爬山算法
一种搜索算法,思想类似走山路,从某点开始不断往四周相邻更高的点走去,当走到某点已经是山峰顶,四周没有比当前点更高的点就停下,认为当前点是目标。
其中“高”是指点的估值,类似A*的那个意思。
但爬山法得出的一定是可行解,但不一定是最优解。
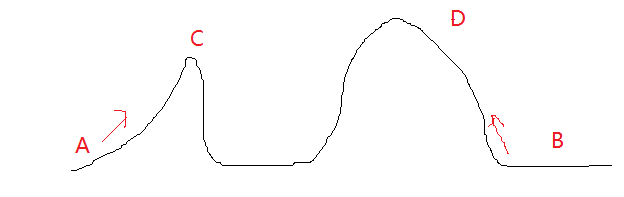
如图,如果从A点出发,则到达C点后因为四周没有比它更低的点就停止了,导致到不了真正的最高点D,而从B点出发却能到达最优解
模拟退火
爬山算法的改进,但仍然是随机算法,不一定求出最优解。跟爬山不同的是:即使四周没有更高的点,我们也以一定概率接受比当前点更低的点,这样就有机会摆脱局部最优而到达最优解,而这个概率会随时间不断减小。一定的概率是多大呢?参考热力学公式:在温度为T时,出现能量差为dE的降温的概率为P(dE)= edE/K∗T ,其中K是玻尔兹曼常数,约等于1。
代码
ans = 初始解
E = val(ans); //解的估值
while(T > T_min){
nE = val(next); //新点的估值
dE = nE - E;
if(dE > 0 || eps(dE/T) > random(0,1) ){ //高度更高或者高度更低但符合概率去接受这个更低点
ans = next;
e = nE; //接受新点的话更新对应值
}
T = T * r; //0<r<1,r越大找到最优解的几率更大,r过小可能陷入局部解
}其中eps(dE/T) > random(0,1)是因为dE < 0则
edE/T
<
e0
, 即eps(dE/T) < 1。随着程序进行,T越来越小,而接受更低点的概率就越来越小。
在具体题目的代码中,T相当于步长,初始的ans和T应能覆盖所有的解,对于每个当前点仅选一个点作为新点是不够的,所以可以选当前点的附近若干个点,再从里面选最大。同时,初始点也可以是个点集,并行扫描效果更佳。且eps(dE/T) > random(0,1) 可以改成其他,只要符合T越小接受的几率越小就行。
还没看懂的可以看下链接:
http://wenku.baidu.com/view/5e0cdfd376eeaeaad1f330f4.html
题目
POJ 1379 Run Away
题意:T组数据 ,在给出长宽的矩形里有n个点,求某点坐标,该点 跟距离跟它最近的点 最远。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <time.h>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
#define RE freopen("1.in","r",stdin);
#define SpeedUp std::cout.sync_with_stdio(false);
const int maxn=1e5+50;
const int inf = 0x7FFFFFFF; //可改勿删,不知名bug,以前遇到过是越界导致,但我并没有找到越界?
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
int n;
double X,Y;
struct Point
{
double x,y;
Point(){}
Point(double _,double __):x(_),y(__){}
void read(){
cin>>x>>y;
}
}p[maxn];
double dis(Point a,Point b){
return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
}
double minDis(Point cur){
double ans = 1e80;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
ans = min(ans,dis(cur,p[i]));
}
return ans;
}
double randNum(){ //rand()生成[0,32767),包装下生成[0,1)
return rand()%10000/10000.0;
}
void solve(Point &ans,double T){
double T_min = 1e-8;
double E = minDis(ans);//当前高度,即估值
int count = 30;//对当前点取周围count个点,再从里面挑最高的当下一个点
while(T > T_min){ //温度,也即本题步长
Point next;
double nE = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i){
Point tmp;
double angle = randNum()*2*PI; //[0,2π)
tmp.x = ans.x + cos(angle)*T; //ans.x + [-1,1)*T
tmp.y = ans.y + sin(angle)*T;
tmp.x = min(X,max(0.0,tmp.x)),tmp.y=min(Y,max(0.0,tmp.y));
double tE = minDis(tmp);
if(tE > nE){ //取周围所有点最高
nE = tE;
next = tmp;
}
}
double dE = nE - E; //新点和原点的高度差
if(dE >= 0.0 || exp(dE/T) > randNum()){ //更高或者随机得符合降温条件
// cout<<"E = "<<E<<"\t("<<next.x<<","<<next.y<<")\t"<<" nE = "<<nE<<endl;
E = nE;
ans = next;
}
T = T * 0.8; //0.8改大则更可能得到最优解,时间更长,改小则可能局部解
}
}
int main(){
// RE
SpeedUp
int t;
srand(time(NULL)); //c++提交,g++会因为这个RE
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>X>>Y>>n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
p[i].read();
}
Point ans = Point(X/2,Y/2); //起始为中心点
double T = sqrt(X*X+Y*Y)/2.0; //步长为对角线长度,包含了整个域
solve(ans,T);
cout <<setiosflags(ios::fixed);
cout<<"The safest point is ("<<setprecision(1)<<ans.x<<", "<<setprecision(1)<<ans.y<<")."<<endl;
}
return 0;
}POJ 2420 A Star not a Tree?
