最近项目中需要用到折线图,发现了一款比较好用的折线图hellocharts,做了炫酷的动画以及折线图,柱状图,混合图都有涉及到,非常的棒,在此推荐一下。
但是使用过程中碰到这样的需求:
①:不同数据点可以显示不同的颜色
②:还要有基准线
这可把我难坏了,看了下hellocharts的源码后,没有看到提供设置不同数据点的颜色以及基准线的接口(可能也是我看得不仔细吧)算了,不管这些了,项目马上要上线了,得赶紧做出来,主要的是去实现功能满足需求,当然了,满足了需求之后还得调整界面以及样式。话不多说,我们开始吧~ Σ(っ°Д°;)っ
来看看我做的效果吧:

接下来结合代码为大家分析一下大致流程(今天我就不直接放代码了,我要一步一步的介绍一下我的流程 ヾ(゚∀゚ゞ) )(可爱的源码君依然是在文章最后):
一、首先将坐标轴X轴Y轴绘制出来
①、大部分的Y轴都用来展示数字类型的数据,X轴可数字类型也可文字类型,这就好办了,定义两个List,一个存Y轴的数字,一个存X轴的字符(数字的话可以转成字符串)
定义一个AxisValue类,用来存放轴上单个点的数据:
/**
* Created by fySpring
* Date : 2017/8/10
* To do :x或y轴上的值
*/
public class AxisValue {
private float value; //值
private String label; //文字
public AxisValue(float value) {
setValue(value);
}
public AxisValue(float value, String label) {
this.value = value;
this.label = label;
}
public AxisValue(AxisValue axisValue) {
this.value = axisValue.value;
this.label = axisValue.label;
}
public float getValue() {
return value;
}
public AxisValue setValue(float value) {
this.value = value;
return this;
}
public AxisValue setLabel(String label) {
this.label = label;
return this;
}
public String getLabel() {
return label;
}
}/**
* Created by fySpring
* Date : 2017/8/10
* To do :x或y轴
*/
public class Axis {
public static final int DEFAULT_TEXT_SIZE_SP = 12;
/**
* X轴间隔,每隔多少显示一个值,默认为1
*/
private int spacingNum = 1;
/**
* 是否显示轴上的刻度线
*/
private boolean hasLines = false;
/**
* 值的颜色
*/
private int textColor = Color.LTGRAY;
/**
* 值的字体大小
*/
private int textSize = DEFAULT_TEXT_SIZE_SP;
/**
* 刻度线的颜色
*/
private int lineColor = Color.LTGRAY;
/**
* 坐标值list
*/
private List<AxisValue> values = new ArrayList<>();
public Axis() {
}
public Axis(List<AxisValue> values) {
this.values = values;
}
public int getSpacingNum() {
return spacingNum;
}
public void setSpacingNum(int spacingNum) {
this.spacingNum = spacingNum;
}
public boolean isHasLines() {
return hasLines;
}
public Axis setHasLines(boolean hasLines) {
this.hasLines = hasLines;
return this;
}
public int getTextColor() {
return textColor;
}
public void setTextColor(int textColor) {
this.textColor = textColor;
}
public int getTextSize() {
return textSize;
}
public void setTextSize(int textSize) {
this.textSize = textSize;
}
public int getLineColor() {
return lineColor;
}
public void setLineColor(int lineColor) {
this.lineColor = lineColor;
}
public List<AxisValue> getValues() {
return values;
}
public void setValues(List<AxisValue> values) {
this.values = values;
}
}
②、关于轴相关的类已经建好,接下来就是绘制轴上的数据。绘制Y轴的数据需要注意一点,由于数据的宽度不一样,我们需要保证数据在Y轴能够右对齐,要先遍历每一个数据,然后测量其宽度,取出最大的宽度,为了保证高度上能够均分,需要预先算出X轴上文字的高度,这样就能保证X轴和Y轴上下都能留出一定的距离给数据展示。
设置Y轴的数据:
//获取数据中的X轴和Y轴
Axis xAxis = data.getAxisX();
Axis yAxis = data.getAxisY();
//设置轴的颜色和字体大小
paint.setColor(xAxis.getTextColor());
paint.setTextSize(sp2px(xAxis.getTextSize()));
//从X轴的数据中取出一个来测量底部需要的高度
String firstStr = "测试";
paint.getTextBounds(firstStr, 0, firstStr.length(), fontRect);
// X轴的起始值,表示距离底部的Y的值
int bottomY = getHeight() - fontRect.height() * 2 - paddingLeft;
//Y轴上每一项的高度,用来均分,一定要用float来计算除法,切记!!!!
