shiro
1.简介
Apache Shiro 是 Java 的一个安全框架。目前,使用 Apache Shiro 的人越来越多,因为它相当简单,对比 Spring Security,可能没有 Spring Security 做的功能强大,但是在实际工作时可能并不需要那么复杂的东西,所以使用小而简单的 Shiro 就足够了。对于它俩到底哪个好,这个不必纠结,能更简单的解决项目问题就好了。
而构建一个后台应用,权限校验管理是很重要的安全措施,这其中主要包含
- 用户认证 - 用户身份识别,即登录
- 用户授权 - 访问控制
- 密码加密 - 加密敏感数据防止被偷窥
- 会话管理 - 与用户相关的时间敏感的状态信息
2.整体结构与重要组件
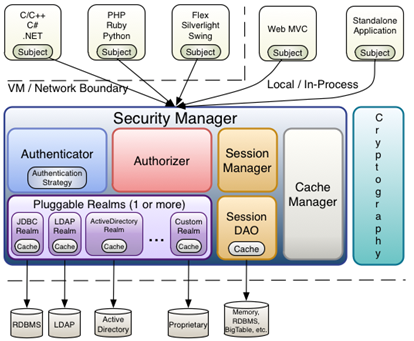
从以上也可以看出,Shiro 不提供维护用户 / 权限,而是通过 Realm 让开发人员自己注入。
-
Subject: 主体,代表了当前的用户,这个用户不一定是一个具体的人,与当前应用交互的任何东西都是Subject,如网络爬虫,机器人等;即一个抽象概念;
-
SecurityManger安全管理器;即所有与安全有关的操作都会与它交互;它管理这所有的Subject,且负责进行认证和授权,及会话等管理;可以看出它是Shiro的心脏。
-
Realm: 域,Shiro从Realm获取安全数据(如用户/角色/权限),就是说SecurityManger要验证用户身份,需要从Realm获取用户信息进行比较以确定用户身份是否合法;也需要从Realm得到用户相应角色/权限来验证用户是否可进行操作;可以把Realm看成DataSource,即安全数据源。
-
Authenticator: 认证器,负责主题认证的,这是一个扩展点,可以自定义实现。
-
Authrizer:授权器,或者访问控制器,用来决定主体是否有权限进行相应的操作;即控制着用户能访问应用中的哪些功能。
-
SessionManager:session管理器;
-
SessionDAO:session的数据访问对象;
-
CacheManager:缓存控制器;
-
Cryptography:密码模块,Shiro 提高了一些常见的加密组件用于如密码加密 / 解密的。
从demo开始分析
官网例子:http://shiro.apache.org/tutorial.html
- shiro.ini
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Users and their (optional) assigned role
# username = password, role1, role2, ..., roleN
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
[users]
root = secret,admin
guest =guest,guest
presidentskroob =12345,president
darkhelmet =ludicrousspeed,darklord,schwartz
lonestarr =vespa,goodguy,schwartz
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Roles with assigned permissions
# roleName = perm1, perm2, ..., permN
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
[roles]
admin = *
schwartz =lightsaber:*
goodguy =winnebago:drive:eagle5
上面的代码,root=secret,admin表示,用户名是root,密码是secret,角色是admin;
schwartz=lightsaber:标识角色schwartz拥有权限lightsaber:,这个文件可以看成是一个Relam,其实就是shiro默认的IniRealm
- 测试类ShiroTest
@Slf4j
public class ShiroTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("My First Apache Shiro Application");
Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
// get the currently executing user:
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// Do some stuff with a Session (no need for a web or EJB container!!!)
Session session = currentUser.getSession();
session.setAttribute("someKey", "aValue");
String value = (String) session.getAttribute("someKey");
if (value.equals("aValue")) {
log.info("Retrieved the correct value! [" + value + "]");
}
// let's login the current user so we can check against roles and permissions:
if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) {
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lonestarr", "vespa");
token.setRememberMe(true);
try {
currentUser.login(token);
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
log.info("There is no user with username of " + token.getPrincipal());
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
log.info("Password for account " + token.getPrincipal() + " was incorrect!");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {
log.info("The account for username " + token.getPrincipal() + " is locked. " +
"Please contact your administrator to unlock it.");
}
// ... catch more exceptions here (maybe custom ones specific to your application?
catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
//unexpected condition? error?
