Laravel拥有两个功能强大的功能来执行数据库操作:Query Builder - 查询构造器和Eloquent ORM。

一、Query Builder简介
Laravel 的 Query Builder 为执行数据库查询提供了一个干净简单的接口。它可以用来进行各种数据库操作,例如:
- Retrieving records - 检索记录
- Inserting new records - 插入记录
- Deleting records - 删除记录
- Updating records - 更新记录
- Performing "Join" queries - 执行 JOIN
- Executing raw SQL queries - 执行「原生」 SQL 语句
- Filtering, grouping and sorting of records - 过滤、分组和排序记录
Query Builder 是一个非常易于使用但很强大的与数据库进行交互的方式。
从 CURD 到 排序 和 过滤,Query Builder 提供了方便的操作符来处理数据库中的数据。这些操作符大多数可以组合在一起,以充分利用单个查询。
Laravel 一般使用 DB facade 来进行数据库查询。当我们执行 DB 的「命令」(、或者说「操作符」)时,Query Builder 会构建一个 SQL 查询,该查询将根据 table() 方法中指定的表执行查询。
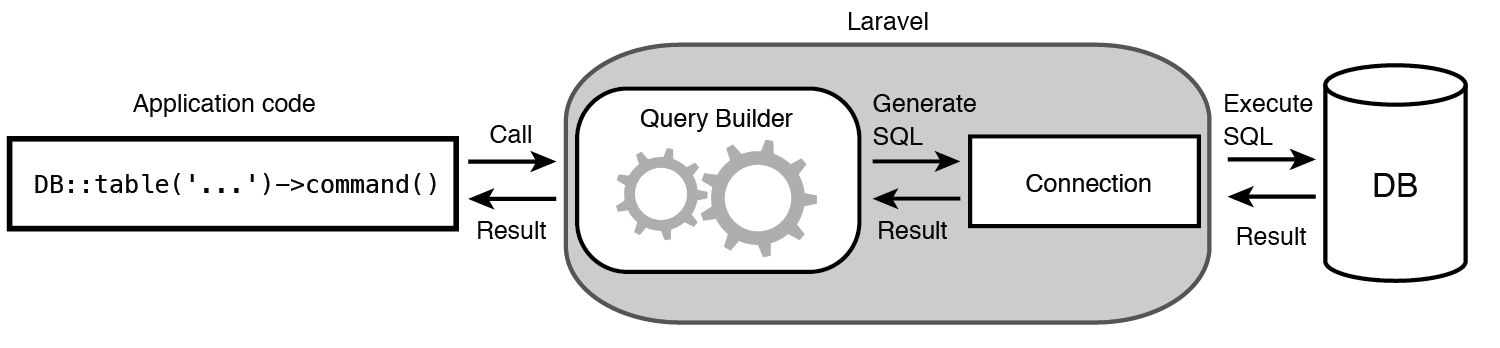
该查询将使用 app/config/database.php 文件中指定的数据库连接执行。 查询执行的结果将返回:检索到的记录、布尔值或一个空结果集。
下表中是 Query Builder 的常用操作符:
| 操作符 | 描述 |
| insert(array(...)) | 接收包含字段名和值的数组,插入数据至数据库 |
| find($id) | 检索一个主键 id 等于给定参数的记录 |
| update(array(...)) | 接收含有字段名和值的数组,更新已存在的记录 |
| delete() | 删除一条记录 |
| get() | 返回一个 Illuminate\Support\Collection 结果,其中每个结果都是一个 PHP StdClass 对象的实例,实例中包含每行记录中的列名及其值 |
| take($number) | 限制查询结果数量 |
1、CURD
假定orders 表如下:
| Key | Column | Type |
| primary | id | int (11), auto-incrementing |
| price | int (11) | |
| product | varchar(255) |
用 DB Facade 来使用 Query Builder如下:
#插入单条纪录
DB::table('orders')->insert(
[
'price' => 200, // 设置 price 字段值
'product' => 'Console', // 设置 product 字段值
]
);
#插入多条纪录
DB::table('orders')->insert(
[
['price' => 400, 'product' => 'Laptop'],
['price' => 200, 'product' => 'Smartphone'],
['price' => 50, 'product' => 'Accessory'],
]
);
#SQL:insertinto`orders`(`price`,`product`)values(?,?),(?,?),(?,?)
#查询某条纪录
$order = DB::table('orders')->find(3);
#SQL:select * from `orders` where `id` = ? limit 1
#查询所有纪录
$orders = DB::table('orders')->get();
#SQL:select * from `orders`
#查询指定列的所有纪录
$orders = DB::table('orders')->get(['id','price']);
#SQL:select `id`, `price` from `orders`
#指定查询纪录数量–>分页查询
$orders = DB::table('orders')->take(50)->get();
#update更新符合条件的所有纪录
DB::table('orders')
->where('price','>','50')
->update(['price' => 100]);
#SQL:update `orders` set `price` = ? where `price` > ?
#update更新所有纪录
DB::table('orders')->update(['product'=>'Headphones']);
#SQL:update `orders` set `product` = ?
#delete符合条件的纪录
DB::table('orders')
->where('product','=','Smartphone')
->delete();
#SQL:delete from `orders` where `product` = ?
#检索 orders 表中 所有 price 大于 100 的记录
$orders = DB::table('orders')
->where('price', '>', 100)
->get();
#获取 orders 表中 price 列的平均值
$averagePrice = DB::table('orders')->avg('price');
#查找 orders 表中所有 price 等于 50 的记录
#把他们 product 字段改为 Laptop
#proce 字段改为 400
DB::table('orders')
->where('price', 50)
->update(['product' => 'Laptop', 'price' => 400]);
2、过滤,排序和分组
| 操作符 | 描述 |
| where('column','comparator','value') | 检索符合条件的记录 |
| orderBy('column','order') | 按指定的列和顺序排序记录(升序asc或降序desc) |
| groupBy('column') | 按列分组 |
Query Chaining - 查询链,查询链接允许在单个查询中运行多个数据库操作。查询链将可以与数据执行的各种动作的顺序相互结合,以获得可以操作的特定结果。通过各种参数过滤、排序数据等等可以表示为对表中的数据执行的一系列操作:

Laravel 允许根据需要将多个查询放在一起。查询链接可以显着减少编写的代码量来执行复杂的数据库操作。 例如,要对 users 表执行上述操作,可以将过滤和排序一起放入单个查询链,如图所示:
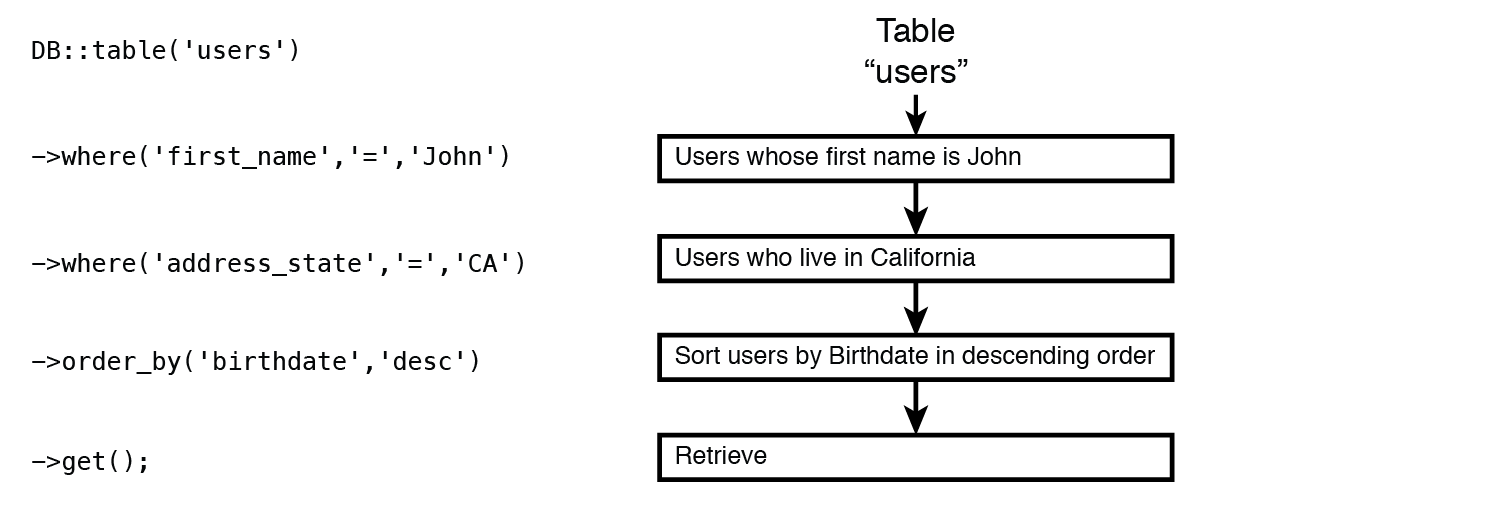
注意:可以使用查询链来执行多个操作,如排序、过滤、分组,以精确定位可以进一步检索、更新或删除的一组数据。 但不能在单个查询中将 insert/get/update/delete 操作混合在一起。
过滤–where
where 的查询由提供用于过滤数据的三个参数组成:
- 用于比较的列名
- 用于比较的运算符
- 用于比较的值

