什么是MVP?
MVP(Model - View - Presenter , 模型 - 视图 - 表示器)模式则是由IBM开发出来的一个针对C++和java的编程模型,大概出现于2000年,是MVC模式的一个变种,主要用来隔离UI、UI逻辑和业务逻辑,数据。
MVP与MVC的区别?
MVP——Model-View-presenter 它是MVC模式的变种,UI容易变化的,且是多样的,一样的数据会有N种显示方式,业务逻辑也是比较容易变化的,为了使得Appcation具有较大的弹性,我们期望将UI、逻辑(UI的逻辑和业务逻辑) 和数据隔离离开来,而MVP是一个很好的选择。
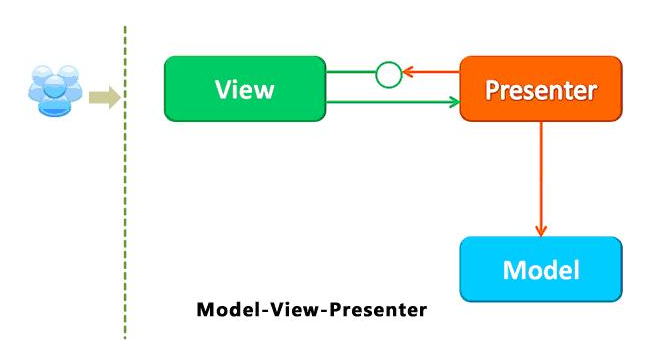
Presenter代替了Controller,它比Controller担当更多的任务,也更加复杂,Presenter处理事件,执行相应的逻辑,这些逻辑映射到Model的Command以操作Model,那些处理UI如何工作的代码基本上都位于Presenter中。Presenter如同一个乐队的指挥家,表现和协调整个Appcation,它负责创建和协调其他对象。
Model和View使用Observer模式进行沟通,而Presenter和View则使用Mediator模式进行通信,Presenter操作Model则使用Command模式来进行的。基本设计和MVC相同,Model存储数据,View是Model的表现,Presenter协调两者之间的通信。在MVP中View接收到事件,然后会将它们传递到Presenter,如何具体处理这些事件,将由Presenter来完成。
MVP的设计图如下:
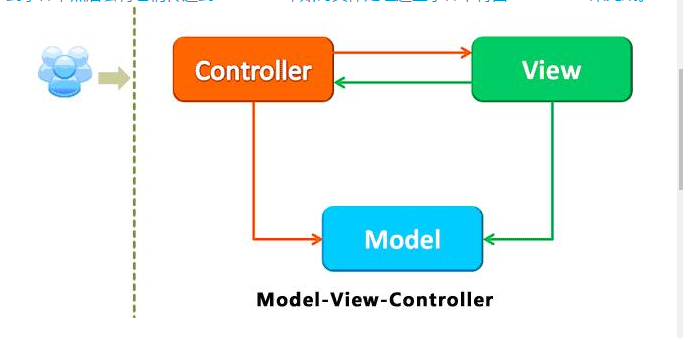
MVC设计图:
为什么使用MVP模式?MVP模式是怎样工作的呢?