题意:给n个点,求到这些点距离和最近的那个点对应的距离和。
这题还是比较中规中举,虽然输入的是int,但处理方便还是用了double存,不过因为这题求的是最近(小),而爬山本身应该是往最高走,所以我们取个符号就行了(也可以把大于小于号反过来)。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <time.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define RE freopen("1.in","r",stdin);
#define SpeedUp std::cout.sync_with_stdio(false);
const int maxn=1e4+5;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
struct Point
{
double x, y, z;
void read() {
cin >> x >> y;
}
} p[maxn];
int n;
double dis(Point a, Point b) {
return sqrt((a.x - b.x) * (a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y) * (a.y - b.y) );
}
double getVal(Point cur){ //距离和的负数
double ans = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
ans += dis(p[i],cur);
}
return -ans;
}
double rand1(){ //[0,1)
return rand()%10000/10000.0;
}
double solve(){
Point ans;
ans.x = 5000,ans.y = 5000;
double T = sqrt(5000.0*5000+5000*5000)/2; //半径
double eps = 1e-6;
double E = getVal(ans);
while(T > eps){
Point next;
double nE = - 1e10; //-inf
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i){ //附近取20个点
Point tmp;
double angle = rand1()*2*PI;
tmp.x = ans.x + cos(angle)*T;
tmp.y = ans.y + sin(angle)*T; //ans为中心的T半价圆内新点
double tE = getVal(tmp);
if(tE > nE){
nE = tE;
next = tmp;
}
}
double dE = nE - E;
if(dE > 0 || exp(-1.0/T) > rand1()){ //公式本身是可以改变的,只要符合T越小接受的几率越小就行
// if(dE > 0 || exp(dE/T) > rand1()){
E = nE;
ans = next;
}
T *= 0.8;
}
return -E;
}
int main(){
// RE
srand(time(NULL));
while(cin>>n){
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
p[i].read();
}
printf("%.0f\n", solve());
}
return 0;
}HDU 3932 Groundhog Build Home
题意:若干个点,求覆盖全部点的圆心和半径,要求半径最小(即原题说:到最远点的距离最小)
这里给两个做法,一个是一个初始点扩散周围若干点的,再挑里面最大(小)当下一个点,另一种是初始一个点集,直接扩散求最大。
法一
/**
一个中心点搜四周40个点(需要足够多),里面挑最大(本题对应是最小)后再按模拟退火来
265 MS
**/
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <time.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define SpeedUp std::cout.sync_with_stdio(false);
const int maxn=1e4+50;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
struct Point
{
double x, y, z;
void read() {
cin >> x >> y;
}
} p[maxn];
int n;
double dis(Point a, Point b) {
return sqrt((a.x - b.x) * (a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y) * (a.y - b.y) );
}
double getVal(Point cur){
double ans = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
ans = max(ans, dis(p[i],cur) );
}
return ans;
}
double rand1(){ //[0,1]
return rand()%10001/10000.0;
}
double X,Y;
Point ans;
double E;
void solve(){
ans.x = X/2,ans.y = Y/2;
double T = sqrt(X*X+Y*Y)/2; //半径
double eps = 1e-6;
E = getVal(ans);
while(T > eps){
Point next;
double nE = 1e10;
for (int i = 0; i < 40; ++i){
Point tmp;
double angle = rand1()*2*PI;
tmp.x = ans.x + cos(angle)*T;
tmp.y = ans.y + sin(angle)*T;
double tE = getVal(tmp);
if(tE < nE){
nE = tE;
next = tmp;
}
}
double dE = nE - E;
if(dE < 0 || exp(dE/T) < rand1()){
E = nE;
ans = next;
}
T *= 0.9;
}
}
int main(){
// RE
srand(time(NULL));
while(cin>>X>>Y>>n){
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
p[i].read();
}
solve();
printf("(%.1f,%.1f).\n%.1f\n", ans.x,ans.y,E);
}
return 0;
}法二
/**
随机多个初始点搜四周20个点,直接往最大的爬去,不给接受更低的机会
733MS
**/
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <time.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define SpeedUp std::cout.sync_with_stdio(false);