float itemHeight = (float) bottomY / yAxis.getValues().size();
//遍历Y轴的数据,取出占用宽度最大的数值,保持Y轴的数据能够右对齐
widthList.clear();
int maxWidth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < yAxis.getValues().size(); i++) {
String contentStr = yAxis.getValues().get(i).getLabel();
//测量字体宽度,取最大宽度
paint.getTextBounds(contentStr, 0, contentStr.length(), fontRect);
widthList.add(fontRect.width());
if (fontRect.width() > maxWidth) maxWidth = fontRect.width();
}
//Y轴的起始值,表示距离左边的X的值
int leftX = maxWidth + paddingLeft * 2;
//绘制Y轴上的值及刻度
for (int i = 0; i < yAxis.getValues().size(); i++) {
String contentStr = yAxis.getValues().get(i).getLabel();
float curY = itemHeight * (yAxis.getValues().size() - i);
//绘制值
canvas.drawText(contentStr, paddingLeft + maxWidth - widthList.get(i), curY + fontRect.height() / 2, paint);
//绘制刻度线,0的时候不需要画刻度
if (i != 0) {
if (yAxis.isHasLines())
canvas.drawLine(leftX, curY, getWidth() - paddingRight, curY, paint);
else
canvas.drawLine(leftX, curY, leftX + scaleHeight, curY, paint);
}
}设置X轴上的数据,在这个地方会出现新的问题,为保证文字能够垂直居中,所以我们需要减去测量文字的高度的一半,但是!!!文字的高度不一样的话,就不会显示在中间。比如文字 一 和 日。咦,我为什么要说日。ノ´▽`)ノ♪ 后来我想到一种做法,在底部放一个矩形,每个矩形的高度一样,然后将文字设置在矩形的中间。并且,宽度还要减去每个文字的宽度的一半。简直完美!
//计算X轴要显示的数据个数
int xUnit = (int) Math.ceil((double) xAxis.getValues().size() / xAxis.getSpacingNum());
//X轴上每一项的宽度,切记,右边一定要记得转float
float itemWidth = (float) (getWidth() - leftX - paddingRight) / xUnit;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < xAxis.getValues().size(); i += xAxis.getSpacingNum()) {
String contentStr = xAxis.getValues().get(i).getLabel();
//测量字体宽度
paint.getTextBounds(contentStr, 0, contentStr.length(), fontRect);
float curX = leftX + index * itemWidth;
//绘制坐标轴上的值,减掉字体宽度的一半是为了对齐刻度线
//设置一个矩形格子,保证文字能够居中
Rect targetRect = new Rect((int) curX - fontRect.width() / 2, bottomY, (int) curX + fontRect.width() / 2, getHeight());
canvas.drawText(contentStr, targetRect.left, targetRect.centerY(), paint);
//绘制坐标轴刻度线
if (i != 0) {
if (xAxis.isHasLines())
canvas.drawLine(curX, 0, curX, bottomY, paint);
else
canvas.drawLine(curX, bottomY - scaleHeight, curX, bottomY, paint);
}
index++;
}
//绘制Y轴的线
canvas.drawLine(leftX, 0, leftX, bottomY, paint);
//绘制X轴的线
canvas.drawLine(leftX, bottomY, getWidth() - paddingRight, bottomY, paint);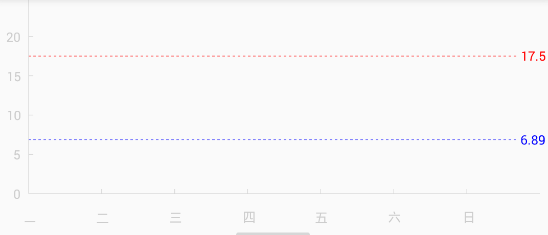
二、坐标轴已经绘制好了,我们开始绘制基准线,定义了一个BaseLine类,这个类里主要放了value和color,就不展示出来了,画线那里用到了DashPathEffect类。这个类的作用就是将Path的线段虚线化。构造函数为DashPathEffect(float[] intervals, float offset),其中intervals为虚线的ON和OFF数组,该数组的length必须大于等于2,offset为绘制时的偏移量。
effects = new DashPathEffect(new float[]{5, 5, 5, 5}, 1);
//绘制基准线
if (data.getBaseLines().size() != 0) {
float maxY = yAxis.getValues().get(yAxis.getValues().size() - 1).getValue();
float minY = yAxis.getValues().get(0).getValue();
for (BaseLine line : data.getBaseLines()) {
path.reset();
//基准值只能在最大值和最小值之间
if (line.getBaseValue() < maxY && line.getBaseValue() > minY) {
String contentStr = String.valueOf(line.getBaseValue());
//测量字体宽度
paint.getTextBounds(contentStr, 0, contentStr.length(), fontRect);
//计算基准线的Y轴的位置
float progress = 1 - (line.getBaseValue() / maxY);
float curY = (bottomY - itemHeight) * progress + itemHeight;
float toX = getWidth() - paddingRight - fontRect.width();
paint.setColor(line.getBaseColor());
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
paint.setPathEffect(effects);
path.moveTo(leftX, curY);
path.lineTo(toX, curY);
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
canvas.drawText(contentStr, toX + paddingRight / 2, curY + fontRect.height() / 2, paint);
}
}
}三、基准线绘制好了,接下来就是绘制点和线了。这里也得注意,先要绘制线,再绘制点,因为点的颜色会不一样,再绘制线的话会盖在点的上面。我的做法是先将每个点在屏幕的坐标位置根据点的X轴Y轴的值计算出来。