请参考以下两篇文章:
关于以上的讲述,还有几篇比较好的文章,大家可以深入了解:
MVP:
Android 架构演化之路
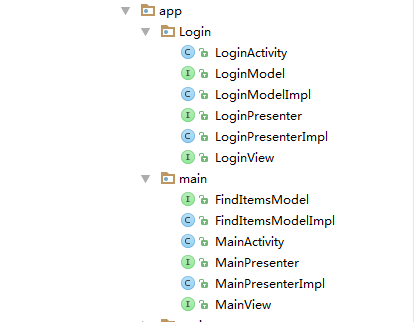
走入我们今天的主题,MVP模式的demo项目结构:
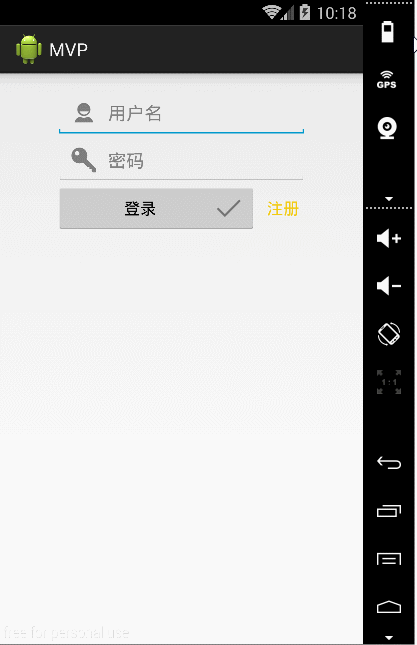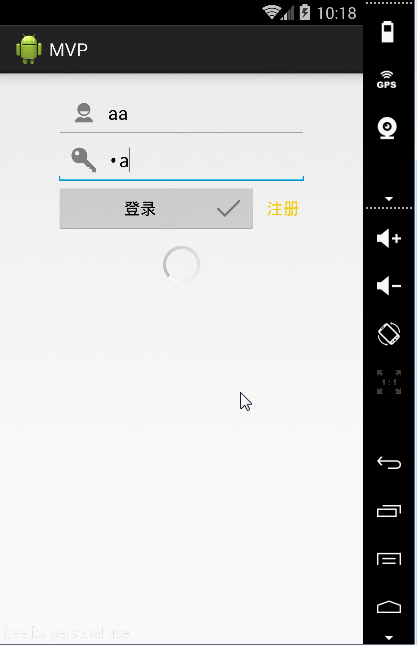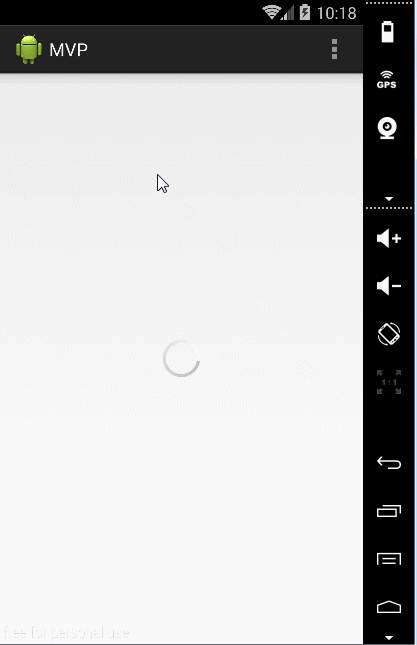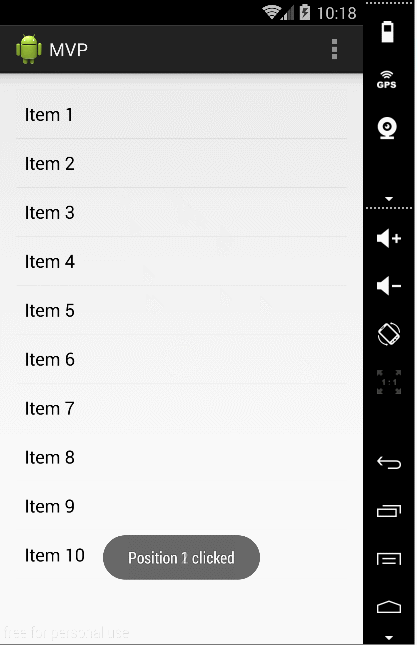
只做了一个简单的登录操作,下面看下整体效果:
接下来我们看下代码:
LoginActivity类:
package com.lai.mvp.app.Login;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.ProgressBar;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.lai.mvp.app.R;
import com.lai.mvp.app.main.MainActivity;
import com.lai.mvp.app.register.RegisterActivity;
public class LoginActivity extends Activity implements LoginView, View.OnClickListener {
private ProgressBar progressBar;
private EditText username;
private EditText password;
private LoginPresenter presenter;
private TextView tv_register;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_login);
progressBar = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.progress);
username = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.username);
password = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.password);
tv_register = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_register);
findViewById(R.id.button).setOnClickListener(this);
presenter = new LoginPresenterImpl(this);
//这个注册的textView只是为了测试浮动提示的效果
tv_register.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
startActivity(new Intent(LoginActivity.this, RegisterActivity.class));
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
presenter.onDestroy();
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public void showProgress() {
progressBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
@Override
public void hideProgress() {
progressBar.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
@Override
public void setUsernameError() {
username.setError(getString(R.string.username_error));
}
@Override
public void setPasswordError() {
password.setError(getString(R.string.password_error));
}
@Override
public void navigateToHome() {
startActivity(new Intent(this, MainActivity.class));
finish();
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
presenter.validateCredentials(username.getText().toString(), password.getText().toString());
}
}
登录界面操作非常简单,实现了LoginView中的方法,下面是LoginView接口:
package com.lai.mvp.app.Login;
public interface LoginView {
void showProgress();//显示progress
void hideProgress();//隐藏progress
void setUsernameError();//用户名错误
void setPasswordError();//密码错误
void navigateToHome();//成功进入主页
}
Model操作也很简单,不废话了,直入主题:
LoginModel:
package com.lai.mvp.app.Login;
public interface LoginModel {
interface OnLoginFinishedListener {
void onUsernameError();//用户名错误
void onPasswordError();//密码错误
void onSuccess();//成功
}
//连接登录时的操作
void login(String username, String password, OnLoginFinishedListener listener);
}
实现Model中的接口:
LoginModelImpl:
package com.lai.mvp.app.Login;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.text.TextUtils;
public class LoginModelImpl implements LoginModel {
@Override
public void login(final String username, final String password, final OnLoginFinishedListener listener) {
//模拟登录。创建一个2s后处理程序的操作
new Handler().postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
boolean error = false;
//判断字符是否为空
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(username)){
listener.onUsernameError();
error = true;
}
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(password)){
listener.onPasswordError();
error = true;
}
if (!error){
listener.onSuccess();
