二叉树值得思考的一些问题!!
1. 求二叉树的高度
- 设二叉树的高度函数为f(
x
),则:
f(x)={0,Max{f(x−>lchild),f(x−>rchild)}+1,if x = NULLothers
int height(node *root)
{
int ldep, rdep;
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
else
{
ldep = height(root->lchild);
rdep = height(root->rchild);
return (ldep > rdep) ? (ldep + 1) : (rdep + 1);
}
}2. 求二叉树的节点个数
- 设二叉树的节点个数函数为f(
x
),则:
f(x)={0,f(x−>lchild)+f(x−>rchild)+1,if x = NULLothers
int nodeNum(node *root)
{
int num1, num2;
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
else
{
num1 = nodeNum(root->lchild);
num2 = nodeNum(root->rchild);
return num1 + num2 + 1;
}
}3. 求二叉树的叶子节点个数
f(x)=⎧⎩⎨0,1,f(x−>lchild)+f(x−>rchild),if x = NULLif x is leaf nodeothers
int leafNum(node *root)
{
int num1, num2;
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
else if (root->lchild == NULL && root->rchild == NULL)
return 1;
else
{
num1 = leafNum(root->lchild);
num2 = leafNum(root->rchild);
return num1 + num2;
}
}4. 二叉树前序、中序、后序遍历的非递归实现
- 用栈模拟
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
char data;
node *lchild, *rchild;
};
node *insert()//建立二叉树
{
char ch;
scanf("%c", &ch);
node *current;
if (ch == '#')
current = NULL;
else
{
current = new node;
current->data = ch;
current->lchild = insert();
current->rchild = insert();
}
return current;
}
void Pre(node *root)//非递归先序遍历
{
stack<node*> Stack;
if (!root)
{
return;
}
while (root || !Stack.empty())
{
while (root)
{
Stack.push(root);
printf("%c ", root->data);
root = root->lchild;
}
root = Stack.top();
Stack.pop();
root = root->rchild;
}
}
void In(node *root)//非递归中序遍历
{
stack<node*> Stack;
if (!root)
{
return;
}
while (root || !Stack.empty())
{
while (root)
{
Stack.push(root);
root = root->lchild;
}
root = Stack.top();
Stack.pop();
printf("%c ", root->data);
root = root->rchild;
}
}
void Post(node *root) //非递归后序遍历
{
stack<node*> s;
node *cur; //当前结点
node *pre = NULL; //前一次访问的结点
s.push(root);
while (!s.empty())
{
cur = s.top();
if ((cur->lchild == NULL && cur->rchild == NULL) || (pre != NULL && (pre == cur->lchild || pre == cur->rchild)))
{
printf("%c ", cur->data);
s.pop();
pre = cur;
}
else
{
if (cur->rchild != NULL)
s.push(cur->rchild);
if (cur->lchild != NULL)
s.push(cur->lchild);
}
}
}
int main()
{
node *root = insert();
Pre(root);
printf("\n");
In(root);
printf("\n");
Post(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}5. 计算二叉树高度的非递归实现
- 二叉树的层次遍历,标记最后一个入队的节点。
int height(node *root)
{
queue<node*>v;
node *flag = root;
int ans = 0;
v.push(root);
while (!v.empty())
{
root = v.front();
v.pop();
if (root->lchild != NULL)
v.push(root->lchild);
if (root->rchild)
v.push(root->rchild);
if (flag == root)
{
flag = v.back();
ans++;
}
}
return ans;
}6. 求二叉树中相距最远的两个节点之间的距离
- 遍历每个节点,找出以当前节点为根的最长路径,然后找出所有最长路径中的最大值
void longestPathUtil(node* root, int& left_len, int& right_len, int& max_len)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
left_len = 0;
right_len = 0;
max_len = 0;
return;
}
int left_len1, right_len1, left_len2, right_len2;
longestPathUtil(root->lchild, left_len1, right_len1, max_len);