①、首先我们需要一个PointValue类来存储点的位置,这里没什么好说的,看名字就能明白:
/**
* Created by fySpring
* Date : 2017/8/10
* To do :点的坐标值及颜色
*/
public class PointValue {
private float xValue; //点在X轴上的值
private float yValue; //点在Y轴上的值
private float xPosition; //点在X轴上的位置
private float yPosition; //点在Y轴上的位置
private String label;
private int pointColor;
public PointValue(float xValue, float yValue) {
setData(xValue, yValue);
}
public PointValue(PointValue pointValue) {
setData(pointValue.xValue, pointValue.yValue);
this.label = pointValue.label;
}
public PointValue setData(float xValue, float yValue) {
this.xValue = xValue;
this.yValue = yValue;
return this;
}
public float getxValue() {
return xValue;
}
public void setxValue(float xValue) {
this.xValue = xValue;
}
public float getyValue() {
return yValue;
}
public void setyValue(float yValue) {
this.yValue = yValue;
}
public float getxPosition() {
return xPosition;
}
public void setxPosition(float xPosition) {
this.xPosition = xPosition;
}
public float getyPosition() {
return yPosition;
}
public void setyPosition(float yPosition) {
this.yPosition = yPosition;
}
public String getLabel() {
return TextUtils.isEmpty(label) ? String.valueOf(yValue) : label;
}
public void setLabel(String label) {
this.label = label;
}
public int getPointColor() {
return pointColor;
}
public PointValue setPointColor(int pointColor) {
this.pointColor = pointColor;
return this;
}
}
/**
* Created by fySpring
* Date : 2017/8/10
* To do :折线图中每条线的数据
*/
public class Line {
private static final int DEFAULT_LINE_STROKE_WIDTH_DP = 1;
private static final int DEFAULT_POINT_RADIUS_DP = 3;
/**
* 线的颜色,默认红色
*/
private int lineColor = Color.RED;
/**
* 圆点的颜色
*/
private int pointColor;
/**
* 线的宽度
*/
private int strokeWidth = DEFAULT_LINE_STROKE_WIDTH_DP;
/**
* 圆点的半径
*/
private int pointRadius = DEFAULT_POINT_RADIUS_DP;
/**
* 是否显示小圆点
*/
private boolean hasPoints = true;
/**
* 是否显示值
*/
private boolean hasLabels = false;
/**
* 折线是否圆滑
*/
private boolean isSmooth = false;
private List<PointValue> values = new ArrayList<>();
public Line(List<PointValue> values) {
this.values = values;
}
public int getLineColor() {
return lineColor;
}
public void setLineColor(int lineColor) {
this.lineColor = lineColor;
}
public int getPointColor() {
//如果没有设置则返回线的颜色
return pointColor == 0 ? lineColor : pointColor;
}
public void setPointColor(int pointColor) {
this.pointColor = pointColor;
}
public int getStrokeWidth() {
return strokeWidth;
}
public void setStrokeWidth(int strokeWidth) {
this.strokeWidth = strokeWidth;
}
public int getPointRadius() {
return pointRadius;
}
public void setPointRadius(int pointRadius) {
this.pointRadius = pointRadius;
}
public boolean isHasPoints() {
return hasPoints;
}
public void setHasPoints(boolean hasPoints) {
this.hasPoints = hasPoints;
}
public boolean isHasLabels() {
return hasLabels;
}
public void setHasLabels(boolean hasLabels) {
this.hasLabels = hasLabels;
}
public boolean isSmooth() {
return isSmooth;
}
public void setSmooth(boolean smooth) {
isSmooth = smooth;
}
public List<PointValue> getValues() {
return values;
}
public void setValues(List<PointValue> values) {
this.values = values;
}
}/**
* Created by fySpring
* Date : 2017/8/10
* To do :折线图数据类
*/
public class LineChartData implements ChartData{
private static final int DEFAULT_TEXT_SIZE_SP = 12;
private Axis axisX;
private Axis axisY;
private int valueLabelTextColor = Color.WHITE;
private int valueLabelTextSize = DEFAULT_TEXT_SIZE_SP;
private List<BaseLine> baseLines = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Line> lines = new ArrayList<>();
public LineChartData(List<Line> lines) {
