_NAME}
fi
if [ "${SYSTEM_USER}" != "root" ] ; then
STARTDAEMON_CHUID="--chuid ${SYSTEM_USER}:${SYSTEM_GROUP}"
fi
if [ -z "${CONFIG_FILE}" ] ; then
CONFIG_FILE=/etc/${PROJECT_NAME}/${PROJECT_NAME}.conf
fi
LOGFILE=/var/log/${PROJECT_NAME}/${NAME}.log
if [ -z "${NO_OPENSTACK_CONFIG_FILE_DAEMON_ARG}" ] ; then
DAEMON_ARGS="${DAEMON_ARGS} --config-file=${CONFIG_FILE}"
fi
# Exit if the package is not installed
[ -x $DAEMON ] || exit 0
# If ran as root, create /var/lock/X, /var/run/X, /var/lib/X and /var/log/X as needed
if [ `whoami` = "root" ] ; then
for i in lock run log lib ; do
mkdir -p /var/$i/${PROJECT_NAME}
chown ${SYSTEM_USER} /var/$i/${PROJECT_NAME}
done
fi
# This defines init_is_upstart which we use later on (+ more...)
. /lib/lsb/init-functions
# Manage log options: logfile and/or syslog, depending on user's choosing
[ -r /etc/default/openstack ] && . /etc/default/openstack
[ -r /etc/default/$NAME ] && . /etc/default/$NAME
[ "x$USE_SYSLOG" = "xyes" ] && DAEMON_ARGS="$DAEMON_ARGS --use-syslog"
[ "x$USE_LOGFILE" != "xno" ] && DAEMON_ARGS="$DAEMON_ARGS --log-file=$LOGFILE"
do_start() {
start-stop-daemon --start --quiet --background ${STARTDAEMON_CHUID} --make-pidfile --pidfile ${PIDFILE} --chdir /var/lib/${PROJECT_NAME} --startas $DAEMON \
--test > /dev/null || return 1
start-stop-daemon --start --quiet --background ${STARTDAEMON_CHUID} --make-pidfile --pidfile ${PIDFILE} --chdir /var/lib/${PROJECT_NAME} --startas $DAEMON \
-- $DAEMON_ARGS || return 2
}
do_stop() {
start-stop-daemon --stop --quiet --retry=TERM/30/KILL/5 --pidfile $PIDFILE
RETVAL=$?
rm -f $PIDFILE
return "$RETVAL"
}
do_systemd_start() {
exec $DAEMON $DAEMON_ARGS
}
case "$1" in
start)
init_is_upstart > /dev/null 2>&1 && exit 1
log_daemon_msg "Starting $DESC" "$NAME"
do_start
case $? in
0|1) log_end_msg 0 ;;
2) log_end_msg 1 ;;
esac
;;
stop)
init_is_upstart > /dev/null 2>&1 && exit 0
log_daemon_msg "Stopping $DESC" "$NAME"
do_stop
case $? in
0|1) log_end_msg 0 ;;
2) log_end_msg 1 ;;
esac
;;
status)
status_of_proc "$DAEMON" "$NAME" && exit 0 || exit $?
