——————/7
[ ]内核态进程,否则用户态进程
PCB进程控制块
task_struct is allocated via slab allocator to provide object reuse and cache coloring
root@lyl:~# cat /proc/slabinfo
root@lyl:~# cat /proc/sys/kernel/pid_max
32768
#define TASK_RUNNING 0
#define TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE 1
#define TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE 2
#define __TASK_STOPPED 4
#define __TASK_TRACED 8
——/
set_task_state(tsk, state_value)
task->state=state;
——————/8
用户线程pthread_create 内核线程kthread_create / kthread_run
Process Resource Limits
root@lyl:~# ulimit -c -n -s
core file size (blocks, -c) 0 //系统崩溃时自动产生
open files (-n) 1024
stack size (kbytes, -s) 8192
root@lyl:~# ulimit –a
root@lyl:~# cat /proc/self/limits
——/
获取/设置资源限制(getrlimit / setrlimit)
——————/9
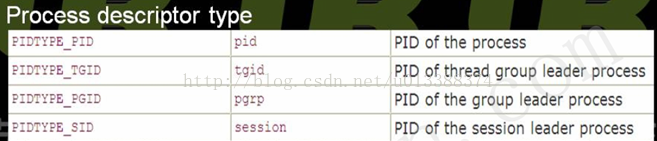
tasks[PIDTYPE_MAX]数组中每个元素都代表了不同含义。
tasks[i]指向一哈希表,如tasks[PIDTYPE_PID]指向PID哈希表。
numbers[1]为upid结构体,numbers数组本意是想表不同pid_namespace。一PID可属不同namespace,numbers[0]表global namespace,numbers[i]表第i层namespace,i越大所在层级越低。目前该数组只有一元素,即global namespace。所以namepace概念虽引入pid,但并未真正使用,在未来的版本可能会用到。
ns指向该pid所处的namespace;
linux内核将所有进程的upid都存放于一哈希表中(pid_hash),以方便查找和统一管理。因此,pid结构体中的numbers[0]指向的upid instance存放在pid_hash中,通过pid_chain就能从pid_hash中找到该upid;
child_reaper指向一进程,作用是当进程结束时为其收尸,因只支持global namespace,故child_reaper指向init_task
level表该namespace处于哪一层,显然是0
parent指向该namespace的父namespace,现在一定是NULL
增加namespace概念的目的是为了虚拟化和方便管理。 如在不同的namespace中可有pid相同的进程,pid_namespace的结构是层次化的,且在child namespace中的进程一定会有parent namespace的映射,如图:
此时pid_hash全局哈希表中会存放15个(9+3+3)upid的instance
介绍了pid,upid,pid_namespace的概念,再来看看其和task_struct的关系:
右下角椭圆形虚线框是全局pid_hash,所有已分配的upid都保存在该hash表中
左下角椭圆形虚线框表pid_namespace关系,当然目前只有一层
PAGE_OFFSET值0xC0000000
——/
/* create a slab on which task_structs can be allocated */
task_struct_cachep =kmem_cache_create ("task_struct", sizeof(struct task_struct),…
#cat /proc/slabinfo
task_struct 317 321 ……
——/
——/
进程退出exit与_exit,内核均do_exit
因父子进程共享内存
父进程退出,子进程并未结束,子进程被init进程领养
clone (slav, (char *)stack + stacksize - 1, SIGCHLD, 0); //此时不再共享内存
——/
/* Scheduling policies */
#define SCHED_NORMAL 0
#define SCHED_FIFO 1 //实时
#define SCHED_RR 2 //实时
#define SCHED_BATCH 3
/* SCHED_ISO: reserved but not implemented yet */
#define SCHED_IDLE 5

