Chessboard
| Time Limit: 2000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 14263 | Accepted: 4436 |
Description
Alice and Bob often play games on chessboard. One day, Alice draws a board with size M * N. She wants Bob to use a lot of cards with size 1 * 2 to cover the board. However, she thinks it too easy to bob, so she makes some holes on the board (as shown in the figure below).
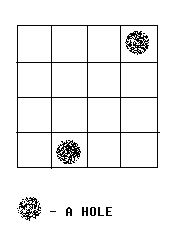
We call a grid, which doesn’t contain a hole, a normal grid. Bob has to follow the rules below:
1. Any normal grid should be covered with exactly one card.
2. One card should cover exactly 2 normal adjacent grids.
Some examples are given in the figures below:
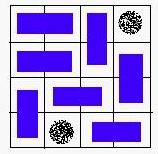
A VALID solution.
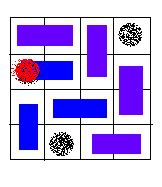
An invalid solution, because the hole of red color is covered with a card.
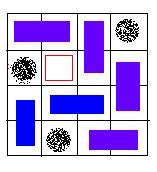
An invalid solution, because there exists a grid, which is not covered.
Your task is to help Bob to decide whether or not the chessboard can be covered according to the rules above.

We call a grid, which doesn’t contain a hole, a normal grid. Bob has to follow the rules below:
1. Any normal grid should be covered with exactly one card.
2. One card should cover exactly 2 normal adjacent grids.
Some examples are given in the figures below:

A VALID solution.

An invalid solution, because the hole of red color is covered with a card.

An invalid solution, because there exists a grid, which is not covered.
Your task is to help Bob to decide whether or not the chessboard can be covered according to the rules above.
Input
There are 3 integers in the first line: m, n, k (0 < m, n <= 32, 0 <= K < m * n), the number of rows, column and holes. In the next k lines, there is a pair of integers (x, y) in each line, which represents a hole in the y-th row, the x-th column.
Output
If the board can be covered, output "YES". Otherwise, output "NO".
Sample Input
4 3 2 2 1 3 3
Sample Output
YES
Hint
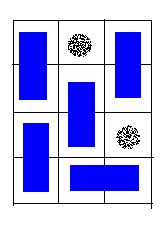
A possible solution for the sample input.
Source
POJ Monthly,charlescpp
这道题与之前的POJ 3020题比较类似,方法几乎是相同的。下面是参考代码。
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#define pb push_back
#define CLR(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define __CLR(x) memset(x,-1,sizeof(x))
using namespace std;
int n,m,k;
int g[40][40],match[1500];
vector<int>G[1500];
bool vis[1500];
int dx[]= {0,0,1,-1};
int dy[]= {1,-1,0,0};
bool dfs(int u)
{
for(int i=0; i<G[u].size(); i++)
{
int t=G[u][i];
if(!vis[t])
{
vis[t]=1;
if(match[t]==-1||dfs(match[t]))
{
match[t]=u;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k))
{
CLR(g);
for(int i=0; i<k; i++)
{
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
g[v][u]=-1;
}
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
for(int j=1; j<=m; j++)
{
if(g[i][j]==0)
{
g[i][j]=++cnt;
}
}
}
if(cnt%2==1)
printf("NO\n");
else
{
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
for(int j=1; j<=m; j++)
{
if(g[i][j]!=-1)
{
for(int k=0; k<4; k++)
{
int x=i+dx[k],y=j+dy[k];
if(x>=1&&x<=n&&y>=1&&y<=m&&g[x][y]!=-1)
{
G[g[i][j]].pb(g[x][y]);
G[g[x][y]].pb(g[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
}
__CLR(match);
int num=0;
for(int i=1; i<=cnt; i++)
{
CLR(vis);
if(dfs(i))
num++;
}
if(num==cnt) printf("YES\n");
else printf("NO\n");
}
for(int i=0; i<1500; i++)
G[i].clear();
}
}






















 948
948

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