;;
systemd-start)
do_systemd_start
;;
restart|force-reload)
init_is_upstart > /dev/null 2>&1 && exit 1
log_daemon_msg "Restarting $DESC" "$NAME"
do_stop
case $? in
0|1)
do_start
case $? in
0) log_end_msg 0 ;;
1) log_end_msg 1 ;; # Old process is still running
*) log_end_msg 1 ;; # Failed to start
esac
;;
*) log_end_msg 1 ;; # Failed to stop
esac
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $SCRIPTNAME {start|stop|status|restart|force-reload|systemd-start}" >&2
exit 3
;;
esac
exit 03.2 upstart
将自己的程序加入到系统的服务启动机制中,可以让其开机自启动。只需要在/etc/init下增加xxx.conf配置文件即可,xxx是service的服务名字。
两个概念:
1. init: upstart主进程,是Linux系统中的“应用程序管理器”,是其他所有进程的源头(PID为1),它会读取配置文件,处理各种服务和应用程序的依赖关系,根据事件(信号)来启动这些功能与服务,并动态地进行管理。
2.initctl:upstart事件管理器,可以被应用程序进程用来通知init哪些事件(信号)发生。
root@controller:~# ls /etc/init/nova-api.conf
/etc/init/nova-api.conf
root@controller:~#
root@controller:~# cat /etc/init/nova-api.conf
description "OpenStack Compute API"
author "Thomas Goirand <zigo@debian.org>"
start on runlevel [2345]
stop on runlevel [!2345]
chdir /var/run
respawn
respawn limit 20 5
limit nofile 65535 65535
pre-start script
for i in lock run log lib ; do
mkdir -p /var/$i/nova
chown nova /var/$i/nova
done
end script
script
[ -x "/usr/bin/nova-api" ] || exit 0
DAEMON_ARGS=""
[ -r /etc/default/openstack ] && . /etc/default/openstack
[ -r /etc/default/$UPSTART_JOB ] && . /etc/default/$UPSTART_JOB
[ "x$USE_SYSLOG" = "xyes" ] && DAEMON_ARGS="$DAEMON_ARGS --use-syslog"
[ "x$USE_LOGFILE" != "xno" ] && DAEMON_ARGS="$DAEMON_ARGS --log-file=/var/log/nova/nova-api.log"
exec start-stop-daemon --start --chdir /var/lib/nova \
--chuid nova:nova --make-pidfile --pidfile /var/run/nova/nova-api.pid \
--exec /usr/bin/nova-api -- --config-file=/etc/nova/nova.conf ${DAEMON_ARGS}
end script
3.3 systemd
root@compute:~# ls /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/
neutron-linuxbridge-agent.service openstack.service rsyslog.service snapd.service
neutron-linuxbridge-cleanup.service open-vm-tools.service snapd.autoimport.service ssh.service
nova-compute.service remote-fs.target snapd.refresh.timer ufw.service
root@compute:~# cat /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nova-compute.service
[Unit]
Description=OpenStack Compute
After=libvirt-bin.service postgresql.service mysql.service keystone.service rabbitmq-server.service ntp.service neutron-ovs-cleanup.service
[Service]
User=nova
Group=nova
Type=simple
WorkingDirectory=/var/lib/nova
PermissionsStartOnly=true
ExecStartPre=/bin/mkdir -p /var/lock/nova /var/log/nova /var/lib/nova
ExecStartPre=/bin/chown nova:nova /var/lock/nova /var/lib/nova
ExecStartPre=/bin/chown nova:adm /var/log/nova
ExecStart=/etc/init.d/nova-compute systemd-start
Restart=on-failure
LimitNOFILE=65535
TimeoutStopSec=15
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetroot@compute:~# ls /etc/init/nova-compute.conf
/etc/init/nova-compute.conf
root@compute:~# ls /etc/init.d/nova-compute
/etc/init.d/nova-compute
4 取消开机自启动
4.1 sysvinit
4.2 upstart
4.3 systemd
5 nova-api调用执行
exec start-stop-daemon --start --chdir /var/lib/nova \
--chuid nova:nova --make-pidfile --pidfile /var/run/nova/nova-api.pid \
--exec /usr/bin/nova-api -- --config-file=/etc/nova/nova.conf ${DAEMON_ARGS}(2) 查看/usr/bin/nova-api
root@controller:~# cat /usr/bin/nova-api
#!/usr/bin/python
# PBR Generated from u'console_scripts'
import sys
from nova.cmd.api import main
if __name__ == "__main__":
sys.exit(main())(3) 查看api.py文件
root@controller:~# python
Python 2.7.6 (default, Oct 26 2016, 20:30:19)
[GCC 4.8.4] on linux2
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import nova
>>> print nova.__path__
['/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/nova']root@controller:/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/nova/cmd# ll api*py
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1514 Nov 22 11:11 api_ec2.py
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1781 Nov 22 11:11 api_metadata.py
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1481 Nov 22 11:11 api_os_compute.py
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1846 Nov 22 11:11 api.py





















 2694
2694

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