}
}
//say who they are:
//print their identifying principal (in this case, a username):
log.info("User [" + currentUser.getPrincipal() + "] logged in successfully.");
//test a role:
if (currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")) {
log.info("May the Schwartz be with you!");
} else {
log.info("Hello, mere mortal.");
}
//test a typed permission (not instance-level)
if (currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wield")) {
log.info("You may use a lightsaber ring. Use it wisely.");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, lightsaber rings are for schwartz masters only.");
}
//a (very powerful) Instance Level permission:
if (currentUser.isPermitted("winnebago:drive:eagle5")) {
log.info("You are permitted to 'drive' the winnebago with license plate (id) 'eagle5'. " +
"Here are the keys - have fun!");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, you aren't allowed to drive the 'eagle5' winnebago!");
}
//all done - log out!
currentUser.logout();
System.exit(0);
}
}
从上面的实例中,我们可以看到常用的API:
#获取当前用户
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
#判断用户是否已经认证
currentUser.isAuthenticated();
#用户登录凭证
UsernamePasswordToken token =new UsernamePasswordToken("用户名","密码");
#记住我
token.setRememberMe(true);
#登录校验
currentUser.login(token);
#判断是否有角色权限
currentUser.hasRole("超管");
#判断是否有资源操作权限
currentuser.isPermitted("发货");
其实稍微梳理一下,可以发现上面代码主要有两个步骤:
认证
#用户登录凭证
UsernamePasswordToken token =new UsernamePasswordToken("用户名","密码");
#记住我
token.setRememberMe(true);
#登录校验
currentUser.login(token);
授权
#判断是否有角色权限
currentUser.hasRole("超管");
#判断是否有资源操作权限
currentuser.isPermitted("发货");
接下来,我们去探讨一下shiro的认证与授权流程,并从源码层去解析一下shiro各个组件之间的关系。
3.认证
身份验证,即在应用中证明他是本人。一般提供一些标识来验证,例如用户名/密码等
在shiro中,用户需要提供 principals(身份) 和 credentials(凭证) 给shiro,从而验证用户身份。
大致的shiro认证流程如下:
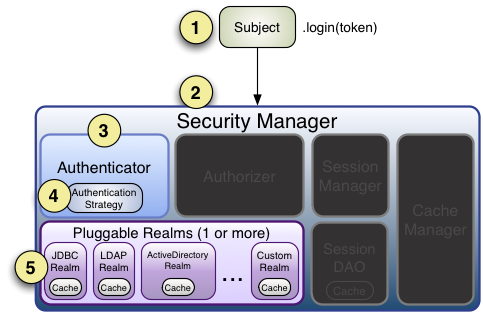
- Subject进行login操作,参数是封装了用户信息的token,例如UsernamePasswordToken,也可以自定义token对象进行特殊信息的传递。
- SecurityManager进行登录操作。
- SecurityManager委托给Authenticator进行认证逻辑处理。
- 调用AuthenticationStrategy进行单个或多Realm身份验证。
- 调用对应的Realm进行校验,可以自定义CredentialsMatcher实现token的比较规则,例如: HashedCredentialsMatcher,认证失败则抛对应异常
debug追踪shiro源码的流程:
#登录
currentUser.login(token);
#Subject调用SecurityManager
public void login(AuthenticationToken token) {
Subject subject = this.securityManager.login(this, token);
}
#SecurityManager委托给Authenticator--AuthenticatingSecurityManager
public AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) {
return this.authenticator.authenticate(token);
}
#Authenticator认证器调用Realm进行验证--AbstractAuthenticator
public final AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) {
AuthenticationInfo info = doAuthenticate(token);
}
protected AuthenticationInfo doAuthenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) {
assertRealmsConfigured();
Collection<Realm> realms = getRealms();
if (realms.size() == 1) {
return doSingleRealmAuthentication(realms.iterator().next(), authenticationToken);
} else {
return doMultiRealmAuthentication(realms, authenticationToken);
}
}
#Realm进行多个Realm或单个Realm验证,(多个Realm可以指定验证策略)--AuthenticatingRealm
public final AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) {
AuthenticationInfo info = getCachedAuthenticationInfo(token);
if (info == null) {
//otherwise not cached, perform the lookup:
info = doGetAuthenticationInfo(token);
log.debug("Looked up AuthenticationInfo [{}] from doGetAuthenticationInfo", info);
if (token != null && info != null) {
cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible(token, info);
}
} else {
log.debug("Using cached authentication info [{}] to perform credentials matching.", info);
}
if (info != null) {
assertCredentialsMatch(token, info);