#yum install crash debuginfo
crash>runq //displays the tasks on the runqueue of each cpu
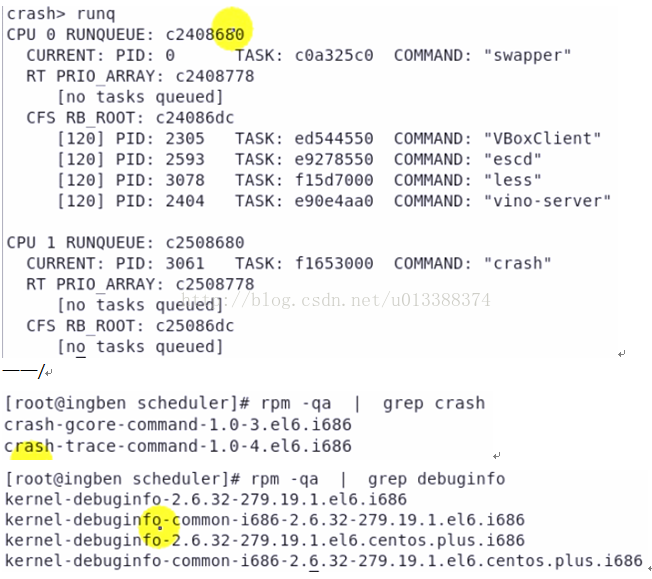
——/
#fuser /dev/crash //列举哪些进程在使用该设备文件
——————/12
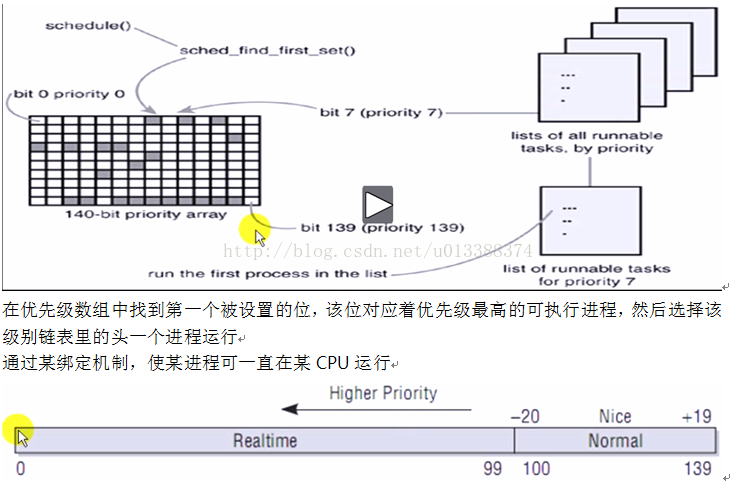
CFS完全公平调度算法

——————/13

——————/14
nice (niceval)
——/
——————/15
内核中调度类:CFS、RT
调度相关系统调用:

多核与多处理器概念异
SMP(Symmetric Multi-Processing):对称多处理器
负载均衡:将任务平分到各CPU(很热门的技术)
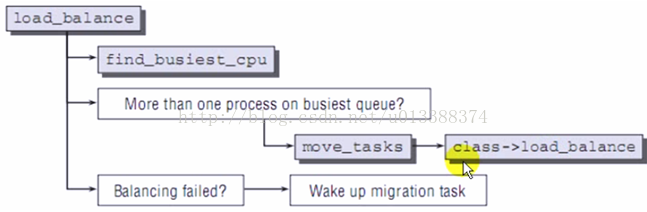


[ ]内核态进程,否则用户态进程
PCB进程控制块
task_struct is allocated via slab allocator to provide object reuse and cache coloring
root@lyl:~# cat /proc/slabinfo
root@lyl:~# cat /proc/sys/kernel/pid_max
32768
struct task_struct {
volatile long state; /* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
pid_t pid;
pid_t tgid;
int prio, static_prio, normal_prio;
struct mm_struct *mm, *active_mm; //进程所占内存
struct files_struct *files; /* open file information */
……
#define TASK_RUNNING 0
#define TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE 1
#define TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE 2
#define __TASK_STOPPED 4
#define __TASK_TRACED 8
——/
set_task_state(tsk, state_value)
task->state=state;
——————/8
用户线程pthread_create 内核线程kthread_create / kthread_run