const int maxn=1e5+50;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
struct Point
{
double x, y, z;
Point(){}
Point(double tx,double ty){x=tx;y=ty;}
void read() {
cin >> x >> y;
}
} p[maxn];
int n;
double dis(Point a, Point b) {
return sqrt((a.x - b.x) * (a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y) * (a.y - b.y) );
}
double getVal(Point cur){
double ans = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
ans = max(ans, dis(p[i],cur) );
}
return ans;
}
double rand1(){ //[0,1]
return rand()%10001/10000.0;
}
double X,Y;
Point randPoint(double X,double Y){
return Point(rand1()*X,rand1()*Y);
}
Point minAns;
double minDis;
void solve(){
int initNum = 15;
double T = sqrt(X*X+Y*Y)/2;
double eps = 1e-4;
double dis[30];
Point ans[30];
for (int i = 0; i < initNum; ++i){
ans[i] = randPoint(X,Y);
dis[i] = getVal(ans[i]);
}
while(T > eps){
for (int i = 0; i < initNum; ++i){
for (int j = 0; j < 20; ++j){ //足够多...
Point tmp;
double angle = rand1()*2*PI;
tmp.x = ans[i].x + cos(angle)*T;
tmp.y = ans[i].y + sin(angle)*T;
if(tmp.x < 0 || tmp.x > X || tmp.y < 0 || tmp.y > Y) continue;
double tDis = getVal(tmp);
if(tDis < dis[i] ){ // || exp((dis[i]-tDis)/T) > rand1() 写了等WA
dis[i] = tDis;
ans[i] = tmp;
}
}
}
T *= 0.8;
}
minDis = 1e30;
for (int i = 0; i < initNum; ++i){
if(dis[i] < minDis){
minDis = dis[i];
minAns = ans[i];
}
}
}
int main(){
SpeedUp
srand(time(NULL));
while(cin>>X>>Y>>n){
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
p[i].read();
}
solve();
printf("(%.1f,%.1f).\n%.1f\n", minAns.x,minAns.y,minDis);
}
return 0;
}POJ 2069 Super Star
题意:若干个三维的点,有个球,求足够覆盖所有点的最小的半径。
球心和半径自己定,看大家说法是:求球心到最远点的距离,然后球心往那边移动,初始球心自定。所以谁跟我说这是退火算法?跟确定算法没啥区别了。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <time.h>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
#define MOD 10009
#define SpeedUp std::cout.sync_with_stdio(false);
const int maxn = 50;
const int inf = 0x7FFFFFFF;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
int n;
double X, Y;
struct Point
{
double x, y, z;
Point() {}
Point(double _, double __, double ___): x(_), y(__), z(___) {}
void read() {
cin >> x >> y >> z;
}
} p[maxn];
double dis(Point a, Point b) {
return sqrt((a.x - b.x) * (a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y) * (a.y - b.y) + (a.z - b.z) * (a.z - b.z));
}
int maxDisIndex(Point cur) { //当前点距离所有点中最远点的下标
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if ( dis(cur, p[ans]) < dis(cur, p[i]) ) {
ans = i;
}
}
return ans;
}
double solve(Point cur) {
double eps = 1e-10;
double T = 100.0;
double ans = 1e20;
while (T > eps) {
int index = maxDisIndex(cur);
double r = dis(cur, p[index]);
ans = min(r, ans);
cur.x += (p[index].x - cur.x ) / r * T;
cur.y += (p[index].y - cur.y ) / r * T;
cur.z += (p[index].z - cur.z ) / r * T;
T = T * 0.98;
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
// RE
SpeedUp
while (cin >> n, n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
p[i].read();
}
Point ans = Point(0, 0, 0);
cout << setiosflags(ios::fixed);
cout << setprecision(5) << solve(ans) << endl;
}
return 0;
}






















 704
704

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