} else {
log.debug("No AuthenticationInfo found for submitted AuthenticationToken [{}]. Returning null.", token);
}
return info;
}
# Realm进行数据源操作--SimpleAccountRealm
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) {
UsernamePasswordToken upToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token;
SimpleAccount account = getUser(upToken.getUsername());
if (account != null) {
if (account.isLocked()) {
throw new LockedAccountException("Account [" + account + "] is locked.");
}
if (account.isCredentialsExpired()) {
String msg = "The credentials for account [" + account + "] are expired";
throw new ExpiredCredentialsException(msg);
}
}
return account;
}
#匹配规则
protected void assertCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) throws AuthenticationException {
CredentialsMatcher cm = getCredentialsMatcher();
if (cm != null) {
if (!cm.doCredentialsMatch(token, info)) {
//not successful - throw an exception to indicate this:
String msg = "Submitted credentials for token [" + token + "] did not match the expected credentials.";
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException(msg);
}
} else {
throw new AuthenticationException("A CredentialsMatcher must be configured in order to verify " +
"credentials during authentication. If you do not wish for credentials to be examined, you " +
"can configure an " + AllowAllCredentialsMatcher.class.getName() + " instance.");
}
}
ok,一条线下来,从login到委托给authenticator,再最后调用realm的doGetAuthenticationInfo方法。
所以,从源码上来看,如果要实现shiro的认证逻辑,至少要准备一个Realm组件、和初始化securityManager组件。
4.授权
授权,也叫访问控制,即在应用中控制谁能访问那些资源(如访问页面/编辑数据/操作按钮等)。在授权中有几个关键对象:主体(Subject)、资源(Resource)、权限(Permission)、角色(Role)
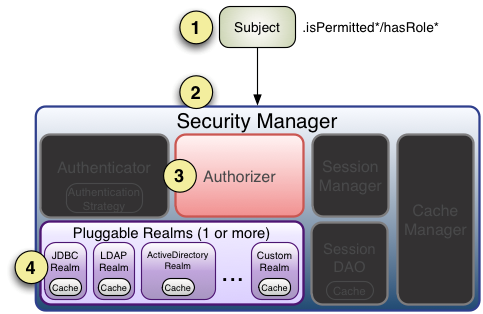
大致的shiro授权流程如下:
- 调用Subject.isPermitted/hasRole接口
- 委托给SecurityManager
- SercurityManager委托Authorizer
- Authorizer会判断Realm的角色、权限是否和传入的匹配
- 匹配如isPermitted/hasRole会返回true,否则返回false
debug追踪shiro源码过程
- url请求被shiro拦截器拦截–AuthorizingMethodInterceptor
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
assertAuthorized(methodInvocation);
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
protected abstract void assertAuthorized(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws AuthorizationException;
- 获取所有Shiro拦截器进行循环执行,一共5个过滤器
public abstract class AnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor extends AuthorizingMethodInterceptor {
protected void assertAuthorized(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws AuthorizationException {
//default implementation just ensures no deny votes are cast:
Collection<AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor> aamis = getMethodInterceptors();
if (aamis != null && !aamis.isEmpty()) {
for (AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor aami : aamis) {
if (aami.supports(methodInvocation)) {
aami.assertAuthorized(methodInvocation);
}
}
}
}
}
public AnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor() {
methodInterceptors = new ArrayList<AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor>(5);
#角色拦截器
methodInterceptors.add(new RoleAnnotationMethodInterceptor());
#权限拦截器
methodInterceptors.add(new PermissionAnnotationMethodInterceptor());
methodInterceptors.add(new AuthenticatedAnnotationMethodInterceptor());
methodInterceptors.add(new UserAnnotationMethodInterceptor());
methodInterceptors.add(new GuestAnnotationMethodInterceptor());
}
3.角色Handler进行解析方法上面的注解
package org.apache.shiro.authz.aop;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.annotation.Logical;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.annotation.RequiresRoles;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class RoleAnnotationHandler extends AuthorizingAnnotationHandler {