Process Resource Limits
root@lyl:~# ulimit -c -n -s
core file size (blocks, -c) 0 //系统崩溃时自动产生
open files (-n) 1024
stack size (kbytes, -s) 8192
root@lyl:~# ulimit –a
root@lyl:~# cat /proc/self/limits
——/
获取/设置资源限制(getrlimit / setrlimit)
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/resource.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define DEATH(mess) { perror(mess); exit(errno); }
void do_limit (int limit, const char *limit_string, struct rlimit *rlim)
{
if (getrlimit (limit, rlim))
fprintf (stderr, "Failed in getrlimit\n");
printf ("%15s=%2d: cur=%20lu, max=%20lu\n", limit_string,
limit, rlim->rlim_cur, rlim->rlim_max);
}
void print_limits (void)
{
struct rlimit rlim;
do_limit (RLIMIT_CPU, "RLIMIT_CPU", &rlim);
do_limit (RLIMIT_FSIZE, "RLMIT_FSIZE", &rlim);
do_limit (RLIMIT_DATA, "RLMIT_DATA", &rlim);
do_limit (RLIMIT_STACK, "RLIMIT_STACK", &rlim);
do_limit (RLIMIT_CORE, "RLIMIT_CORE", &rlim);
do_limit (RLIMIT_RSS, "RLIMIT_RSS", &rlim);
do_limit (RLIMIT_NPROC, "RLIMIT_NPROC", &rlim);
do_limit (RLIMIT_NOFILE, "RLIMIT_NOFILE", &rlim);
do_limit (RLIMIT_MEMLOCK, "RLIMIT_MEMLOCK", &rlim);
do_limit (RLIMIT_AS, "RLIMIT_AS", &rlim);
do_limit (RLIMIT_LOCKS, "RLIMIT_LOCKS", &rlim);
}
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct rlimit rlim;
pid_t pid = 0;
int status = 0, nchildren = 3, i;
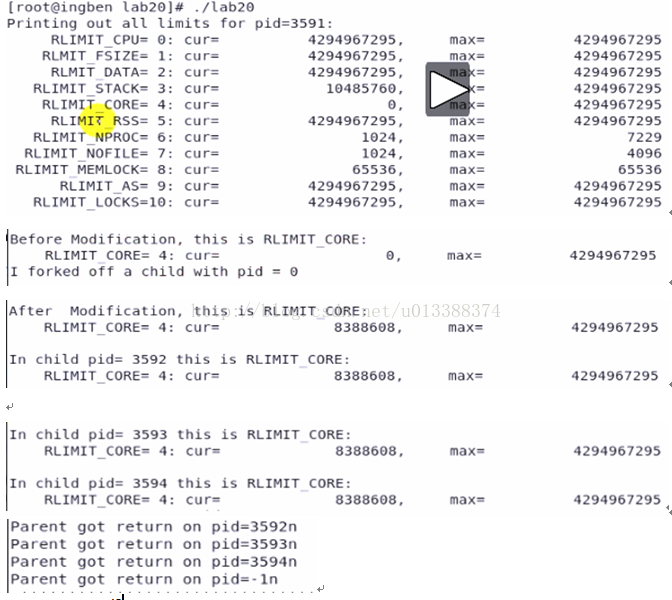
printf ("Printing out all limits for pid=%d:\n", getpid ());
print_limits ();
/* change and printout the limit for core file size */
printf ("\nBefore Modification, this is RLIMIT_CORE:\n");
do_limit (RLIMIT_CORE, "RLIMIT_CORE", &rlim);
rlim.rlim_cur = 8 * 1024 * 1024;
printf ("I forked off a child with pid = %d\n", (int)pid);
setrlimit (RLIMIT_CORE, &rlim);
printf ("\nAfter Modification, this is RLIMIT_CORE:\n");
do_limit (RLIMIT_CORE, "RLIMIT_CORE", &rlim);
/* fork off the nchildren */
fflush (stdout);
for (i = 0; i < nchildren; i++)
{
pid = fork ();
if (pid < 0)
DEATH ("Failed in fork");
if (pid == 0)
{ /* any child */
printf ("\nIn child pid= %d this is RLIMIT_CORE:\n",(int)getpid ());
do_limit (RLIMIT_CORE, "RLIMIT_CORE", &rlim);
fflush (stdout);
sleep (3);
exit (0);
}
}
while (pid > 0)
{ /* parent */
pid = wait (&status); //无子进程,调用就会失败,返回-1
printf ("Parent got return on pid=%dn\n", (int)pid);
}
exit (0);
}