this.lines = lines;
}
@Override
public Axis getAxisX() {
return axisX;
}
@Override
public void setAxisX(Axis axisX) {
this.axisX = axisX;
}
@Override
public Axis getAxisY() {
return axisY;
}
@Override
public void setAxisY(Axis axisY) {
this.axisY = axisY;
}
@Override
public int getValueLabelTextColor() {
return valueLabelTextColor;
}
@Override
public void setValueLabelsTextColor(int valueLabelTextColor) {
this.valueLabelTextColor = valueLabelTextColor;
}
@Override
public int getValueLabelTextSize() {
return valueLabelTextSize;
}
@Override
public void setValueLabelTextSize(int valueLabelTextSize) {
this.valueLabelTextSize = valueLabelTextSize;
}
public List<Line> getLines() {
return lines;
}
public List<BaseLine> getBaseLines() {
return baseLines;
}
public void setBaseLines(List<BaseLine> baseLines) {
this.baseLines = baseLines;
}
}
④、最后再来根据线的个数去绘制点和线,通过Y的最大值来计算点的Y轴的位置
//计算点在屏幕中的位置
if (data.getLines().size() != 0) {
float maxY = yAxis.getValues().get(yAxis.getValues().size() - 1).getValue();
for (Line line : data.getLines()) {
for (PointValue value : line.getValues()) {
//根据横纵坐标计算点在屏幕中的位置,如果没有线的话可以在这里画点
float xProgress = value.getxValue() / xAxis.getValues().size();
float yProgress = 1 - (value.getyValue() / maxY);
//点的坐标
float centerX = leftX + (getWidth() - leftX - paddingRight) * xProgress;
float centerY = (bottomY - itemHeight) * yProgress + itemHeight;
value.setxPosition(centerX);
value.setyPosition(centerY);
}
//根据数据值画线与点
drawLineAndPoint(canvas, line);
}
}最关键的绘制线的地方在这里,由于比较复杂,我就单独封装了一个方法,记得绘制之前将path和paint给reset一下。(这里可得注意点,一不留心就会出问题)
/**
* 根据点绘制贝赛尔曲线和点,绘制贝赛尔曲线每次需要三个点
*
* @param canvas
* @param line
*/
private void drawLineAndPoint(Canvas canvas, Line line) {
path.reset();
paint.reset();
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
paint.setColor(line.getLineColor());
paint.setStrokeWidth(dip2px(line.getStrokeWidth()));
if (line.isSmooth()) {
//绘制圆滑曲线
float prePreviousPointX = Float.NaN;
float prePreviousPointY = Float.NaN;
float previousPointX = Float.NaN;
float previousPointY = Float.NaN;
float currentPointX = Float.NaN;
float currentPointY = Float.NaN;
float nextPointX = Float.NaN;
float nextPointY = Float.NaN;
int valueSize = line.getValues().size();
for (int valueIndex = 0; valueIndex < valueSize; valueIndex++) {
if (Float.isNaN(currentPointX)) {
PointValue linePoint = line.getValues().get(valueIndex);
currentPointX = linePoint.getxPosition();
currentPointY = linePoint.getyPosition();
}
if (Float.isNaN(previousPointX)) {
if (valueIndex > 0) {
PointValue linePoint = line.getValues().get(valueIndex - 1);
previousPointX = linePoint.getxPosition();
previousPointY = linePoint.getyPosition();
} else {
previousPointX = currentPointX;
previousPointY = currentPointY;
}
}
if (Float.isNaN(prePreviousPointX)) {
if (valueIndex > 1) {
PointValue linePoint = line.getValues().get(valueIndex - 2);
prePreviousPointX = linePoint.getxPosition();
prePreviousPointY = linePoint.getyPosition();
} else {
prePreviousPointX = previousPointX;
prePreviousPointY = previousPointY;
}
}
// 设置当前点的下一个点的坐标
if (valueIndex < valueSize - 1) {
PointValue linePoint = line.getValues().get(valueIndex + 1);
nextPointX = linePoint.getxPosition();
nextPointY = linePoint.getyPosition();
} else {
nextPointX = currentPointX;
nextPointY = currentPointY;
}
if (valueIndex == 0) {
// 将第一个点设为起始点
path.moveTo(currentPointX, currentPointY);
} else {
// 计算出每个点的控制点
final float firstDiffX = (currentPointX - prePreviousPointX);
final float firstDiffY = (currentPointY - prePreviousPointY);
final float secondDiffX = (nextPointX - previousPointX);
final float secondDiffY = (nextPointY - previousPointY);
