面试:你懂什么是分布式系统吗?Redis分布式锁都不会?>>> 
Android事件处理机制是基于Listener实现的,比如触摸屏相关的事件,是通过OnTouchListener实现的;而手势是通过OnGestureListener实现的,那么这两者有什么关联呢?
OnTouchListener
OnTouchListener接口中包含一个onTouch()方法,直接看一个例子:
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnTouchListener {
public void onCreate(Bundle outState) {
super.onCreate(outState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv);
tv.setOnTouchListener(this);
}
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Touch Touch", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return false ;
}
}
我们可以通过MotionEvent的getAction()方法来获取Touch事件的类型,包括 ACTION_DOWN(按下触摸屏), ACTION_MOVE(按下触摸屏后移动受力点), ACTION_UP(松开触摸屏)和ACTION_CANCEL(不会由用户直接触发)。借助对于用户不同操作的判断,结合getRawX()、 getRawY()、getX()和getY()等方法来获取坐标后,我们可以实现诸如拖动某一个按钮,拖动滚动条等功能。
可以看到OnTouchListener只能监听到三种触摸事件,即按下,移动,松开,如果想要监听到双击、滑动、长按等复杂的手势操作,这个时候就必须得用到OnGestureListener了。
OnGestureListener
接着上面的例子,这次加入手势监听:
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnTouchListener, OnGestureListener {
private GestureDetector mGestureDetector;
public void onCreate(Bundle outState) {
super.onCreate(outState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
mGestureDetector = new GestureDetector(this);
TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv);
tv.setOnTouchListener(this);
}
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
return mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
// 用户轻触触摸屏,由1个MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN触发
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent arg0) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDown");
Toast.makeText(this, "onDown", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return true;
}
// 用户轻触触摸屏,尚未松开或拖动,由一个1个MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN触发, 注意和onDown()的区别,强调的是没有松开或者拖动的状态
public void onShowPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onShowPress");
Toast.makeText(this, "onShowPress", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
// 用户(轻触触摸屏后)松开,由一个1个MotionEvent ACTION_UP触发
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onSingleTapUp");
Toast.makeText(this, "onSingleTapUp", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return true;
}
// 用户按下触摸屏、快速移动后松开,由1个MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN, 多个ACTION_MOVE, 1个ACTION_UP触发
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX, float velocityY) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onFling");
Toast.makeText(this, "onFling", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
// 用户按下触摸屏,并拖动,由1个MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN, 多个ACTION_MOVE触发
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float distanceX, float distanceY) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onScroll");
Toast.makeText(this, "onScroll", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
// 用户长按触摸屏,由多个MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN触发
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onLongPress");
Toast.makeText(this, "onLongPress", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
本示例中,用到了OnGestureListener接口的onScroll()和OnFling()方法,涉及到了Android系统坐标及触摸MotionEvent e1和e2、速度velocityX、velocityY等值,那么这里就顺便补充下Android屏幕坐标系如下图:
(1)MotionEvent中 e1是手指第一次按上屏幕的起点,e2是抬起手指离开屏幕的终点,根据上图Android屏幕坐标系可知: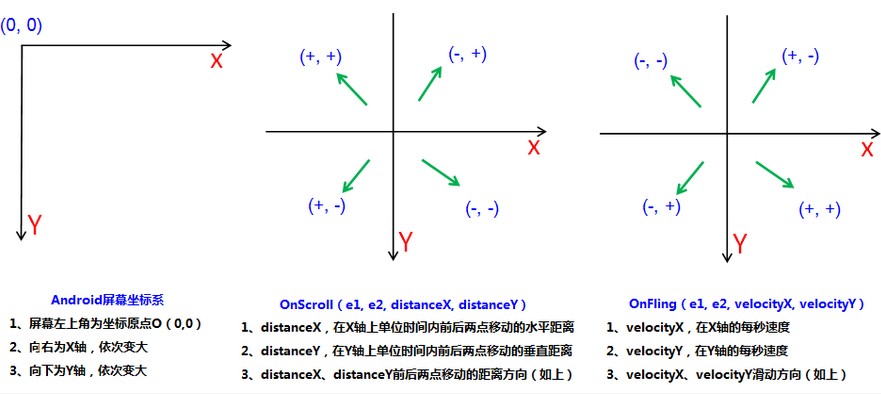
手指向右滑动,终点(e2)在起点(e1)的右侧,有e2.getX() - e1.getX() 大于0 手指向左滑动,终点(e2)在起点(e1)的左侧,有e2.getX() - e1.getX() 小于0 手指向下滑动,终点(e2)在起点(e1)的下侧,有e2.getY() - e1.getY() 大于0 手指向上滑动,终点(e2)在起点(e1)的上侧,有e2.getY() - e1.getY() 小于0
(2)onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float distanceX, float distanceY)
distanceX,是前后两次call的X距离,不是e2与e1的水平距离 distanceX,是前后两次call的Y距离,不是e2与e1的垂直距离 具体数值的方向,请详见上图(中)
(3)onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX, float velocityY)
velocityX,是X轴的每秒速度 velocityY,是Y轴的每秒速度 具体数值的方向,请详见上图(右) 仔细观察可以发现:velocityX、velocityY的方向与distanceX、distanceY方向正好相反






















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