/**
* Default no-argument constructor that ensures this handler looks for
* {@link org.apache.shiro.authz.annotation.RequiresRoles RequiresRoles} annotations.
*/
public RoleAnnotationHandler() {
super(RequiresRoles.class);
}
/**
* Ensures that the calling <code>Subject</code> has the Annotation's specified roles, and if not, throws an
* <code>AuthorizingException</code> indicating that access is denied.
*
* @param a the RequiresRoles annotation to use to check for one or more roles
* @throws org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationException
* if the calling <code>Subject</code> does not have the role(s) necessary to
* proceed.
*/
public void assertAuthorized(Annotation a) throws AuthorizationException {
if (!(a instanceof RequiresRoles)) return;
RequiresRoles rrAnnotation = (RequiresRoles) a;
String[] roles = rrAnnotation.value();
if (roles.length == 1) {
getSubject().checkRole(roles[0]);
return;
}
if (Logical.AND.equals(rrAnnotation.logical())) {
getSubject().checkRoles(Arrays.asList(roles));
return;
}
if (Logical.OR.equals(rrAnnotation.logical())) {
// Avoid processing exceptions unnecessarily - "delay" throwing the exception by calling hasRole first
boolean hasAtLeastOneRole = false;
for (String role : roles) if (getSubject().hasRole(role)) hasAtLeastOneRole = true;
// Cause the exception if none of the role match, note that the exception message will be a bit misleading
if (!hasAtLeastOneRole) getSubject().checkRole(roles[0]);
}
}
}
4.权限handler进行验证
package org.apache.shiro.authz.aop;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.annotation.Logical;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.annotation.RequiresPermissions;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.annotation.RequiresRoles;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
public class PermissionAnnotationHandler extends AuthorizingAnnotationHandler {
public PermissionAnnotationHandler() {
super(RequiresPermissions.class);
}
protected String[] getAnnotationValue(Annotation a) {
RequiresPermissions rpAnnotation = (RequiresPermissions) a;
return rpAnnotation.value();
}
public void assertAuthorized(Annotation a) throws AuthorizationException {
if (!(a instanceof RequiresPermissions)) return;
RequiresPermissions rpAnnotation = (RequiresPermissions) a;
String[] perms = getAnnotationValue(a);
Subject subject = getSubject();
if (perms.length == 1) {
subject.checkPermission(perms[0]);
return;
}
if (Logical.AND.equals(rpAnnotation.logical())) {
getSubject().checkPermissions(perms);
return;
}
if (Logical.OR.equals(rpAnnotation.logical())) {
// Avoid processing exceptions unnecessarily - "delay" throwing the exception by calling hasRole first
boolean hasAtLeastOnePermission = false;
for (String permission : perms) if (getSubject().isPermitted(permission)) hasAtLeastOnePermission = true;
// Cause the exception if none of the role match, note that the exception message will be a bit misleading
if (!hasAtLeastOnePermission) getSubject().checkPermission(perms[0]);
}
}
}
5.举权限验证的例子,角色同理,getSubject().isPermitted(permission)进行验证,
并委托给SecurityManager
public boolean isPermitted(String permission) {
return hasPrincipals() && securityManager.isPermitted(getPrincipals(), permission);
}
7.SecurityManager委托Authorizer
public abstract class AuthorizingSecurityManager extends AuthenticatingSecurityManager {
public boolean hasRole(PrincipalCollection principals, String roleIdentifier) {
return this.authorizer.hasRole(principals, roleIdentifier);
}
public boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, String permissionString) {
return this.authorizer.isPermitted(principals, permissionString);