longestPathUtil(root->rchild, left_len2, right_len2, max_len);
left_len = 1 + max(left_len1, right_len1);
right_len = 1 + max(left_len2, right_len2);
max_len = max(left_len + right_len - 1, max_len);
}
int longestPath(node* root)
{
int left_len, right_len, max_len;
longestPathUtil(root, left_len, right_len, max_len);
return max_len;
}
7. 判断二叉树是否平衡二叉树
平衡二叉树的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
- 调用函数求每个节点左右孩子的深度,然后进行比较
int height(node *root)
{
int ldep, rdep;
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
else
{
ldep = height(root->lchild);
rdep = height(root->rchild);
return (ldep > rdep) ? (ldep + 1) : (rdep + 1);
}
}
bool isBalance(node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return true;
int num1 = height(root->lchild);
int num2 = height(root->rchild);
int ans = num1 - num2;
if (ans > 1 || ans < -1)
return false;
return isBalance(root->lchild) && isBalance(root->rchild);
}8. 指定二叉树,给定两节点求其最近共同父节点
- LCA - Tarjan
9. 二叉树的广度遍历、逐层打印二叉树节点数据、只打印某层节点数据
- 二叉树的广度遍历、逐层打印二叉树节点数据、只打印某层节点数据。
Input:ABDH##I##EJ##K##CFL##M##GN##O##
逐层打印:用一个flag指针标记,刚开始指向根节点root。二叉树的广度遍历,即层次遍历,用队列实现。在每一层的节点都进队完之后,flag标记到该层的最后一个节点,在此之前flag都标记的是上一层节点的最后一个节点。刚开始的时候flag指向根节点root,就是第一层的最后一个节点。函数bfs中的形参root在第一次调用printf()函数后就已经没用了,所以用来保存出队的节点,重新利用起来,就不用再定义节点。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
char data;
node *lchild,*rchild;
};
node *insert()//建立二叉树
{
char ch;
scanf("%c",&ch);
node *current;
if(ch=='#')
current=NULL;
else
{
current=new node;
current->data=ch;
current->lchild=insert();
current->rchild=insert();
}
return current;
}
void bfs(node *root)//层次遍历1
{
queue<node*>v;
node *flag=root;
v.push(root);
while (!v.empty())
{
root=v.front();
v.pop();
printf("%c",root->data);
if (root->lchild!=NULL)
v.push(root->lchild);
if (root->rchild)
v.push(root->rchild);
if (flag!=root)
{
printf("~");
}
else
{
printf("\n");
flag=v.back();
}
}
}
// void bfs(node *root)//层次遍历2
// {
// if (root==NULL)
// {
// return ;
// }
// queue<node*>v;
// node *flag=root;
// while (true)
// {
// if (root->lchild!=NULL)
// v.push(root->lchild);
// if (root->rchild!=NULL)
// v.push(root->rchild);
// printf("%c",root->data);
// if (flag!=root)
// {
// printf("~");
// }
// else
// {
// printf("\n");
// if (v.empty())
// break;
// flag=v.back();
// }
// root=v.front();
// v.pop();
// }
// }
int main()
{
node *root=insert();
printf("\nbfs\n");
bfs(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}- 只打印某层节点的数据:如只打印第四层节点的数据。在标记flag指针的基础上再加一个标记变量layer,初值为1,每次在flag指针标记上每一层最后一个节点时,layer++,再判断layer是否等于4输出即可!
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
char data;
node *lchild,*rchild;
};
node *insert()//建立二叉树
{
char ch;
scanf("%c",&ch);
node *current;
if(ch=='#')
current=NULL;
else
{
current=new node;
current->data=ch;
current->lchild=insert();
current->rchild=insert();
}
return current;
}
void bfs(node *root)//层次遍历1
{
queue<node*>v;
node *flag=root;
int layer=1;
v.push(root);
while (!v.empty())
{
root=v.front();
v.pop();
if (root->lchild!=NULL)
