一篇比较老的文章。
repost:https://blog.cloudera.com/how-hiveserver2-brings-security-and-concurrency-to-apache-hive/
Apache Hive was one of the first projects to bring higher-level languages to Apache Hadoop. Specifically, Hive enables the legions of trained SQL users to use industry-standard SQL to process their Hadoop data.
However, as you probably have gathered from all the recent community activity in the SQL-over-Hadoop area, Hive has a few limitations for users in the enterprise space. Until recently, two in particular – concurrency and security – were largely unaddressed.
To address these gaps, for Hive release 0.11, Cloudera engineers built and contributed new infrastructure for meeting these needs. In this post, you’ll learn why it’s needed, and how it works.
Customer Requirements
As you probably know, relational databases almost universally have a server process to support clients connecting over IPC or network connections. The clients may be native command-line editors or applications/tools using a driver such as ODBC or JDBC.
In Hive, a component called HiveServer serves this purpose. But over the past few years, as adoption of Hive increased, more and more customers reported two major requirements unaddressed by HiveServer:
- To run more users concurrently against Hive in traditional client/server architecture
- To authenticate users to prevent untrusted user access and to enforce authorization around permissions to their data assets
Because Hive is so important for our customers, these requirements motivated us to implement a new server process for Hive 0.11. The goal was to create a framework that handles multiple concurrent clients, supports popular authentication mechanisms, and is easy to adopt for open client implementations like JDBC and ODBC.
The result of that effort, HiveServer2 (HIVE-2935), finally brings concurrency, authentication, and a foundation for authorization to Hive. Next, we’ll provide some details about these new features.
HiveServer2 Architecture
HiveServer2 is now available in Hive 0.11 and all other releases of Hive in CDH 4.1 and later. It implements a new Thrift-based RPC interface that can handle concurrent clients. The current release supports Kerberos, LDAP, and custom pluggable authentication. The new RPC interface also has better options for JDBC and ODBC clients, especially for metadata access.

Like the original HiveServer, HiveServer2 is a container for the Hive execution engine. For each client connection, it creates a new execution context that serves Hive SQL requests from the client. The new RPC interface enables the server to associate this Hive execution context with the thread serving the client’s request.
Clients for HiveServer2
JDBC: Hive 0.11 includes a new JDBC driver that works with HiveServer2, enabling users to write JDBC applications against Hive. The application needs to use the JDBC driver class and specify the network address and port in the connection URL in order to connect to Hive. The following code snippet shows how to connect to HiveServer2 from JDBC:
Class.forName("org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver");
Connection con = DriverManager.
getConnection("jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000/default",
"hive", "passwd");
You can review a detailed example on the Hive wiki.
Beeline CLI: Hive 0.11 also includes a new command-line interface (CLI) called Beeline that works with HiveServer2. Beeline is a JDBC application based on the SQLLine CLI that supports embedded and remote-client modes. The embedded mode is where the Hive runtime is part of the client process itself; there’s no server involved. (You can explore the detailed documentation for SQLLine, which is also applicable to Beeline, here.) Note that HiveServer2 doesn’t support the original Hive CLI client, as the Beeline CLI is a functional replacement designed for the HiveServer2 interface.
ODBC: Although Hive 0.11 currently doesn’t include a ODBC driver that works with HiveServer2, Cloudera makes one available.
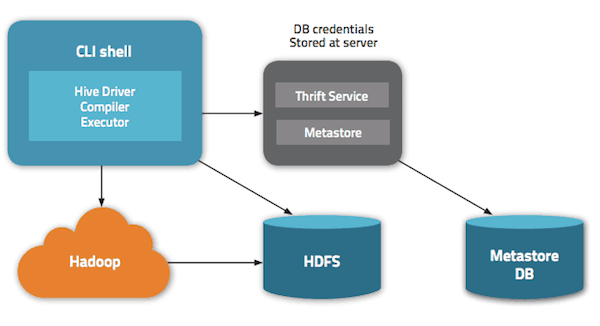
Metastore Considerations
The Hive metastore service runs in its own JVM process. Clients other than Hive, like Apache Pig, connect to this service via HCatalog for metadata access. HiveServer2 supports local as well as remote metastore modes – which is useful when you have more than one service (Pig, Cloudera Impala, and so on) that needs access to metadata. This is the recommended deployment mode with HiveServer2:
Authentication
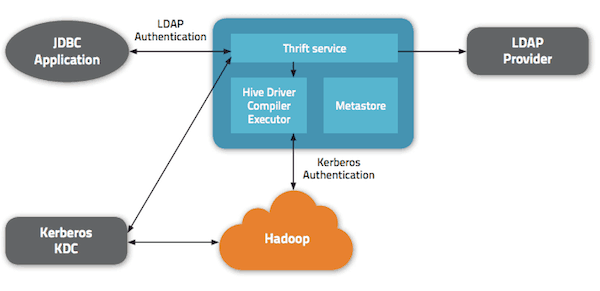
Authentication support is another major feature of HiveServer2. In the original HiveServer, if you can access the host/port over the network, you can access the data – so it relies on support for multiple authentication options to restrict access.
In contrast, HiveServer2 support Kerberos, pass-through LDAP, and pass-through plug-able custom authentication. All client types – JDBC, ODBC, as well as Beeline CLI — support these authentication modes. This enables the Hive deployment to easily integrate with existing authentication services.
Gateway to Secure Hadoop
Today, the Hadoop ecosystem only supports Kerberos for authentication. That means for accessing secure Hadoop, one needs to get a Kerberos ticket. However, enabling Kerberos on every client box can be a very challenging task and thus can restrict access to Hive and Hadoop.
To address that issue, HiveServer2 can authenticate clients over non-Kerberos connections (eg. LDAP) and run queries against Kerberos-secured Hadoop data. This approach allows users to securely access Hive without complex security infrastructure or limitations.
Foundation for Fine-grained Authorization
As a stopgap until fine-grained authorization is available, HiveServer2 also supports access to Hadoop as itself or by impersonating the connected user. (This behavior is configurable.) In this so-called impersonation mode, MapReduce jobs are submitted as the user connecting to HiveServer2. If the underlying Hadoop cluster is secure, the service principle used by Hive needs Hadoop proxy privileges to impersonate the connecting users. This interim solution provides coarse-grained authorization based on ownership and permissions on files and directories in HDFS (as opposed to Hive tables and views), which unblocks some usage.
HiveServer2’s strong authentication and revamped server-side architecture also provides the foundation for fine-grained authorization in Hive in the very near future. Stay tuned! (Update: read “With Sentry, Cloudera Closes Hadoop’s Enterprise Security Gap”)
Conclusion
In this post, you have received an overview of how Cloudera’s contribution of HiveServer2 brings concurrency, authentication, and a foundation for fine-grained authorization (more on this in a future post) to Hive. For further reading, you may want to explore the docs on Setting up HiveServer2 and HiveServer2 Clients.
Prasad Mujumdar is a Software Engineer on the Platform team.























 172
172











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