}
}
8.Authorizer调用Realm进行验证
public abstract class AuthorizingRealm extends AuthenticatingRealm
implements Authorizer, Initializable, PermissionResolverAware, RolePermissionResolverAware {
public boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, Permission permission) {
AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationInfo(principals);
return isPermitted(permission, info);
}
}
9.通过Realm进行获取授权信息 getAuthorizationInfo(principals)
protected AuthorizationInfo getAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
if (info == null) {
// Call template method if the info was not found in a cache
info = doGetAuthorizationInfo(principals);
// If the info is not null and the cache has been created, then cache the authorization info.
if (info != null && cache != null) {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Caching authorization info for principals: [" + principals + "].");
}
Object key = getAuthorizationCacheKey(principals);
cache.put(key, info);
}
}
return info;
}
10.调用自定义Realm的doGetAuthorizationInfo覆盖方法进行获取授权信息
public class AuthRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Autowired
private ShiroService shiroService;
@Override
/**
* 授权 获取用户的角色和权限
*@param [principals]
*@return org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo
*/
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
//1. 从 PrincipalCollection 中来获取登录用户的信息
User user = (User) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal();
//Integer userId = user.getUserId();
//2.添加角色和权限
SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
for (Role role : user.getRoles()) {
//2.1添加角色
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addRole(role.getRoleName());
for (Permission permission : role.getPermissions()) {
//2.1.1添加权限
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addStringPermission(permission.getPermission());
}
}
return simpleAuthorizationInfo;
}
@Override
/**
* 认证 判断token的有效性
*@param [token]
*@return org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo
*/
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//获取token,既前端传入的token
String accessToken = (String) token.getPrincipal();
//1. 根据accessToken,查询用户信息
SysToken tokenEntity = shiroService.findByToken(accessToken);
//2. token失效
if (tokenEntity == null || tokenEntity.getExpireTime().isBefore(LocalDateTime.now())) {
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException("token失效,请重新登录");
}
//3. 调用数据库的方法, 从数据库中查询 username 对应的用户记录
User user = shiroService.findByUserId(tokenEntity.getUserId());
//4. 若用户不存在, 则可以抛出 UnknownAccountException 异常
if (user == null) {
throw new UnknownAccountException("用户不存在!");
}
//5. 根据用户的情况, 来构建 AuthenticationInfo 对象并返回. 通常使用的实现类为: SimpleAuthenticationInfo
SimpleAuthenticationInfo info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, accessToken,this.getName());
return info;
}
}
11.最后继续执行第8步的isPermitted方法验证
protected boolean isPermitted(Permission permission, AuthorizationInfo info) {
Collection<Permission> perms = getPermissions(info);
if (perms != null && !perms.isEmpty()) {
for (Permission perm : perms) {
if (perm.implies(permission)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
spring跟shiro整合配置
/**
* shrio配置文件
*/
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
/**
* 注册shiro的Filter,拦截请求
*/
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean(SecurityManager securityManager) throws Exception {
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistration = new FilterRegistrationBean();
filterRegistration.setFilter((Filter) shiroFilter(securityManager).getObject());
filterRegistration.addInitParameter("targetFilterLifecycle", "true");