final float firstControlPointX = previousPointX + (LINE_SMOOTHNESS * firstDiffX);
final float firstControlPointY = previousPointY + (LINE_SMOOTHNESS * firstDiffY);
final float secondControlPointX = currentPointX - (LINE_SMOOTHNESS * secondDiffX);
final float secondControlPointY = currentPointY - (LINE_SMOOTHNESS * secondDiffY);
path.cubicTo(firstControlPointX, firstControlPointY, secondControlPointX, secondControlPointY,
currentPointX, currentPointY);
}
// 将值后移
prePreviousPointX = previousPointX;
prePreviousPointY = previousPointY;
previousPointX = currentPointX;
previousPointY = currentPointY;
currentPointX = nextPointX;
currentPointY = nextPointY;
}
} else {
//绘制直线
for (int i = 0; i < line.getValues().size(); i++) {
PointValue value = line.getValues().get(i);
//第一个点不需要连接
if (i == 0) {
path.moveTo(value.getxPosition(), value.getyPosition());
} else {
path.lineTo(value.getxPosition(), value.getyPosition());
}
}
}
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
//如果有点的话就进行画圆点
if (line.isHasPoints()) {
paint.setTextSize(defaultTextSize);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
for (PointValue pointValue : line.getValues()) {
if (pointValue.getPointColor() != 0) {
paint.setColor(pointValue.getPointColor());
} else {
paint.setColor(line.getPointColor());
}
//画圆点
canvas.drawCircle(pointValue.getxPosition(), pointValue.getyPosition(), dip2px(line.getPointRadius()), paint);
if (line.isHasLabels()) {
String contentStr = pointValue.getLabel();
//测量字体宽高
paint.getTextBounds(contentStr, 0, contentStr.length(), fontRect);
//绘制点的顶部数据
canvas.drawText(contentStr, pointValue.getxPosition() - fontRect.width() / 2, pointValue.getyPosition() - 20, paint);
}
}
}
}最后再放上完整的LineChartView吧,好方便大家对应着去看:
public class LineChartView extends View {
private static final float LINE_SMOOTHNESS = 0.16f;
private Context context;
private LineChartData data;
private int paddingLeft;
private int paddingRight;
//刻度的高度,只在hasLine为false的情况下显示
private int scaleHeight;
//绘制虚线
private PathEffect effects;
private Paint paint;
private Path path;//路径
private Rect fontRect; //测量字体
private List<Integer> widthList;
private int defaultTextSize;
public LineChartView(Context context) {
super(context, null, 0);
this.context = context;
init();
}
public LineChartView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs, 0);
this.context = context;
init();
}
public LineChartView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
this.context = context;
init();
}
private void init() {
paint = new Paint();
path = new Path();
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
fontRect = new Rect();
widthList = new ArrayList<>();
effects = new DashPathEffect(new float[]{5, 5, 5, 5}, 1);
paddingLeft = dip2px(10);
paddingRight = dip2px(10);
scaleHeight = dip2px(5);
defaultTextSize = sp2px(12);
}
public void setData(LineChartData data) {
this.data = data;
invalidate();
}
public LineChartData getData() {
return data;
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
if (data != null && data.getAxisY().getValues().size() != 0 && data.getAxisX().getValues().size() != 0) {
path.reset();
paint.setStrokeWidth(1);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
//获取数据中的X轴和Y轴
Axis xAxis = data.getAxisX();
Axis yAxis = data.getAxisY();
//设置轴的颜色和字体大小
paint.setColor(xAxis.getTextColor());
paint.setTextSize(sp2px(xAxis.getTextSize()));
//从X轴的数据中取出一个来测量底部需要的高度
String firstStr = "测试";
paint.getTextBounds(firstStr, 0, firstStr.length(), fontRect);
// X轴的起始值,表示距离底部的Y的值
int bottomY = getHeight() - fontRect.height() * 2 - paddingLeft;
//Y轴上每一项的高度,用来均分,一定要用float来计算除法,切记!!!!