——————/9
struct pid
{
atomic_t count; //该结构体引用计数
unsigned int level;
/* lists of tasks that use this pid */
struct hlist_head tasks[PIDTYPE_MAX];
struct rcu_head rcu; //同步机制
struct upid numbers[1];
};
tasks[PIDTYPE_MAX]数组中每个元素都代表了不同含义。
enum pid_type
{
PIDTYPE_PID,
PIDTYPE_PGID,
PIDTYPE_SID,
PIDTYPE_MAX
};
tasks[i]指向一哈希表,如tasks[PIDTYPE_PID]指向PID哈希表。
numbers[1]为upid结构体,numbers数组本意是想表不同pid_namespace。一PID可属不同namespace,numbers[0]表global namespace,numbers[i]表第i层namespace,i越大所在层级越低。目前该数组只有一元素,即global namespace。所以namepace概念虽引入pid,但并未真正使用,在未来的版本可能会用到。
struct upid {
/* Try to keep pid_chain in the same cacheline as nr for find_vpid */
int nr;
struct pid_namespace *ns;
struct hlist_node pid_chain;
};
ns指向该pid所处的namespace;
linux内核将所有进程的upid都存放于一哈希表中(pid_hash),以方便查找和统一管理。因此,pid结构体中的numbers[0]指向的upid instance存放在pid_hash中,通过pid_chain就能从pid_hash中找到该upid;
struct pid_namespace {
struct pidmap pidmap[PIDMAP_ENTRIES];
int last_pid;
struct task_struct *child_reaper;
struct kmem_cache *pid_cachep;
unsigned int level;
struct pid_namespace *parent;
gid_t pid_gid;
int hide_pid;
int reboot; /* group exit code if this pidns was rebooted */
……;
};
child_reaper指向一进程,作用是当进程结束时为其收尸,因只支持global namespace,故child_reaper指向init_task
level表该namespace处于哪一层,显然是0
parent指向该namespace的父namespace,现在一定是NULL
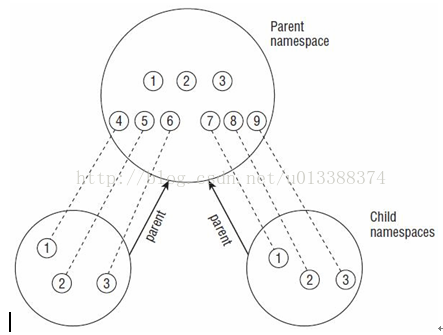
增加namespace概念的目的是为了虚拟化和方便管理。 如在不同的namespace中可有pid相同的进程,pid_namespace的结构是层次化的,且在child namespace中的进程一定会有parent namespace的映射,如图:

此时pid_hash全局哈希表中会存放15个(9+3+3)upid的instance
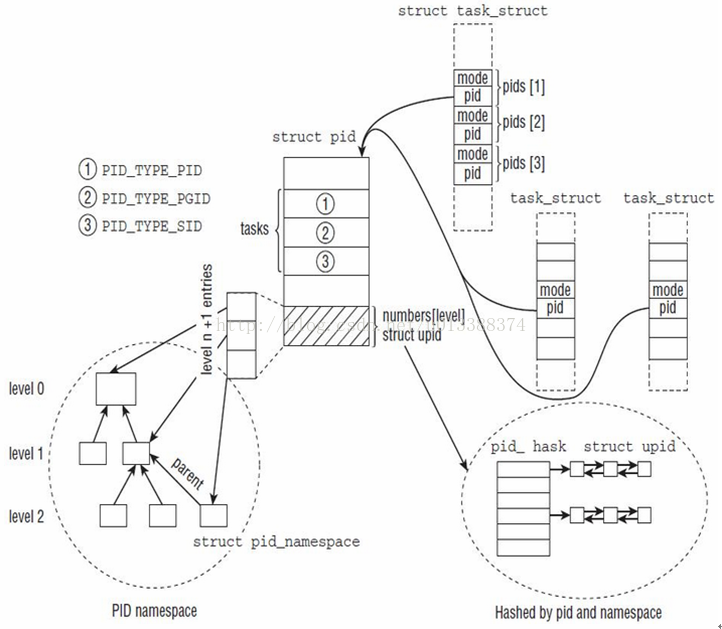
介绍了pid,upid,pid_namespace的概念,再来看看其和task_struct的关系:

右下角椭圆形虚线框是全局pid_hash,所有已分配的upid都保存在该hash表中
左下角椭圆形虚线框表pid_namespace关系,当然目前只有一层
static inline struct pid *task_pid(struct task_struct *task)
{
return task->pids[PIDTYPE_PID].pid;
}
PAGE_OFFSET值0xC0000000
——/
do_fork
copy_process
task_pid_vnr //确定pid
if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK)
init_completion(&vfork); //initialize vfork completion handler and ptrace flags
wake_up_new_task
if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK)
wait_for_completion //completion完成量,用于并发控制
copy_process
//check flags
dup_task_struct(current)
alloc_task_struct
kmem_cache_alloc (task_struct_cachep //slab机制
arch_dup_task_struct //体系结构相关
//check resource limits
//initialize task_struct
sched_fork //Perform scheduler related setup.Assign this task to a CPU.
copy_files
copy_fs
copy_signal
copy_mm
copy_namespaces
copy_thread
copy_io
/* create a slab on which task_structs can be allocated */
task_struct_cachep =kmem_cache_create ("task_struct", sizeof(struct task_struct),…
#cat /proc/slabinfo
task_struct 317 321 ……
——/
struct thread_info //线程描述结构体,核心仍为task_struct
struct task_struct *task;
copy_mm
struct mm_struct * mm
mm=dup_mm
struct mm_struct *oldmm = current->mm;
mm = allocate_mm();
kmem_cache_alloc(mm_cachep
mm_cachep = kmem_cache_create("mm_struct"
memcpy(mm, oldmm, sizeof(*mm));
tsk->mm = mm
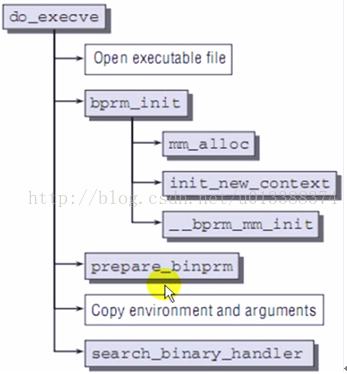
execve
sys_execve
do_execve
/*This structure is used to hold the arguments when loading binaries.*/
struct linux_binprm *bprm;
struct file *file;
file = open_exec(filename); //打开二进制文件
do_filp_open
path_lookup_open
bprm->file = file;
bprm->filename = filename;
prepare_binprm(bprm);
struct inode * inode = ……
unsigned long i_ino; //保存inode号
权限检查
search_binary_handler (bprm,regs);
//找到能处理该二进制文件的handler并调用
struct linux_binfmt *fmt;
int (*fn)(struct linux_binprm *, struct pt_regs *) = fmt->load_binary;
fn(bprm, regs); //真正意义执行

——/
进程退出exit与_exit,内核均do_exit
do_exit
exit_signals
exit_mm
exit_sem
exit_files
exit_fs
struct fs_struct *fs = tsk->fs;
free_fs_struct(fs);
kmem_cache_free(fs_cachep, fs);
exit_thread
preempt_disable
tsk->state = TASK_DEAD;
schedule
int main(void)
{
printf("hello world");
//exit(0); //flush
_exit(0); //not flush
}
#include <sched.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int param = 0;
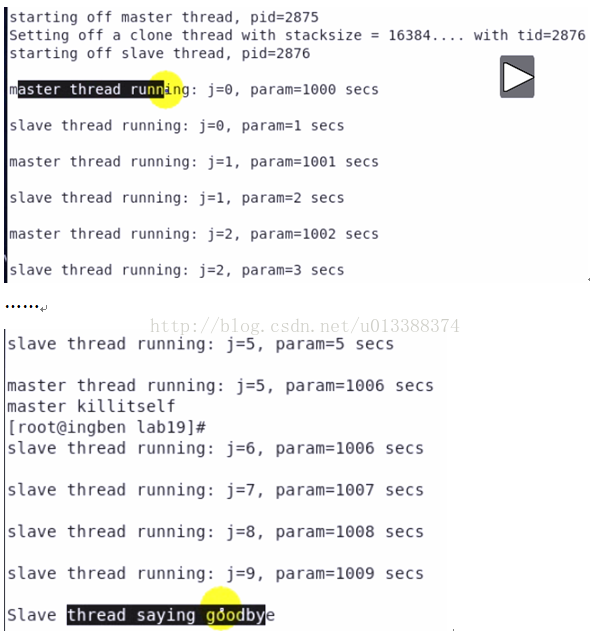
int slav (void *data)
{
int j;
printf ("starting off slave thread, pid=%d\n", getpid ());
for (j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
param = j + 1000;
sleep (1);
printf ("\nslave thread running: j=%d, param=%d secs\n", j, param);
}
printf ("\nSlave thread saying goodbye\n");
return 0;
}
int main ()
{
int j, tid, pagesize, stacksize;
void *stack;
printf ("starting off master thread, pid=%d\n", getpid ());
pagesize = getpagesize ();
stacksize = 4 * pagesize;
/* could probably just use malloc(), but this is safer */
/* stack = (char *)memalign (pagesize, stacksize); */
posix_memalign (&stack, pagesize, stacksize);
printf ("Setting off a clone thread with stacksize = %d....", stacksize);
tid = clone (slav, (char *)stack + stacksize - 1, CLONE_VM | SIGCHLD, 0);
printf (" with tid=%d\n", tid);
if (tid < 0)
exit (1);
/* could do a wait (&status) here if required */
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++)
{
param = j;
sleep (1);
printf ("\nmaster thread running: j=%d, param=%d secs\n", j, param);
}
printf ("master killitself\n");
free (stack);
exit (0);
}