filterRegistration.setAsyncSupported(true);
filterRegistration.setEnabled(true);
filterRegistration.setDispatcherTypes(DispatcherType.REQUEST);
return filterRegistration;
}
@Bean
public Authenticator authenticator() {
ModularRealmAuthenticator authenticator = new ModularRealmAuthenticator();
//设置两个Realm,一个用于用户登录验证和访问权限获取;一个用于jwt token的认证
authenticator.setRealms(Arrays.asList(jwtRealm(), jwtUserRealm()));
//设置多个realm认证策略,一个成功即跳过其它的
authenticator.setAuthenticationStrategy(new FirstSuccessfulStrategy());
return authenticator;
}
/**
* 禁用session, 不保存用户登录状态。保证每次请求都重新认证。
* 需要注意的是,如果用户代码里调用Subject.getSession()还是可以用session,
* 如果要完全禁用,要配合下面的noSessionCreation的Filter来实现
*/
@Bean
protected SessionStorageEvaluator sessionStorageEvaluator() {
DefaultWebSessionStorageEvaluator sessionStorageEvaluator = new DefaultWebSessionStorageEvaluator();
sessionStorageEvaluator.setSessionStorageEnabled(false);
return sessionStorageEvaluator;
}
@Bean
public DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager() {
DefaultWebSecurityManager manager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
manager.setAuthenticator(authenticator());
manager.setAuthorizer(authorizer());
return manager;
}
@Bean
public Authorizer authorizer() {
ModularRealmAuthorizer authorizer = new ModularRealmAuthorizer();
//设置授权Realm
authorizer.setRealms(Arrays.asList(jwtRealm(), jwtUserRealm()));
return authorizer;
}
@Bean
public HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher() {
HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
//加密方式
hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("md5");
//加密次数
hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(2);
//存储散列后的密码是否为16进制
hashedCredentialsMatcher.isStoredCredentialsHexEncoded();
return hashedCredentialsMatcher;
}
@Bean("jwtUserRealm")
public Realm jwtUserRealm() {
return new JwtUserRealm(hashedCredentialsMatcher());
}
@Bean("jwtRealm")
public Realm jwtRealm() {
return new JwtRealm();
}
/**
* 设置过滤器
*/
@Bean("shiroFilter")
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilter(SecurityManager securityManager) {
ShiroFilterFactoryBean factoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
Map<String, Filter> filterMap = factoryBean.getFilters();
filterMap.put("authcToken", createAuthFilter());
factoryBean.setFilters(filterMap);
factoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(shiroFilterChainDefinition().getFilterChainMap());
return factoryBean;
}
public JwtAuthFilter createAuthFilter() {
return new JwtAuthFilter();
}
@Bean
protected ShiroFilterChainDefinition shiroFilterChainDefinition() {
DefaultShiroFilterChainDefinition chainDefinition = new DefaultShiroFilterChainDefinition();
chainDefinition.addPathDefinition("/bloom/**", "noSessionCreation,authcToken");
return chainDefinition;
@Bean
public LifecycleBeanPostProcessor lifecycleBeanPostProcessor() {
return new LifecycleBeanPostProcessor();
}
@Bean
public AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager) {
AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
return advisor;
}
}
shiro内置过滤器
在项目中,有一些url请求是不必被拦截来校验角色或者权限的,例如登录、验证码接口等。所以shiro通过内置过滤器来解决这个问题
public enum DefaultFilter {
#无需认证即可访问
anon(AnonymousFilter.class),
#需要认证才能访问
authc(FormAuthenticationFilter.class),
authcBasic(BasicHttpAuthenticationFilter.class),
logout(LogoutFilter.class),
noSessionCreation(NoSessionCreationFilter.class),
perms(PermissionsAuthorizationFilter.class),
port(PortFilter.class),
rest(HttpMethodPermissionFilter.class),
roles(RolesAuthorizationFilter.class),
ssl(SslFilter.class),
user(UserFilter.class);
}





















 1388
1388











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








