内省、BeanUtils、注解
1、JavaBean:是一种特殊的java类,主要用于传递数据信息,这种java类中的方法,主要用于访问私有字段。
Introspector.getBeanInfo(类名.class).getPropertyDescriptors(),可以得到该类的所有属性(包括父类的属性)
Introspector.getBeanInfo(类名.class,父类类名.class).getPropertyDescriptors() 可以得到该类的所有属性(不包括父类的属性)
PropertyDescriptor(“字段名”,类名.class)得到操作属性的类对象,getPropertyType()可以得到类型,getWriteMethod()得到些方法,
getReadMethod()得到读方法,invoke()方法执行。
要操作的类
package com.xiaozhi.introspector;
//该类共有5个属性
public class Person {
private String name;
private String password;
private int age;
public void setAb(int a){
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
package com.xiaozhi.introspector;
import java.beans.BeanInfo;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//得到所有的属性
// // 这样得到的属性包括Object的属性:Class
// BeanInfo beanInfo1 = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Person.class);
// // 去除Object的属性
// BeanInfo beanInfo2 = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Person.class,Object.class);
// PropertyDescriptor[] descriptors = beanInfo1.getPropertyDescriptors();
// for(PropertyDescriptor descriptor:descriptors)
// {
// System.out.println(descriptor.getName());
// }
//操作制定属性:age
Person person=new Person();
PropertyDescriptor descriptor=new PropertyDescriptor("age",Person.class);
//获取属性的类型
System.out.println(descriptor.getPropertyType());
//得到属性的写方法,为属性赋值
Method method= descriptor.getWriteMethod();
method.invoke(person, 22);//为age赋值22
//得到属性的读方法
method=descriptor.getReadMethod();
System.out.println(method.invoke(person, null));//读取age的值22
}
}2、BeanUtils操作javabean
使用beanUtils操作bean属性更加方便很多,beanUtils支持八种基本数据类型自动用String转换
但是对于时间等其他类型要注册转换器,可以自己写,也可以用api中已经写好的。
Person.class
package com.xiaozhi.beanutils;
import java.util.Date;
public class Person {
private String name;
private String password;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}Test.java
package com.xiaozhi.beanutils;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.Date;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.ConvertUtils;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.locale.converters.DateLocaleConverter;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception, InvocationTargetException {
//使用beanUtils操纵bean的属性
// Person person=new Person();
// BeanUtils.setProperty(person, "name", "xiaozhi");
// System.out.println(person.getName());
// System.out.println(BeanUtils.getProperty(person, "name"));
//beanUtilsz支持八种类型自动转换
// String name="xiaozhi";
// String age="22";
// String password="123456";
//
// Person person=new Person();
// BeanUtils.setProperty(person, "name", name);
// BeanUtils.setProperty(person, "age", age);
// BeanUtils.setProperty(person, "password", password);
//
// System.out.println(person.getName());
// System.out.println(person.getAge());
// System.out.println(person.getPassword());
//对于时间类型,要注册转换器
String birthday ="1992-09-28";
ConvertUtils.register(new DateLocaleConverter(), Date.class);
Person person=new Person();
BeanUtils.setProperty(person, "birthday", birthday);
System.out.println(person.getBirthday());
}
}_______________________注解的学习_____________________________
1、@SuppressWarnings@deprecated@override的介绍
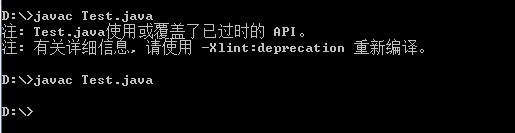
没加@SuppressWarnings(“deprecation”)注解,编译时会提示使用了过时的API
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.runFinalizersOnExit(true);
}
}
加了@SuppressWarnings(“deprecation”)注解,编译时没有提示
public class Test {
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.runFinalizersOnExit(true);
}
}
_______________________________________________________________________________________
加了@deprecated注解,当调用这个方法时,会提示过时
加@override注解,是覆盖父类方法
package com.xiaozhi.annotacation;
public class Test {
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.runFinalizersOnExit(true);
}
@Deprecated
public static void sayHello()
{
System.out.println("传智播客!");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
}
2、自己动手写注解,以及@Retention@Target的介绍:
public @interface MyAnnotation {
}
Test.java
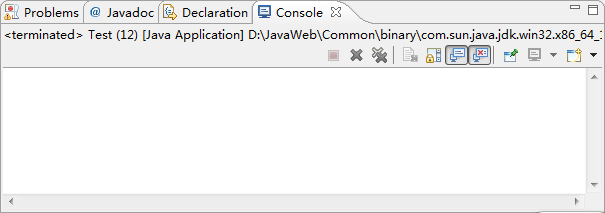
@MyAnnotation
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if(Test.class.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)){
MyAnnotation myAnnotation=Test.class.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(myAnnotation);
}
}
}
运行结果
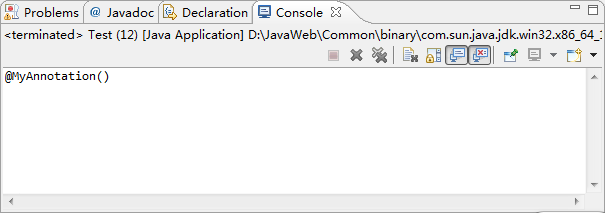
在自己写的注解前加一个元注解,保证这个注解在运行时仍然存在。
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
}
运行结果:
_______________________________________________________________________________________
@Retention元注解,有三个取值,RetetionPolicy.SOURCE、RetetionPolicy.CLASS、Retetion.RUNTIME,分别对应
java源文件--------------->class文件--------------->内存中的字节码
@override和@SuppressWarnings是在源文件时存在
@Deprecated是在runtime时存在(因为我们需要调用方法才知道方法过时,首先需要把类加载到内存中)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD , ElementType.TYPE})//这个注解可以加在方法和类上
3、为注解增加属性,以及使用反射得到注解以及注解内的属性
如果注解中有一个名称为value的属性,且你只想设置value的属性(即其他属性都采用默认值或者只有一个value属性),那么可以省略value=部分。
如果数组属性中只有一个元素,这时候属性值部分可以省略大括号
@Target(value={ElementType.TYPE})可以省略value=部分,由于数组只有一个元素,所以可以省略大括号。简写成@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
MyAnnotation.java
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value={ElementType.TYPE})
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String color() default"green";
String value();
int [] array() default {1,2,3,3};
Grade grade() default Grade.A;
MyAnnotation2 annotation();
}
enum Grade{
A("90-100"){
public String getScore(){
return "优";
}
},
B("80-90"){
public String getScore(){
return "良";
}
},
C("70-80"){
public String getScore(){
return "中";
}
},
D("60-70"){
public String getScore(){
return "差";
}
};
private String value;
private Grade(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
public abstract String getScore();
}
public @interface MyAnnotation2 {
String value();
}
@MyAnnotation(color="blue",value="hello",array={1,2,2},grade=Grade.B,annotation=@MyAnnotation2(value="haha"))
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if(Test.class.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)){
MyAnnotation myAnnotation=Test.class.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(myAnnotation.color());
System.out.println(myAnnotation.value());
System.out.println(myAnnotation.array().length);
System.out.println(myAnnotation.grade());
System.out.println(myAnnotation.annotation().value());
}
}
}
---------------------- ASP.Net+Unity开发、 .Net培训、期待与您交流! ----------------------






















 4306
4306

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