float itemHeight = (float) bottomY / yAxis.getValues().size();
//遍历Y轴的数据,取出占用宽度最大的数值,保持Y轴的数据能够右对齐
widthList.clear();
int maxWidth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < yAxis.getValues().size(); i++) {
String contentStr = yAxis.getValues().get(i).getLabel();
//测量字体宽度,取最大宽度
paint.getTextBounds(contentStr, 0, contentStr.length(), fontRect);
widthList.add(fontRect.width());
if (fontRect.width() > maxWidth) maxWidth = fontRect.width();
}
//Y轴的起始值,表示距离左边的X的值
int leftX = maxWidth + paddingLeft * 2;
//绘制Y轴上的值及刻度
for (int i = 0; i < yAxis.getValues().size(); i++) {
String contentStr = yAxis.getValues().get(i).getLabel();
float curY = itemHeight * (yAxis.getValues().size() - i);
//绘制值
canvas.drawText(contentStr, paddingLeft + maxWidth - widthList.get(i), curY + fontRect.height() / 2, paint);
//绘制刻度线,0的时候不需要画刻度
if (i != 0) {
if (yAxis.isHasLines())
canvas.drawLine(leftX, curY, getWidth() - paddingRight, curY, paint);
else
canvas.drawLine(leftX, curY, leftX + scaleHeight, curY, paint);
}
}
//计算X轴要显示的数据个数
int xUnit = (int) Math.ceil((double) xAxis.getValues().size() / xAxis.getSpacingNum());
//X轴上每一项的宽度,切记,右边一定要记得转float
float itemWidth = (float) (getWidth() - leftX - paddingRight) / xUnit;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < xAxis.getValues().size(); i += xAxis.getSpacingNum()) {
String contentStr = xAxis.getValues().get(i).getLabel();
//测量字体宽度
paint.getTextBounds(contentStr, 0, contentStr.length(), fontRect);
float curX = leftX + index * itemWidth;
//绘制坐标轴上的值,减掉字体宽度的一半是为了对齐刻度线
//设置一个矩形格子,保证文字能够居中
Rect targetRect = new Rect((int) curX - fontRect.width() / 2, bottomY, (int) curX + fontRect.width() / 2, getHeight());
canvas.drawText(contentStr, targetRect.left, targetRect.centerY(), paint);
//绘制坐标轴刻度线
if (i != 0) {
if (xAxis.isHasLines())
canvas.drawLine(curX, 0, curX, bottomY, paint);
else
canvas.drawLine(curX, bottomY - scaleHeight, curX, bottomY, paint);
}
index++;
}
//绘制Y轴的线
canvas.drawLine(leftX, 0, leftX, bottomY, paint);
//绘制X轴的线
canvas.drawLine(leftX, bottomY, getWidth() - paddingRight, bottomY, paint);
//绘制基准线
if (data.getBaseLines().size() != 0) {
float maxY = yAxis.getValues().get(yAxis.getValues().size() - 1).getValue();
float minY = yAxis.getValues().get(0).getValue();
for (BaseLine line : data.getBaseLines()) {
path.reset();
//基准值只能在最大值和最小值之间
if (line.getBaseValue() < maxY && line.getBaseValue() > minY) {
String contentStr = String.valueOf(line.getBaseValue());
//测量字体宽度
paint.getTextBounds(contentStr, 0, contentStr.length(), fontRect);
//计算基准线的Y轴的位置
float progress = 1 - (line.getBaseValue() / maxY);
float curY = (bottomY - itemHeight) * progress + itemHeight;
float toX = getWidth() - paddingRight - fontRect.width();
paint.setColor(line.getBaseColor());
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
paint.setPathEffect(effects);
path.moveTo(leftX, curY);
path.lineTo(toX, curY);
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
canvas.drawText(contentStr, toX + paddingRight / 2, curY + fontRect.height() / 2, paint);
}
}
}
//计算点在屏幕中的位置
if (data.getLines().size() != 0) {
float maxY = yAxis.getValues().get(yAxis.getValues().size() - 1).getValue();
for (Line line : data.getLines()) {
for (PointValue value : line.getValues()) {
//根据横纵坐标计算点在屏幕中的位置,如果没有线的话可以在这里画点
float xProgress = value.getxValue() / xAxis.getValues().size();
float yProgress = 1 - (value.getyValue() / maxY);
//点的坐标
float centerX = leftX + (getWidth() - leftX - paddingRight) * xProgress;
float centerY = (bottomY - itemHeight) * yProgress + itemHeight;
value.setxPosition(centerX);
value.setyPosition(centerY);
}
//根据数据值画线与点