| 运算符 | 描述 |
| = | 等于 |
| < | 小于 |
| > | 大于 |
| <= | 小于等于 |
| >= | 大于等于 |
| != | 不等于 |
| like | 模糊查询 |
| not like | 模糊查询 |
例如:
#where and语句
$users = DB::table('users')
// Match users whose last_name column starts with “A”
->where('last_name', 'like','A%')
// Match users whose age is less than 50
->where('age','<' ,50)
// Retrieve the records as an array of objects
->get();
#SQL:select * from `users` where `last_name` like ? and `age` < ?
#除了使用单个 where 操作符,还可可以链接多个 where 来进一步过滤结果。 Laravel 会在 SQL 语句中自动将 AND 链接在 where 操作符之间。
#orwhere语句
$orders = DB::table('orders')
// Match orders that have been marked as processed
->where('processed', 1)
// Match orders that have price lower than or equal to 250
->orWhere('price','<=' ,250)
// Delete records that match either criterion
->delete();
#SQL:delete from `orders` where `processed` = ? or `price` <= ?
#whereBetween
$users = DB::table('users')
// Match users that have the value of “credit” column between 100 and 300
->whereBetween('credit', [100,300])
// Retrieve records as an array of objects
->get();
#SQL:select * from `users` where `credit` between ? and ?
排序–orderBy
Query Builder 的 orderBy 操作符提供了一种简单的方法来对从数据库检索的数据进行排序。 orderBy 类似于 SQL 中的 ORDER BY 子句。要通过一些列对一组数据进行排序,需要将两个参数传递给 orderBy :排序数据的列和排序方向(升序或降序)

例如:
$products = DB::table('products')
// Sort the products by their price in ascending order
->orderBy('price', 'asc')
// Retrieve records as an array of objects
->get();
$products = DB::table('products')
// Get products whose name contains letters “so”
->where('name','like','%so%')
// Get products whose price is greater than 100
->where('price','>', 100)
// Sort products by their price in ascending order
->orderBy('price', 'asc')
// Retrieve products from the table as an array of objects
->get();像 where 一样,orderBy 操作符是可链接的,可以组合多个 orderBy 以获取需要实现的排序结果。
分组–groupBy
可以使用类似于 SQL 中 GROUP BY 子句的 groupBy 操作符将记录组合在一起。 它只接受一个参数:用于对记录进行分组的列。
$products = DB::table('products')
// Group products by the “name” column
->groupBy('name')
// Retrieve products from the table as an array of objects
->get();
联结–join
Laravel 的 Query Builder 支持数据库所有类型的 Join 语句。 联结语句用于组合具有这些表共同值的多个表中的记录。 例如有两个表 users 和 orders ,其内容如图所示:

注意:如果联结的表具有相同名称的列,则应小心。 可以使用 select() 来代替重复的列。
例如:
#inner join
#Use table “users” as first table
$usersOrders = DB::table('users')
// Perform a Join with the “orders” table, checking for the presence of matching
// “user_id” column in “orders” table and “id” column of the “user” table.
->join('orders', 'users.id', '=', 'orders.user_id')
// Retrieve users from the table as an array of objects containing users and
// products that each user has purchased
->get();
#SQL:select * from `users` inner join `orders` on `users`.`id` = `orders`.`user_id`
#left join
#Use table “users” as first table
$usersOrders = DB::table('users')
// Perform a Left Join with the “orders” table, checking for the presence of
// matching “user_id” column in “orders” table and “id” column of the “user” table.
->leftJoin('orders', 'users.id', '=', 'orders.user_id')
// Retrieve an array of objects containing records of “users” table that have
// a corresponding record in the “orders” table and also all records in “users”
// table that don’t have a match in the “orders” table
->get();
#SQL:select * from `users` left join `orders` on `users`.`id` = `orders`.`user_id`
// Right Join
join('orders', 'users.id', '=', 'orders.user_id','right') // Right Outer Join
join('orders', 'users.id', '=', 'orders.user_id','right outer')
// Excluding Right Outer Join
join('orders', 'users.id', '=', 'orders.user_id','right outer') ->where('orders.user_id',NULL)
// Left Join
join('orders', 'users.id', '=', 'orders.user_id','left') // Left Outer Join
join('orders', 'users.id', '=', 'orders.user_id','left outer')
// Excluding Left Outer Join
join('orders', 'users.id', '=', 'orders.user_id','left outer') ->where('orders.user_id',NULL)
// Cross join
join('orders', 'users.id', '=', 'orders.user_id','cross')
二、Query builder常用语句
1CURD
1)从数据表中取得单一数据列
$user= DB::table('users')->where('name','John')->first();2)检索表中的所有行
$users = DB::table('users')->get();
foreach ($users as $user) {
var_dump($user->name);
}3)从表检索单个行
$user = DB::table('users')->where('name', 'John')->first();
var_dump($user->name);检索单个列的行
$name = DB::table('users')->where('name', 'John')->pluck('name');检索一个列值列表
$roles = DB::table('roles')->lists('title');该方法将返回一个数组标题的作用。你也可以指定一个自定义的键列返回的数组
$roles = DB::table('roles')->lists('title', 'name');指定一个Select子句
$users = DB::table('users')->select('name', 'email')->get();
$users = DB::table('users')->distinct()->get();
$users = DB::table('users')->select('name as user_name')->get();Select子句添加到一个现有的查询$query = DB::table('users')->select('name');
$users = $query->addSelect('age')->get();where
$users = DB::table('users')->where('votes', '>', 100)->get();OR
$users = DB::table('users')->where('votes', '>', 100)->orWhere('name', 'John')->get();Where Between
$users = DB::table('users')->whereBetween('votes', array(1, 100))->get();Where Not Between
$users = DB::table('users')->whereNotBetween('votes', array(1, 100))->get();Where In With An Array
$users = DB::table('users')->whereIn('id', array(1, 2, 3))->get();
$users = DB::table('users')->whereNotIn('id', array(1, 2, 3))->get();Using Where Null To Find Records With Unset Values
$users = DB::table('users')->whereNull('updated_at')->get();Order By, Group By, And Having
$users = DB::table('users')->orderBy('name', 'desc')->groupBy('count')->having('count', '>', 100)->get();Offset & Limit
$users = DB::table('users')->skip(10)->take(5)->get();2、连接
Joins
查询构建器也可以用来编写连接语句。看看下面的例子:
Basic Join Statement
DB::table('users')
->join('contacts', 'users.id', '=', 'contacts.user_id')
->join('orders', 'users.id', '=', 'orders.user_id')
->select('users.id', 'contacts.phone', 'orders.price')
->get();左连接语句
DB::table('users')
->leftJoin('posts', 'users.id', '=', 'posts.user_id')
->get();
DB::table('users')
->join('contacts', function($join)
{
$join->on('users.id', '=', 'contacts.user_id')->orOn(...);
})
->get();
DB::table('users')
->join('contacts', function($join)
{
$join->on('users.id', '=', 'contacts.user_id')
->where('contacts.user_id', '>', 5);
})
->get();3、分组
有时候,您可能需要创建更高级的where子句,如“存在”或嵌套参数分组。Laravel query builder可以处理这些:
DB::table('users')
->where('name', '=', 'John')
->orWhere(function($query)
{
$query->where('votes', '>', 100)
->where('title', '<>', 'Admin');
})
->get();上面的查询将产生以下SQL:
select * from users where name = 'John' or (votes > 100 and title
<> 'Admin')
Exists Statements
DB::table('users')
->whereExists(function($query)
{
$query->select(DB::raw(1))
->from('orders')
->whereRaw('orders.user_id = users.id');
})
->get();4、事务
laravel transaction : laravel 的事务是不支持eloquent的, 要用DB::的方式
你可以使用 transaction 方法,去执行一组数据库事务处理的操作:
DB::transaction(function()
{
DB::table('users')->update(['votes' => 1]);
DB::table('posts')->delete();
});注意: 在
transaction闭包若抛出任何异常会导致事务自动回滚。
有时候你可能需要自己开始一个事务:
DB::beginTransaction();你可以通过 rollback 的方法回滚事务:
DB::rollback();最后,你可以通过 commit 的方法提交事务:
DB::commit();若要使用多个连接,可以通过 DB::connection 方法取用:
$users = DB::connection('foo')->select(...);你也可以取用原始底层的 PDO 实例:
$pdo = DB::connection()->getPdo();有时候你可能需要重新连接到特定的数据库:
DB::reconnect('foo');如果你因为超过了底层 PDO 实例的 max_connections 的限制,需要关闭特定的数据库连接,可以通过 disconnect 方法:
DB::disconnect('foo');Laravel 可以在内存里访问这次请求中所有的查找语句。然而在有些例子下要注意,比如一次添加 大量的数据,可能会导致应用程序耗损过多内存。 如果要启用日志,可以使用 enableQueryLog 方法:
DB::connection()->enableQueryLog();要得到执行过的查找纪录数组,你可以使用 getQueryLog 方法:
$queries = DB::getQueryLog();参考:https://laravel-china.org/articles/6286/principles-and-usage-of-laravel-query-builder






















 582
582

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