}
}
}, 2000);
}
}
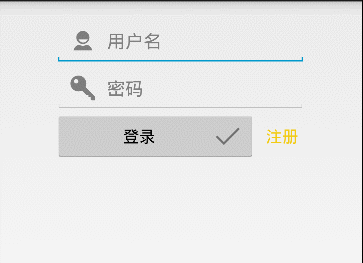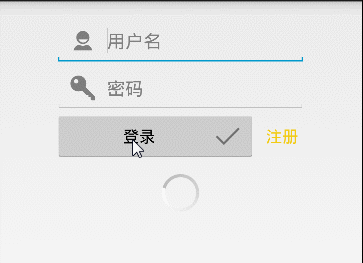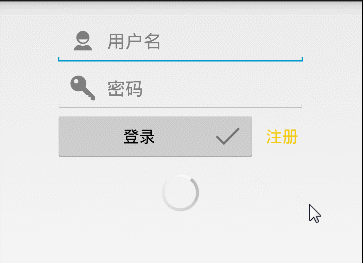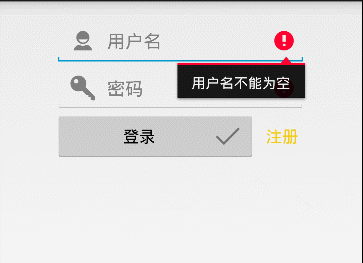
这边做了字符是否为空的判断,与后面的LoginPresenterImpl 构造中实现通信,在LoginActivity中直接操作用户名密码为空后的操作,效果如下:
这里说明了Model和View必须要通过Presenter才能完成通信,所以Presenter是连接View和Model的中间者,我也是用了接口的方式去实现了,看代码:
LoginPresenter:
package com.lai.mvp.app.Login;
public interface LoginPresenter {
void validateCredentials(String username, String password);//验证用户名密码
void onDestroy();
}
而需要操作的事情,全部放在PresenterImpl中,在前面的LoginActivity中也并没有看到一些逻辑性的操作:
LoginPresenterImpl :
package com.lai.mvp.app.Login;
public class LoginPresenterImpl implements LoginPresenter, LoginModel.OnLoginFinishedListener {
private LoginView loginView;
private LoginModel loginModel;
public LoginPresenterImpl(LoginView loginView) {
this.loginView = loginView;
this.loginModel = new LoginModelImpl();
}
/**
* 校验用户名密码
* @param username
* @param password
*/
@Override
public void validateCredentials(String username, String password) {
if (loginView != null) {
loginView.showProgress();
}
loginModel.login(username, password, this);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
loginView = null;
}
//用户名错误
@Override
public void onUsernameError() {
if (loginView != null) {
loginView.setUsernameError();
loginView.hideProgress();
}
}
//密码错误
@Override
public void onPasswordError() {
if (loginView != null) {
loginView.setPasswordError();
loginView.hideProgress();
}
}
//成功之后
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
if (loginView != null) {
loginView.navigateToHome();
}
}
}
在Activity中(也就是View),它是直接跟Presenter接触的,并不是跟Model碰面,在设计图中可以看出,加载代码的逻辑,就更清晰了。在LoginActivity中也有了LoginPresenter presenter=new LoginPresenterImpl(this);去完成与Presenter的交接,所以整个流程也就这样形成了。
MainActivity的操作也是一样的,代码我就不贴出来了,整体来说,代码清晰度好了很多(逻辑方面,不是指代码量),平时在开发中,我们大多都是把所有的逻辑操作,写在LoginActivity中,不仅代码量大,而且看起来也比较复杂,但是,请注意,我们虽然只做了一个简单的登录操作,有没有发现,我们项目中,多出了很多class?所以MVP架构模式只适合大点的项目,简单的demo没必要,这点需要慎重,如果你的项目用了MVP模式,必须要写下去。
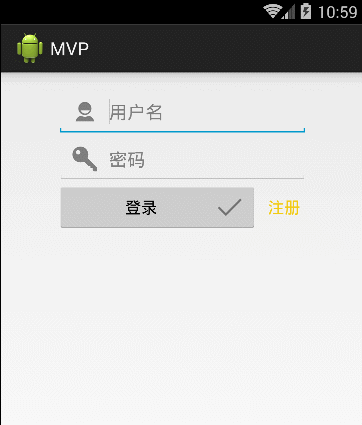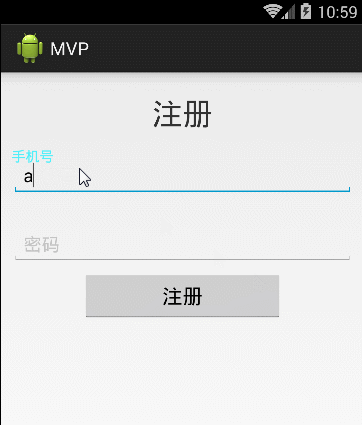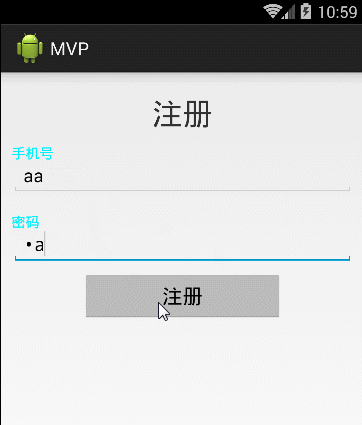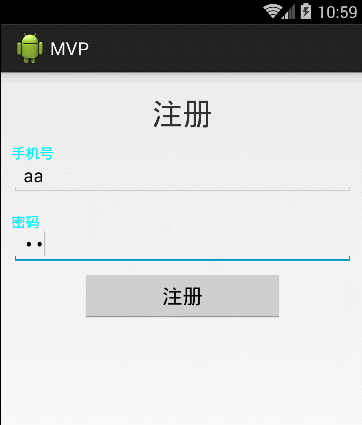
好了,在这当中我还插了一个自定义view的小例子,先看下效果:
这个view类通用的,贴出来给大家:
package com.lai.mvp.app.view;
import android.annotation.TargetApi;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.ColorStateList;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.os.Build;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Parcelable;
import android.text.Editable;
import android.text.InputType;
import android.text.TextWatcher;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.FrameLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.lai.mvp.app.R;
public class FloatLabel extends FrameLayout {
private static final String SAVE_STATE_KEY_EDIT_TEXT = "saveStateEditText";
private static final String SAVE_STATE_KEY_LABEL = "saveStateLabel";
private static final String SAVE_STATE_PARENT = "saveStateParent";
private static final String SAVE_STATE_TAG = "saveStateTag";
private static final String SAVE_STATE_KEY_FOCUS = "saveStateFocus";
/**
* 参照编辑
*/
private EditText mEditText;
/**
* 当初始化完成后,孩子的意见可以不再增加
*/
private boolean mInitComplete = false;
/**
* 参考用作标签的方法
*/
private TextView mLabel;
/**
* label标签消失
*/
private LabelAnimator mLabelAnimator = new DefaultLabelAnimator();
/**
* label是否显示
*/
private boolean mLabelShowing;
/**
* 保存状态,如果有任何等待恢复
*/
private Bundle mSavedState;
/**
*
* 一旦更新文本,则设置为true
*/
private boolean mSkipAnimation = false;