drawLineAndPoint(canvas, line);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 根据点绘制贝赛尔曲线和点,绘制贝赛尔曲线每次需要三个点
*
* @param canvas
* @param line
*/
private void drawLineAndPoint(Canvas canvas, Line line) {
path.reset();
paint.reset();
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
paint.setColor(line.getLineColor());
paint.setStrokeWidth(dip2px(line.getStrokeWidth()));
if (line.isSmooth()) {
//绘制圆滑曲线
float prePreviousPointX = Float.NaN;
float prePreviousPointY = Float.NaN;
float previousPointX = Float.NaN;
float previousPointY = Float.NaN;
float currentPointX = Float.NaN;
float currentPointY = Float.NaN;
float nextPointX = Float.NaN;
float nextPointY = Float.NaN;
int valueSize = line.getValues().size();
for (int valueIndex = 0; valueIndex < valueSize; valueIndex++) {
if (Float.isNaN(currentPointX)) {
PointValue linePoint = line.getValues().get(valueIndex);
currentPointX = linePoint.getxPosition();
currentPointY = linePoint.getyPosition();
}
if (Float.isNaN(previousPointX)) {
if (valueIndex > 0) {
PointValue linePoint = line.getValues().get(valueIndex - 1);
previousPointX = linePoint.getxPosition();
previousPointY = linePoint.getyPosition();
} else {
previousPointX = currentPointX;
previousPointY = currentPointY;
}
}
if (Float.isNaN(prePreviousPointX)) {
if (valueIndex > 1) {
PointValue linePoint = line.getValues().get(valueIndex - 2);
prePreviousPointX = linePoint.getxPosition();
prePreviousPointY = linePoint.getyPosition();
} else {
prePreviousPointX = previousPointX;
prePreviousPointY = previousPointY;
}
}
// 设置当前点的下一个点的坐标
if (valueIndex < valueSize - 1) {
PointValue linePoint = line.getValues().get(valueIndex + 1);
nextPointX = linePoint.getxPosition();
nextPointY = linePoint.getyPosition();
} else {
nextPointX = currentPointX;
nextPointY = currentPointY;
}
if (valueIndex == 0) {
// 将第一个点设为起始点
path.moveTo(currentPointX, currentPointY);
} else {
// 计算出每个点的控制点
final float firstDiffX = (currentPointX - prePreviousPointX);
final float firstDiffY = (currentPointY - prePreviousPointY);
final float secondDiffX = (nextPointX - previousPointX);
final float secondDiffY = (nextPointY - previousPointY);
final float firstControlPointX = previousPointX + (LINE_SMOOTHNESS * firstDiffX);
final float firstControlPointY = previousPointY + (LINE_SMOOTHNESS * firstDiffY);
final float secondControlPointX = currentPointX - (LINE_SMOOTHNESS * secondDiffX);
final float secondControlPointY = currentPointY - (LINE_SMOOTHNESS * secondDiffY);
path.cubicTo(firstControlPointX, firstControlPointY, secondControlPointX, secondControlPointY,
currentPointX, currentPointY);
}
// 将值后移
prePreviousPointX = previousPointX;
prePreviousPointY = previousPointY;
previousPointX = currentPointX;
previousPointY = currentPointY;
currentPointX = nextPointX;
currentPointY = nextPointY;
}
} else {
//绘制直线
for (int i = 0; i < line.getValues().size(); i++) {
PointValue value = line.getValues().get(i);
//第一个点不需要连接
if (i == 0) {
path.moveTo(value.getxPosition(), value.getyPosition());
} else {
path.lineTo(value.getxPosition(), value.getyPosition());
}
}
}
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
//如果有点的话就进行画圆点
if (line.isHasPoints()) {
paint.setTextSize(defaultTextSize);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
for (PointValue pointValue : line.getValues()) {
if (pointValue.getPointColor() != 0) {
paint.setColor(pointValue.getPointColor());
} else {
paint.setColor(line.getPointColor());
}
//画圆点
canvas.drawCircle(pointValue.getxPosition(), pointValue.getyPosition(), dip2px(line.getPointRadius()), paint);
if (line.isHasLabels()) {