v.push(root->lchild);
if (root->rchild)
v.push(root->rchild);
if (flag!=root)
{
if (layer==4)
printf("%c~",root->data);
}
else
{
if (layer==4)
printf("%c\n",root->data);
flag=v.back();
layer+=1;
}
}
}
// void bfs(node *root)//层次遍历2
// {
// if (root==NULL)
// {
// return ;
// }
// queue<node*>v;
// node *flag=root;
// int layer=1;
// while (true)
// {
// if (root->lchild!=NULL)
// v.push(root->lchild);
// if (root->rchild!=NULL)
// v.push(root->rchild);
// if (flag!=root)
// {
// if(layer==4)
// printf("%c~",root->data);
// }
// else
// {
// if (layer==4)
// printf("%c\n",root->data);
// if (v.empty())
// break;
// flag=v.back();
// layer++;
// }
// root=v.front();
// v.pop();
// }
// }
int main()
{
node *root=insert();
printf("\nbfs\n");
bfs(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
10. 在二叉树中找出和(叶子到根节点路径上的所有节点的数据和)为指定值的所有路径
- 从根开始一直DFS。
void findPath(node *root, int sum, int currSum)
{
if (!root) return;
currSum += root->data;
stack[top++] = root;
if (!root->lchild && !root->rchild && currSum == sum) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < top; i++)
printf("%d ", stack[i]->data); //打印路径节点的值
printf("\n");
}
else {
findPath(root->lchild, sum, currSum);
findPath(root->rchild, sum, currSum);
}
currSum -= root->data;
top--;
}11. 求二叉树的镜像
- 遍历二叉树,交换左子树和右子树。
void MirroR(node *root)
{
if (NULL == root)
return;
if (NULL == root->lchild && NULL == root->rchild)
return;
node *pTemp = root->lchild;
root->lchild = root->rchild;
root->rchild = pTemp;
if (root->lchild)
MirroR(root->lchild);
if (root->rchild)
MirroR(root->rchild);
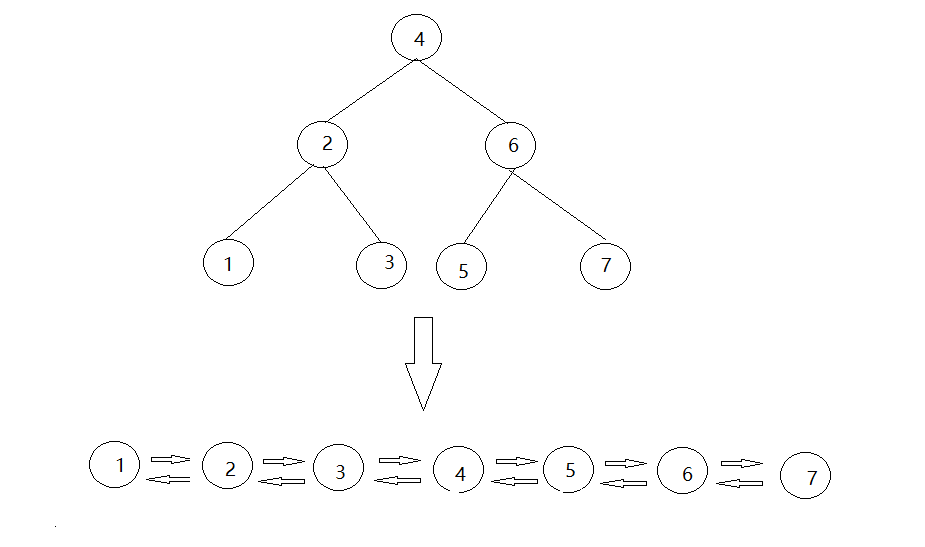
}12. 将二叉查找树转为有序的双链表
- 二叉查找树中,左节点的值小于根节点,右节点的值大于根节点。与双向链表的区别在于两个指针的指向不同。我们会发现,中序遍历二叉查找树后,可以得到从小到大排好序的数组。
- 对于1,2,3这课子树,让节点2的左指针指向前一个节点(节点1),节点2的右指针指向后一个节点(节点3);
- 节点3的左指针指向前一个节点(节点2),节点3的右指针指向后一个节点(节点4);
- 对于5,6,7这课子树,同1,2,3。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
char data;
node *lchild, *rchild;
};
node *insert()//建立二叉树
{
char ch;
scanf("%c", &ch);
node *current;
if (ch == '#')
current = NULL;
else
{
current = new node;
current->data = ch;
current->lchild = insert();
current->rchild = insert();
}
return current;
}
node* FindLeftmostNode(node *tree)
{
if (tree == NULL)
return NULL;
while (tree->lchild != NULL)
tree = tree->lchild;
return tree;
}
void ConvertNode(node *tree, node **last_node)
{
if (tree == NULL)
return;
if (tree->lchild != NULL)
ConvertNode(tree->lchild, last_node);
printf("%c--\n", tree->data);
tree->lchild = *last_node;
if (*last_node != NULL)
(*last_node)->rchild = tree;
*last_node = tree;
if (tree->rchild != NULL)
ConvertNode(tree->rchild, last_node);
}
node *BSTreeToList(node *tree)
{
if (tree == NULL)
return NULL;
node *head = FindLeftmostNode(tree);
node *last_node = NULL;
ConvertNode(tree, &last_node);
return head;
}
//Input:
//421##3##65##7##
int main()
{
node *root = insert();
node *p = BSTreeToList(root);
return 0;
}
13. 连接二叉树同一层上的结点
???






















 466
466

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