/**
* 对标签的TextView提供自定义动画界面。
*/
public interface LabelAnimator {
/**
* 当标签变成可见的时候
*
* @param label TextView不可见
*/
public void onDisplayLabel(View label);
/**
* 当标签变成不可见的时候
*
* @param label
*/
public void onHideLabel(View label);
}
public FloatLabel(Context context) {
this(context, null, 0);
}
public FloatLabel(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public FloatLabel(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init(context, attrs, defStyle);
}
@Override
public void addView(View child) {
if (mInitComplete) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("You cannot add child views to a FloatLabel");
} else {
super.addView(child);
}
}
@Override
public void addView(View child, int index) {
if (mInitComplete) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("You cannot add child views to a FloatLabel");
} else {
super.addView(child, index);
}
}
@Override
public void addView(View child, int index, android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
if (mInitComplete) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("You cannot add child views to a FloatLabel");
} else {
super.addView(child, index, params);
}
}
@Override
public void addView(View child, int width, int height) {
if (mInitComplete) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("You cannot add child views to a FloatLabel");
} else {
super.addView(child, width, height);
}
}
@Override
public void addView(View child, android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
if (mInitComplete) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("You cannot add child views to a FloatLabel");
} else {
super.addView(child, params);
}
}
/**
* Returns the EditText portion of this View
*
* @return the EditText portion of this View
*/
public EditText getEditText() {
return mEditText;
}
/**
* Returns the label portion of this View
*
* @return the label portion of this View
*/
public TextView getLabel() {
return mLabel;
}
/**
* Sets the text to be displayed above the EditText if the EditText is
* nonempty or as the EditText hint if it is empty
*
* @param resid int String resource ID
*/
public void setLabel(int resid) {
setLabel(getContext().getString(resid));
}
/**
* Sets the text to be displayed above the EditText if the EditText is
* nonempty or as the EditText hint if it is empty
*
* @param hint CharSequence to set as the label
*/
public void setLabel(CharSequence hint) {
mEditText.setHint(hint);
mLabel.setText(hint);
}
/**
* Specifies a new LabelAnimator to handle calls to show/hide the label
*
* @param labelAnimator LabelAnimator to use; null causes use of the default LabelAnimator
*/
public void setLabelAnimator(LabelAnimator labelAnimator) {
if (labelAnimator == null) {
mLabelAnimator = new DefaultLabelAnimator();
} else {
mLabelAnimator = labelAnimator;
}
}
/**
* Sets the EditText's text with animation
*
* @param resid int String resource ID
*/
public void setText(int resid) {
mEditText.setText(resid);
}
/**
* Sets the EditText's text with label animation
*
* @param text char[] text
* @param start int start of char array to use
* @param len int characters to use from the array
*/
public void setText(char[] text, int start, int len) {
mEditText.setText(text, start, len);
}
/**
* Sets the EditText's text with label animation
*
* @param resid int String resource ID
* @param type TextView.BufferType
*/
public void setText(int resid, TextView.BufferType type) {
mEditText.setText(resid, type);
}
/**