因父子进程共享内存
父进程退出,子进程并未结束,子进程被init进程领养
clone (slav, (char *)stack + stacksize - 1, SIGCHLD, 0); //此时不再共享内存
——/
/* Scheduling policies */
#define SCHED_NORMAL 0
#define SCHED_FIFO 1 //实时
#define SCHED_RR 2 //实时
#define SCHED_BATCH 3
/* SCHED_ISO: reserved but not implemented yet */
#define SCHED_IDLE 5

#yum install crash debuginfo
crash>runq //displays the tasks on the runqueue of each cpu

——/
#fuser /dev/crash //列举哪些进程在使用该设备文件
——————/12
CFS完全公平调度算法

——————/13

schedule
preempt_disable //避免其它进程抢占本进程
cpu = smp_processor_id(); //获取当前cpuId
rq = cpu_rq(cpu); //获取该cpu上运行队列
prev = rq->curr; //将当前进程作为上一进程
next = pick_next_task(rq); /* Pick up the highest-prio task */
struct task_struct * pfair_sched_class.pick_next_task(rq);
pick_next_task_fair
struct cfs_rq *cfs_rq = &rq->cfs;
struct sched_entity *se = pick_next_entity(cfs_rq);
__pick_next_entity(cfs_rq);
rb_entry(left, struct sched_entity, run_node);
sched_info_switch(prev, next);
rq->nr_switches++;
rq->curr = next;
context_switch(rq, prev, next); //上下文切换
preempt_enable_no_resched

——————/14
nice (niceval)
——/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/resource.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main ()
{
pid_t mypid;
int old_prio, new_prio, i, rc;
mypid = getpid ();
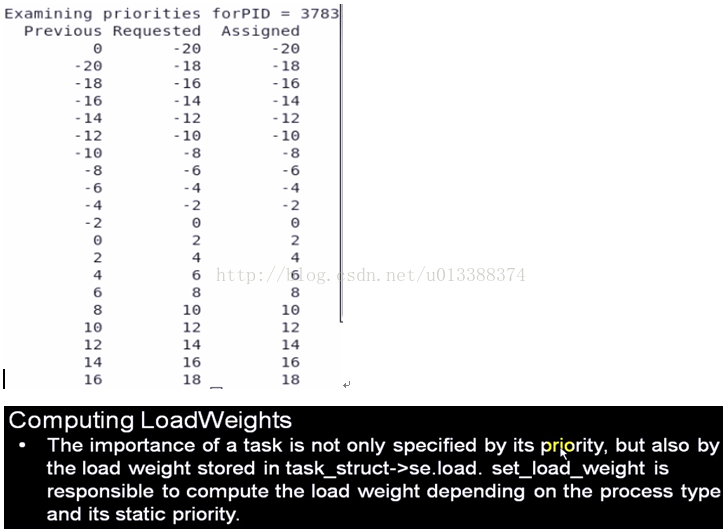
printf ("\nExamining priorities forPID = %d \n", mypid);
printf ("%10s%10s%10s\n", "Previous", "Requested", "Assigned");
for (i = -20; i < 20; i += 2)
{
old_prio = getpriority (PRIO_PROCESS, (int)mypid);
rc = setpriority (PRIO_PROCESS, (int)mypid, i);
if (rc)
fprintf (stderr, "setpriority() failed ");
errno = 0;
new_prio = getpriority (PRIO_PROCESS, (int)mypid);
printf ("%10d%10d%10d\n", old_prio, i, new_prio);
}
exit (0);
}

