链表的算法:
package lian.biao;
public class 链表 {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
a a=new a();
a.add(1);
a.add(2);
a.add(3);
a.add(4);
a.output();
}
}
//链表储存类
class a{
private node root;//根节点
//链表的插入
public void add(int data){
if(root!=null){
root.add(data);
}
else{
root=new node(data);
}
}
public void output(){
if(root!=null){
System.out.println(root.data);
root.output();
}
}
//链表内部类
class node {
private node next;
private int data;
public node(int data){
this.data=data;
}
public void add(int data){
//判断是否为空,调用递归进行添加
if(this.next==null){
next=new node(data);
}
else{
next.add(data);
}
}
public void output(){
//判断是否为空,调用递归进行输出
if(this.next!=null){
System.out.println(next.data);
next.output();
}
}
}
}
二叉树的算法:
其实原理和上面一样的,都是采用递归和内部类进行实现的。
算法:
package lian.biao;
public class 二叉树 {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
a a=new a();
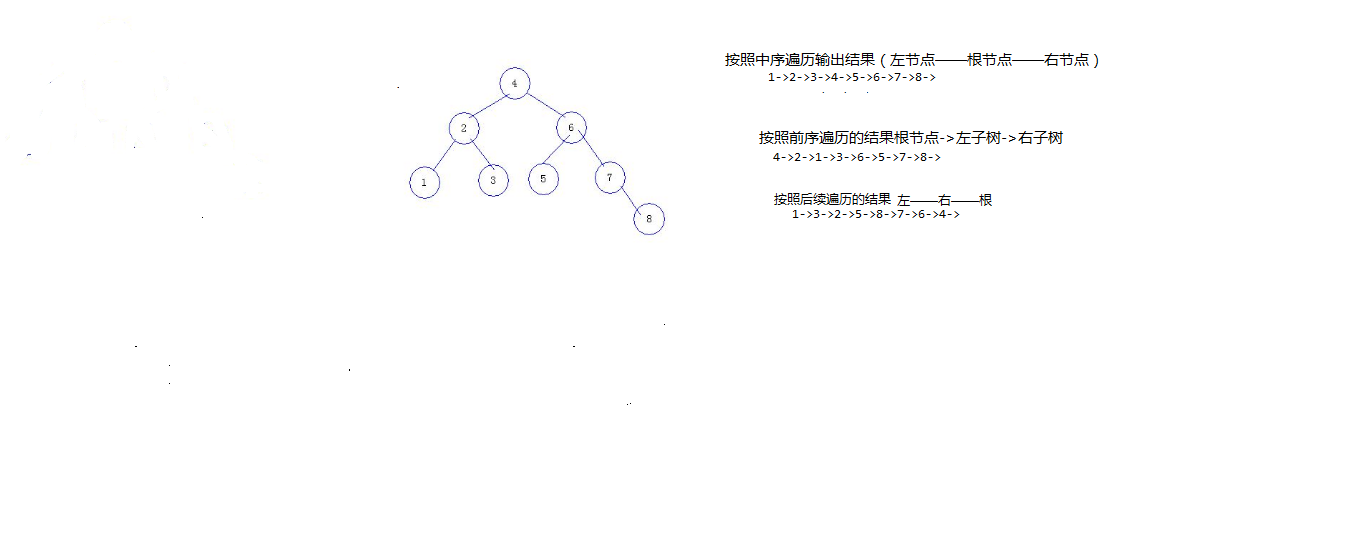
a.add(4);
a.add(2);
a.add(1);
a.add(3);
a.add(6);
a.add(5);
a.add(7);
a.add(8);
a.output();
System.out.println("");
// a.before();
}
}
//二叉树的储存类
class a{
private node root;//根节点
//二叉树的添加
public void add(int data){
if(root!=null){
root.add(data);
}
else{
root=new node(data);
}
}
//
public void output(){
if(root!=null){
// System.out.println(root.data);
root.output();
}
}
//二叉树的内部类
class node {
private node left,right;
private int data;
public node(int data){
this.data=data;
}
public void add(int data){
if(data>this.data){
if(right!=null){
right.add(data);
}
else{
right=new node(data);
}
}else if(data<=this.data){
if(left!=null){
left.add(data);
}
else{
left=new node(data);
}
}
}
//二叉树的输出,按照中序遍历(左中右进行输出)
public void output(){
//System.out.print(data+"->");前序遍历
if(left!=null){
left.output();
}
System.out.print(data+"->");//中序遍历
if(right!=null){
right.output();
}
//System.out.print(data+"->");后续遍历
}
}
}






















 823
823











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