* Sets the EditText's text with label animation
*
* @param text CharSequence to set
*/
public void setText(CharSequence text) {
mEditText.setText(text);
}
/**
* Sets the EditText's text with label animation
*
* @param text CharSequence to set
* @param type TextView.BufferType
*/
public void setText(CharSequence text, TextView.BufferType type) {
mEditText.setText(text, type);
}
/**
* Sets the EditText's text without animating the label
*
* @param resid int String resource ID
*/
public void setTextWithoutAnimation(int resid) {
mSkipAnimation = true;
mEditText.setText(resid);
}
/**
* Sets the EditText's text without animating the label
*
* @param text char[] text
* @param start int start of char array to use
* @param len int characters to use from the array
*/
public void setTextWithoutAnimation(char[] text, int start, int len) {
mSkipAnimation = true;
mEditText.setText(text, start, len);
}
/**
* Sets the EditText's text without animating the label
*
* @param resid int String resource ID
* @param type TextView.BufferType
*/
public void setTextWithoutAnimation(int resid, TextView.BufferType type) {
mSkipAnimation = true;
mEditText.setText(resid, type);
}
/**
* Sets the EditText's text without animating the label
*
* @param text CharSequence to set
*/
public void setTextWithoutAnimation(CharSequence text) {
mSkipAnimation = true;
mEditText.setText(text);
}
/**
* Sets the EditText's text without animating the label
*
* @param text CharSequence to set
* @param type TextView.BufferType
*/
public void setTextWithoutAnimation(CharSequence text, TextView.BufferType type) {
mSkipAnimation = true;
mEditText.setText(text, type);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
final int childLeft = getPaddingLeft();
final int childRight = right - left - getPaddingRight();
int childTop = getPaddingTop();
final int childBottom = bottom - top - getPaddingBottom();
layoutChild(mLabel, childLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom);
layoutChild(mEditText, childLeft, childTop + mLabel.getMeasuredHeight(), childRight, childBottom);
}
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR1)
private void layoutChild(View child, int parentLeft, int parentTop, int parentRight, int parentBottom) {
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int width = child.getMeasuredWidth();
final int height = child.getMeasuredHeight();
int childLeft;
final int childTop = parentTop + lp.topMargin;
int gravity = lp.gravity;
if (gravity == -1) {
gravity = Gravity.TOP | Gravity.START;
}
final int layoutDirection;
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR1) {
layoutDirection = LAYOUT_DIRECTION_LTR;
} else {
layoutDirection = getLayoutDirection();
}
final int absoluteGravity = Gravity.getAbsoluteGravity(gravity, layoutDirection);
switch (absoluteGravity & Gravity.HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK) {
case Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL:
childLeft = parentLeft + (parentRight - parentLeft - width) / 2 + lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin;
break;
case Gravity.END:
childLeft = parentRight - width - lp.rightMargin;
break;
case Gravity.START:
default:
childLeft = parentLeft + lp.leftMargin;
}
child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childLeft + width, childTop + height);
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// Restore any state that's been pending before measuring
if (mSavedState != null) {
Parcelable childState = mSavedState.getParcelable(SAVE_STATE_KEY_EDIT_TEXT);
