首先,Thread.currentThread().getName() 和 this.getName()都可以用来获得线程的名称,但是它们是有区别滴,不能乱用!
下面分别对这两个方法进行剖析:
先来说说currentThread()方法,它的源码如下,它是一个本地方法,方法返回一个Thread对象:
/**
* Returns a reference to the currently executing thread object.
*
* @return the currently executing thread.
*/
public static native Thread currentThread();接下来看看 getName()方法,它是Thread类中的一个方法(并不是Object类中的方法),源码如下:
/**
* Returns this thread's name.
*
* @return this thread's name.
* @see #setName(String)
*/
public final String getName() {
return String.valueOf(name);
}其中,name是Thread类中的一个域,是char[],getName()方法可以返回当前线程的名称。
所以我们可以总结:Thread.currentThread().getName()可以在任何情况下使用;而this.getName()必须在Thread类的子类中使用,this指代的必须是Thread对象!
为了更好的说明两者的差别,可以看以下代码:
public class MyThread extends Thread{
public MyThread() {
System.out.println(".....MyThread begin.....");
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName() = "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("this.getName() = "+this.getName());
System.out.println(".....MyThread end.......");
System.out.println();
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(".....run begin.....");
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName() = "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("this.getName() = "+this.getName());
System.out.println(".....run end.......");
}
}
public class MyThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
Thread t = new Thread(mt);
t.setName("A");
t.start();
}
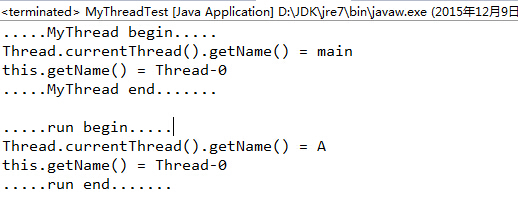
}输出结果为:
其中,Thread.currentThread().getName()调用的是执行此行代码的线程的getName方法;this.getName()调用的是mt对象的getName方法。区别显著有木有!!!
这里比较让人疑惑的是“this.getName() = Thread-0”,这个Thread-0是什么鬼???
通过查看Thread源码发现,在Thread类的构造方法中,会自动给name赋值,赋值代码:
"Thread-" + nextThreadNum()有兴趣的同学可以自己去查源码!
这就解释了为什么“this.getName() = Thread-0”。






















 7728
7728

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