——————/15
内核中调度类:CFS、RT
task_struct
struct sched_class *sched_class; //调度类
pick_next_task
void (*enqueue_task) (struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int wakeup); //入队
void (*dequeue_task) (struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int sleep); //出队
move_one_task
void (*pre_schedule) (struct rq *this_rq, struct task_struct *task);
调度相关系统调用:

#include <sched.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define DEATH(mess) { perror(mess); exit(errno); }
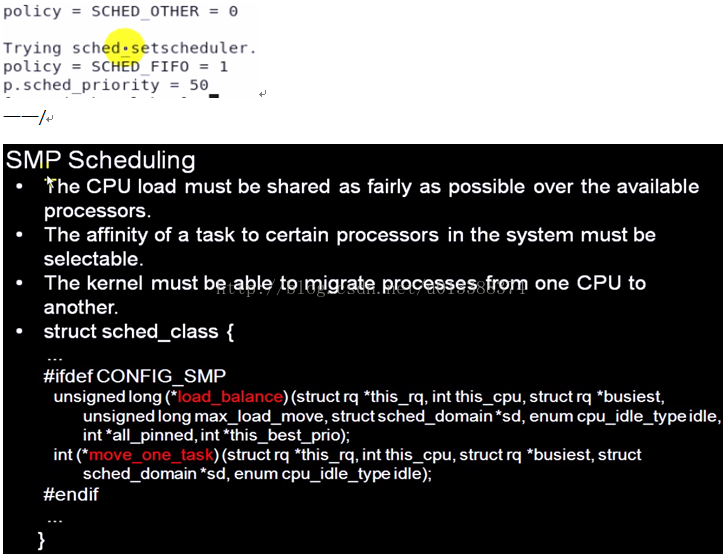
void printpolicy (int policy)
{
if (policy == SCHED_OTHER)
printf ("policy = SCHED_OTHER = %d\n", policy);
if (policy == SCHED_FIFO)
printf ("policy = SCHED_FIFO = %d\n", policy);
if (policy == SCHED_RR)
printf ("policy = SCHED_RR = %d\n", policy);
}
int main (int argc, char **argv)
{
int policy;
struct sched_param p;
/* obtain current scheduling policy for this process */
policy = sched_getscheduler (0); //0获取当前进程
printpolicy (policy);
/* reset scheduling policy */
printf ("\nTrying sched_setscheduler...\n");
policy = SCHED_FIFO;
printpolicy (policy);
p.sched_priority = 50;
if (sched_setscheduler (0, policy, &p))
DEATH ("sched_setscheduler:");
printf ("p.sched_priority = %d\n", p.sched_priority);
exit (0);
}

多核与多处理器概念异
SMP(Symmetric Multi-Processing):对称多处理器
负载均衡:将任务平分到各CPU(很热门的技术)

load_balance
move_tasks
class->load_balance(......
struct rq
struct task_struct *migration_thread;

// callback that gets triggered when a CPU is added
migration_call
struct task_struct *p kthread_create(migration_thread, hcpu, "migration/%d",cpu);
kthread_bind(p, cpu); //线程与CPU绑定
migration_thread
BUG_ON(rq->migration_thread != current);
__migrate_task (struct task_struct *p, int src_cpu, int dest_cpu)
rq_src = cpu_rq(src_cpu);
rq_dest = cpu_rq(dest_cpu);
deactivate_task (struct task_struct *p, struct rq *rq)
dec_nr_running(p, rq);
dequeue_task(p, p->array);
set_task_cpu(p, dest_cpu);
__activate_task(p, rq_dest);























 4248
4248











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