mEditText.onRestoreInstanceState(childState);
childState = mSavedState.getParcelable(SAVE_STATE_KEY_LABEL);
mLabel.onRestoreInstanceState(childState);
if (mSavedState.getBoolean(SAVE_STATE_KEY_FOCUS, false)) {
mEditText.requestFocus();
}
mSavedState = null;
}
measureChild(mEditText, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
measureChild(mLabel, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(measureWidth(widthMeasureSpec), measureHeight(heightMeasureSpec));
}
@Override
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {
if (state instanceof Bundle) {
final Bundle savedState = (Bundle) state;
if (savedState.getBoolean(SAVE_STATE_TAG, false)) {
// Save our state for later since children will have theirs restored after this
// and having more than one FloatLabel in an Activity or Fragment means you have
// multiple views of the same ID
mSavedState = savedState;
super.onRestoreInstanceState(savedState.getParcelable(SAVE_STATE_PARENT));
return;
}
}
super.onRestoreInstanceState(state);
}
@Override
protected Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() {
final Parcelable superState = super.onSaveInstanceState();
final Bundle saveState = new Bundle();
saveState.putParcelable(SAVE_STATE_KEY_EDIT_TEXT, mEditText.onSaveInstanceState());
saveState.putParcelable(SAVE_STATE_KEY_LABEL, mLabel.onSaveInstanceState());
saveState.putBoolean(SAVE_STATE_KEY_FOCUS, mEditText.isFocused());
saveState.putBoolean(SAVE_STATE_TAG, true);
saveState.putParcelable(SAVE_STATE_PARENT, superState);
return saveState;
}
private int measureHeight(int heightMeasureSpec) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int result = 0;
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
result = specSize;
} else {
result = mEditText.getMeasuredHeight() + mLabel.getMeasuredHeight();
result += getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
result = Math.max(result, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
result = Math.min(result, specSize);
}
}
return result;
}
private int measureWidth(int widthMeasureSpec) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int result = 0;
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
result = specSize;
} else {
result = Math.max(mEditText.getMeasuredWidth(), mLabel.getMeasuredWidth());
result = Math.max(result, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
result += getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
result = Math.min(result, specSize);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* Initializes the view's default values and values from attrs, if not null
*
* @param context Context to access styled attributes
* @param attrs AttributeSet from constructor or null
* @param defStyle int resource ID of style to use for defaults
*/
private void init(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
// Load custom attributes
final int layout;
int editTextId = R.id.edit_text;
int floatLabelId = R.id.float_label;
final CharSequence text;
final CharSequence hint;
final ColorStateList hintColor;
final int floatLabelColor;
final int imeOptions;
final int inputType;
final int nextFocusDownId;
final int nextFocusForwardId;
final int nextFocusLeftId;
final int nextFocusRightId;
final int nextFocusUpId;
if (attrs == null) {
layout = R.layout.float_label;
text = null;
hint = null;
hintColor = null;
floatLabelColor = 0;
imeOptions = 0;
inputType = 0;
nextFocusDownId = NO_ID;
nextFocusForwardId = NO_ID;
nextFocusLeftId = NO_ID;