String contentStr = pointValue.getLabel();
//测量字体宽高
paint.getTextBounds(contentStr, 0, contentStr.length(), fontRect);
//绘制点的顶部数据
canvas.drawText(contentStr, pointValue.getxPosition() - fontRect.width() / 2, pointValue.getyPosition() - 20, paint);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 根据手机的分辨率从 dp 的单位 转成为 px(像素)
*/
private int dip2px(float dpValue) {
float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
return (int) (dpValue * scale + 0.5f);
}
/**
* 将sp值转换为px值,保证文字大小不变
*
* @param spValue (DisplayMetrics类中属性scaledDensity)
* @return
*/
public int sp2px(float spValue) {
float fontScale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().scaledDensity;
return (int) (spValue * fontScale + 0.5f);
}
}
好了,基本上主要的内容就是以上的这些了。来看看在界面中如何使用:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private String rankColors[] = new String[]{"#98D675", "#8DD0EA", "#F6CE6E", "#FF7077", "#C15667"};
private LineChartView chartView;
private Button addPointBtn;
private List<String> xValueList = new ArrayList<>();
private List<PointValue> pointValues = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Line> lineList = new ArrayList<>();
private Random random = new Random();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
chartView = (LineChartView) findViewById(R.id.line_chart_view);
addPointBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.add_new_point_btn);
for (int i = 1; i < 16; i++) {
xValueList.add("测试"+i);
}
pointValues.add(new PointValue(0f,15f));
lineList = initDataLine(pointValues);
chartView.setData(initData(lineList,xValueList));
addPointBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
addNewPoint();
}
});
}
private void addNewPoint(){
float x = random.nextInt(15);
float y = random.nextInt(20);
int colorInt = random.nextInt(5);
//生成随机颜色,随机位置的点在坐标轴上
pointValues.add(new PointValue(x,y).setPointColor(Color.parseColor(rankColors[colorInt])));
lineList = initDataLine(pointValues);
chartView.setData(initData(lineList,xValueList));
}
/**
* 初始化线属性
*
* @return
*/
private List<Line> initDataLine(List<PointValue> pointValueList) {
List<Line> lineList = new ArrayList<>();
//这里可以设置多条数据线,目前我这里展示只有一条
Line bgLine = new Line(pointValueList);
bgLine.setSmooth(true);
bgLine.setHasLabels(true);
bgLine.setPointColor(Color.RED);
bgLine.setLineColor(Color.GREEN);
bgLine.setHasPoints(true);
lineList.add(bgLine);
return lineList;
}
/**
* 初始化记录曲线
*
* @return
*/
private LineChartData initData(List<Line> lines, List<String> xDatas) {
LineChartData data = new LineChartData(lines);
Axis axisY = new Axis();
Axis axisX = new Axis();
axisX.setSpacingNum(3);
//设置x轴数值
List<AxisValue> xValues = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < xDatas.size(); i++) {
AxisValue value = new AxisValue(i);
String label = xDatas.get(i);
value.setLabel(label);
xValues.add(value);
}
axisX.setValues(xValues);
//设置y轴数值
List<AxisValue> yValues = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= 20; i += 5) {
AxisValue value = new AxisValue(i);
String label = String.valueOf(i);
value.setLabel(label);
yValues.add(value);
}
axisY.setValues(yValues);
//设置X轴Y轴
data.setAxisY(axisY);
data.setAxisX(axisX);
//设置基准线
List<BaseLine> baseLineList = new ArrayList<>();
BaseLine baseLine1 = new BaseLine().setBaseValue(17.5f).setBaseColor(Color.RED);
BaseLine baseLine2 = new BaseLine().setBaseValue(6.89f).setBaseColor(Color.BLUE);
baseLineList.add(baseLine1);
baseLineList.add(baseLine2);
data.setBaseLines(baseLineList);
return data;
}
}
好啦,基本上就是这些了,各位老铁觉得不错的话不妨点个赞? 罒ω罒
























 3933
3933

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