nextFocusRightId = NO_ID;
nextFocusUpId = NO_ID;
} else {
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.FloatLabel, defStyle, 0);
// Main attributes
layout = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.FloatLabel_android_layout, R.layout.float_label);
editTextId = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.FloatLabel_editTextId, R.id.edit_text);
floatLabelId = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.FloatLabel_labelId, R.id.float_label);
text = a.getText(R.styleable.FloatLabel_android_text);
hint = a.getText(R.styleable.FloatLabel_android_hint);
hintColor = a.getColorStateList(R.styleable.FloatLabel_android_textColorHint);
floatLabelColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.FloatLabel_floatLabelColor, 0);
imeOptions = a.getInt(R.styleable.FloatLabel_android_imeOptions, 0);
inputType = a.getInt(R.styleable.FloatLabel_android_inputType, InputType.TYPE_CLASS_TEXT);
// Next focus views
nextFocusDownId = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.FloatLabel_android_nextFocusDown, NO_ID);
nextFocusForwardId = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.FloatLabel_android_nextFocusForward, NO_ID);
nextFocusLeftId = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.FloatLabel_android_nextFocusLeft, NO_ID);
nextFocusRightId = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.FloatLabel_android_nextFocusRight, NO_ID);
nextFocusUpId = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.FloatLabel_android_nextFocusUp, NO_ID);
// Done with TypedArray
a.recycle();
}
inflate(context, layout, this);
mEditText = (EditText) findViewById(editTextId);
if (mEditText == null) {
// fallback to default value
mEditText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edit_text);
}
if (mEditText == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Your layout must have an EditText whose ID is @id/edit_text");
}
if (editTextId != R.id.edit_text) {
mEditText.setId(editTextId);
}
mEditText.setHint(hint);
mEditText.setText(text);
if (hintColor != null) {
mEditText.setHintTextColor(hintColor);
}
if (imeOptions != 0) {
mEditText.setImeOptions(imeOptions);
}
if (inputType != 0) {
mEditText.setInputType(inputType);
}
// Set all next focus views
mEditText.setNextFocusDownId(nextFocusDownId);
mEditText.setNextFocusForwardId(nextFocusForwardId);
mEditText.setNextFocusLeftId(nextFocusLeftId);
mEditText.setNextFocusRightId(nextFocusRightId);
mEditText.setNextFocusUpId(nextFocusUpId);
// Set up the label view
mLabel = (TextView) findViewById(floatLabelId);
if (mLabel == null) {
// fallback to default value
mLabel = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.float_label);
}
if (mLabel == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Your layout must have a TextView whose ID is @id/float_label");
}
if (floatLabelId != R.id.float_label) {
mLabel.setId(floatLabelId);
}
mLabel.setText(mEditText.getHint());
if (floatLabelColor != 0)
mLabel.setTextColor(floatLabelColor);
// Listen to EditText to know when it is empty or nonempty
mEditText.addTextChangedListener(new EditTextWatcher());
// Check current state of EditText
if (mEditText.getText().length() == 0) {
mLabel.setAlpha(0);
mLabelShowing = false;
} else {
mLabel.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mLabelShowing = true;
}
// Mark init as complete to prevent accidentally breaking the view by
// adding children
mInitComplete = true;
}
/**
* LabelAnimator that uses the traditional float label Y shift and fade.
*
* @author Ian G. Clifton
*/
private static class DefaultLabelAnimator implements LabelAnimator {
@Override
public void onDisplayLabel(View label) {
final float offset = label.getHeight() / 2;
final float currentY = label.getY();
if (currentY != offset) {
label.setY(offset);
}
label.animate().alpha(1).y(0);
}
@Override
public void onHideLabel(View label) {
final float offset = label.getHeight() / 2;
final float currentY = label.getY();
if (currentY != 0) {
label.setY(0);
}
label.animate().alpha(0).y(offset);
}
}
/**
* TextWatcher that notifies FloatLabel when the EditText changes between
* having text and not having text or vice versa.
*
* @author Ian G. Clifton
*/
private class EditTextWatcher implements TextWatcher {
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {
if (mSkipAnimation) {
mSkipAnimation = false;
if (s.length() == 0) {
// TextView label should be gone
if (mLabelShowing) {
mLabel.setAlpha(0);
mLabelShowing = false;
}
} else if (!mLabelShowing) {
// TextView label should be visible
mLabel.setAlpha(1);
mLabel.setY(0);
mLabelShowing = true;
}
return;
}
if (s.length() == 0) {
// Text is empty; TextView label should be invisible
if (mLabelShowing) {
mLabelAnimator.onHideLabel(mLabel);
mLabelShowing = false;
}
} else if (!mLabelShowing) {
// Text is nonempty; TextView label should be visible
mLabelShowing = true;
mLabelAnimator.onDisplayLabel(mLabel);
}
}
@Override
public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after) {
// Ignored
}
@Override
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {
// Ignored
}
}
}
在values新建的attrs.xml中添加如下:
<declare-styleable name="FloatLabel">
<attr name="android:hint" />
<attr name="android:imeOptions" />
<attr name="android:inputType" />
<attr name="android:layout" />
<attr name="android:nextFocusDown" />
<attr name="android:nextFocusForward" />
<attr name="android:nextFocusLeft" />
<attr name="android:nextFocusRight" />
<attr name="android:nextFocusUp" />
<attr name="android:text" />
<attr name="android:textColorHint" />
<attr name="floatLabelColor" format="color" />
<attr name="labelId" format="reference" />
<attr name="editTextId" format="reference" />
</declare-styleable>再新建一个ids.xml,加上:
<item type="id" name="float_label" />
<item type="id" name="edit_text" />然后在layout中写一个float_label.xml 添加以下布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<TextView
android:id="@id/float_label"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:focusable="false"
android:focusableInTouchMode="false"
android:lines="1"
android:textIsSelectable="true"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmall" />
<EditText
android:id="@id/edit_text"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="-7dp"
android:inputType="text|textAutoCorrect|textCapSentences|textAutoComplete" />
</merge>之后就可以直接使用了,例如:
<com.lai.mvp.app.view.FloatLabel
android:id="@+id/label_phone"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dip"
android:layout_marginRight="10dip"
android:layout_marginTop="10dip"
android:hint="手机号"
android:layout="@layout/float_label"
app:floatLabelColor="#00f0ff"
android:textColorHint="#c5c5c5"
/>本篇结束了,源码下载地址如下:






















 605
605











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








